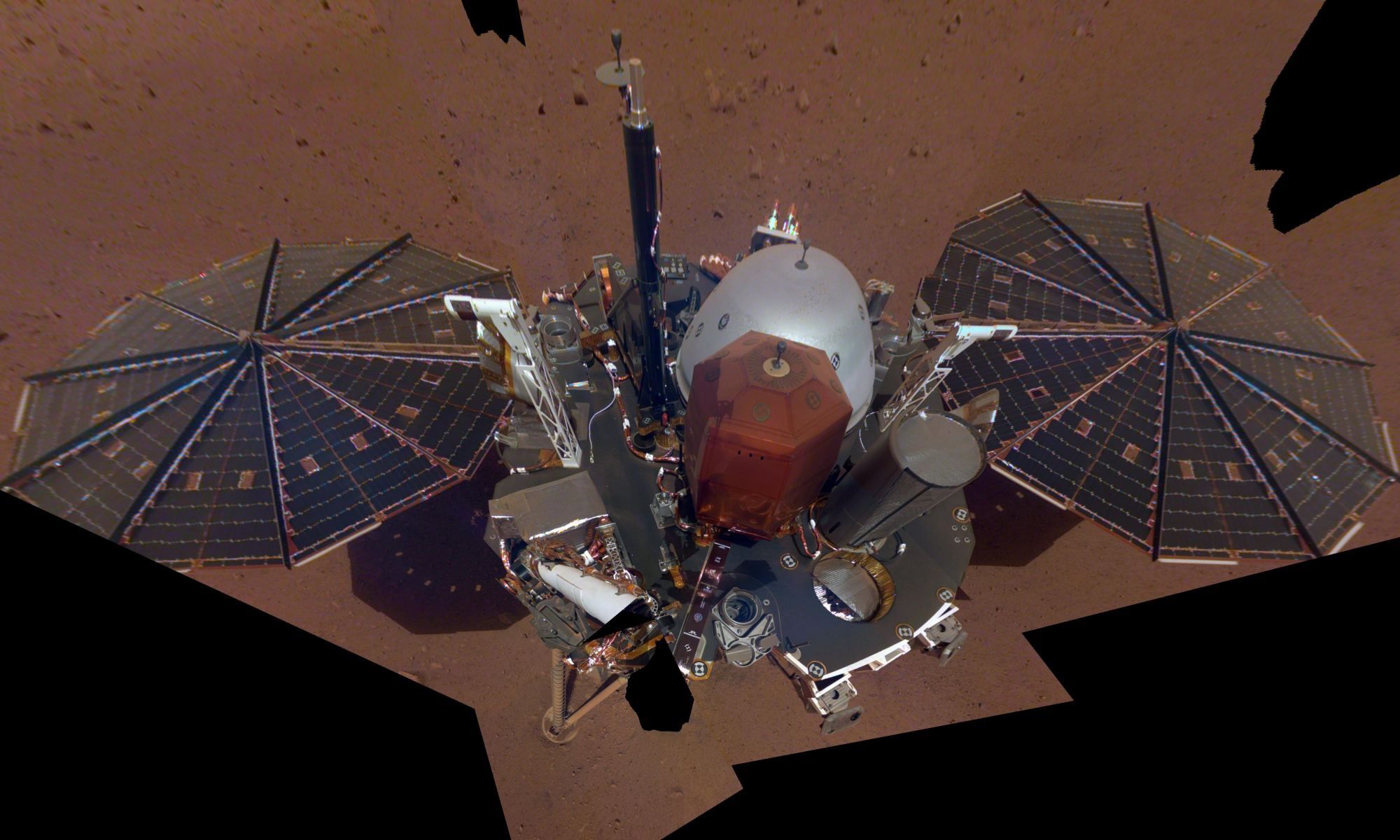
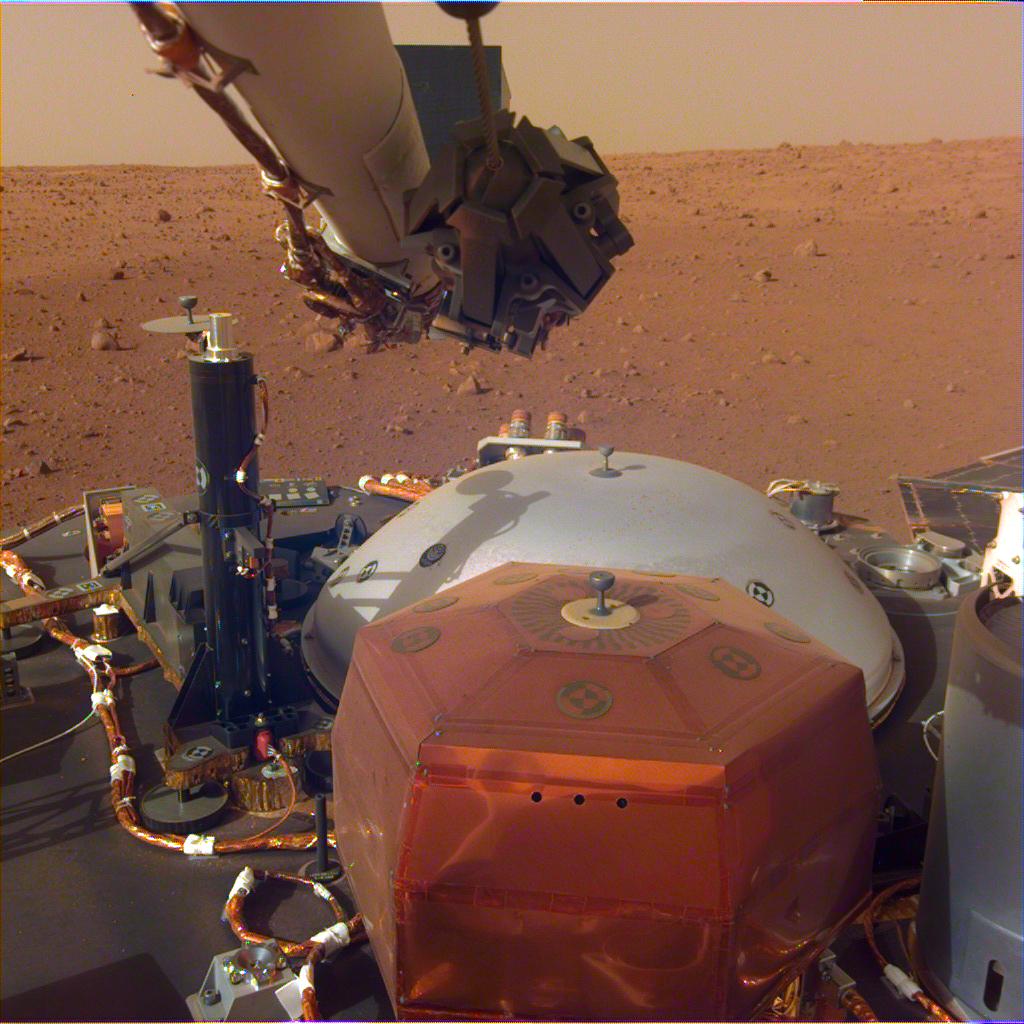
InSight has been on the Martian surface for almost three weeks, prepping itself for all the science it’s going to do. But in the meantime, it’s doing what any self-respecting, modern robotic lander does: Taking pictures of itself. And now NASA has released InSight’s first selfie for all the lander’s adoring fans and Instagram followers.
InSight is on Mars to study the interior of the rocky planet, and provide clues into how rocky planets form, both here in our Solar System, and in distant systems. It’s got a suite of instruments to do that with, including a device that will drill 5m (16 ft.) deep into the planet to measure how heat flows through the core of Mars. But it’s taking a cautious approach to that, using its time wisely to select the perfect spot to deploy its instruments.
In the meantime, holiday snaps!
Continue reading “Of Course You’ll Want to See InSight’s First Selfie.”