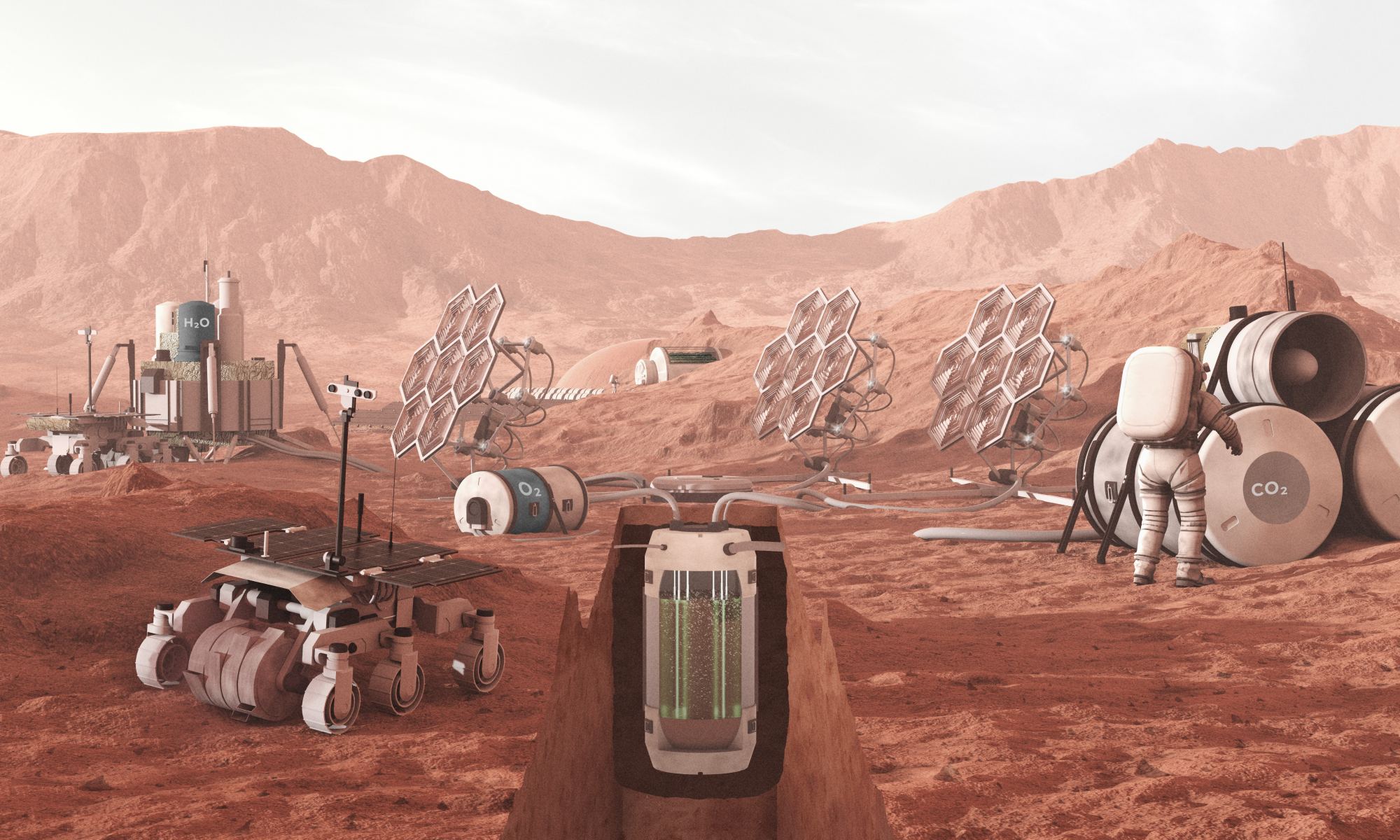
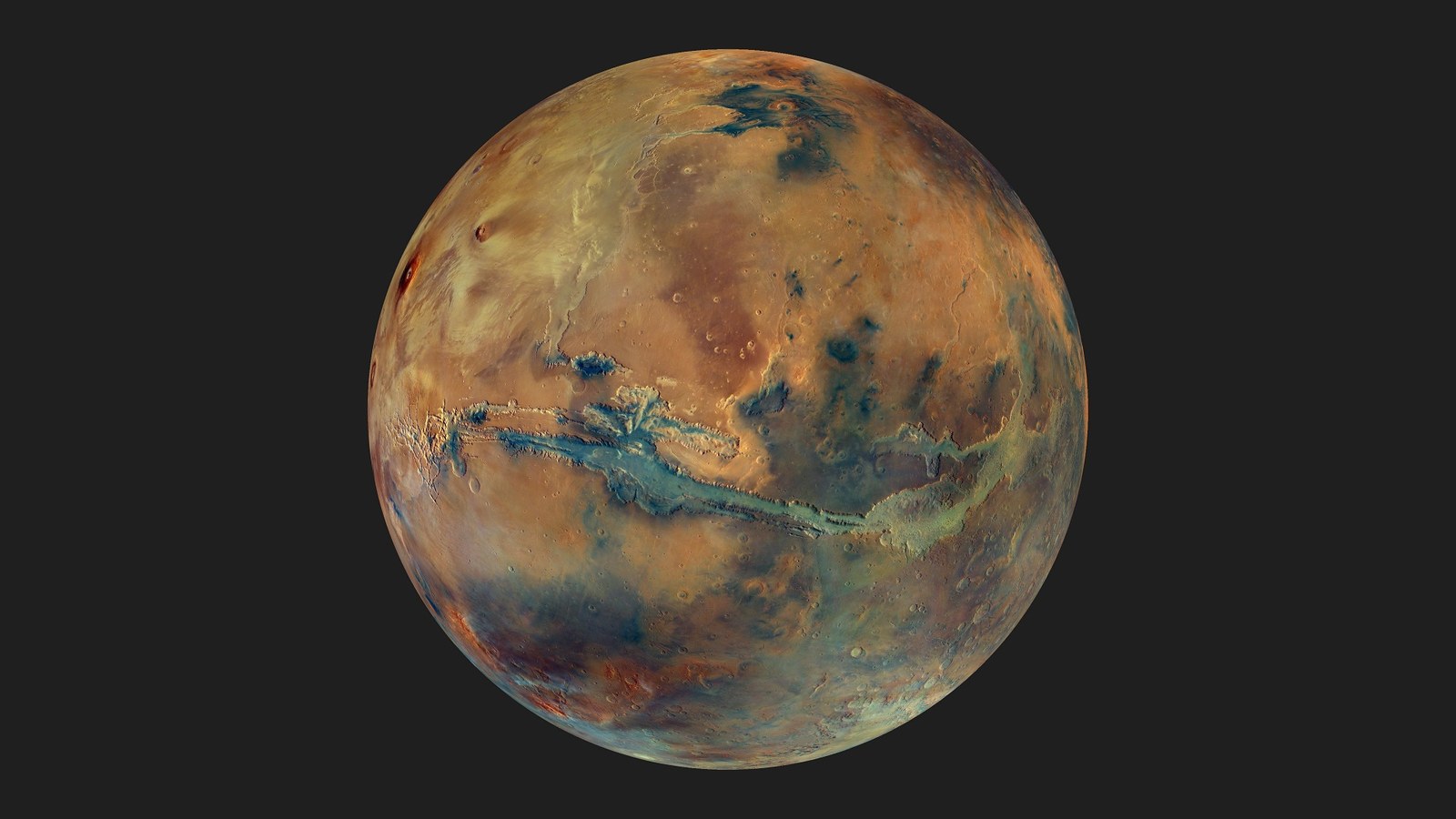
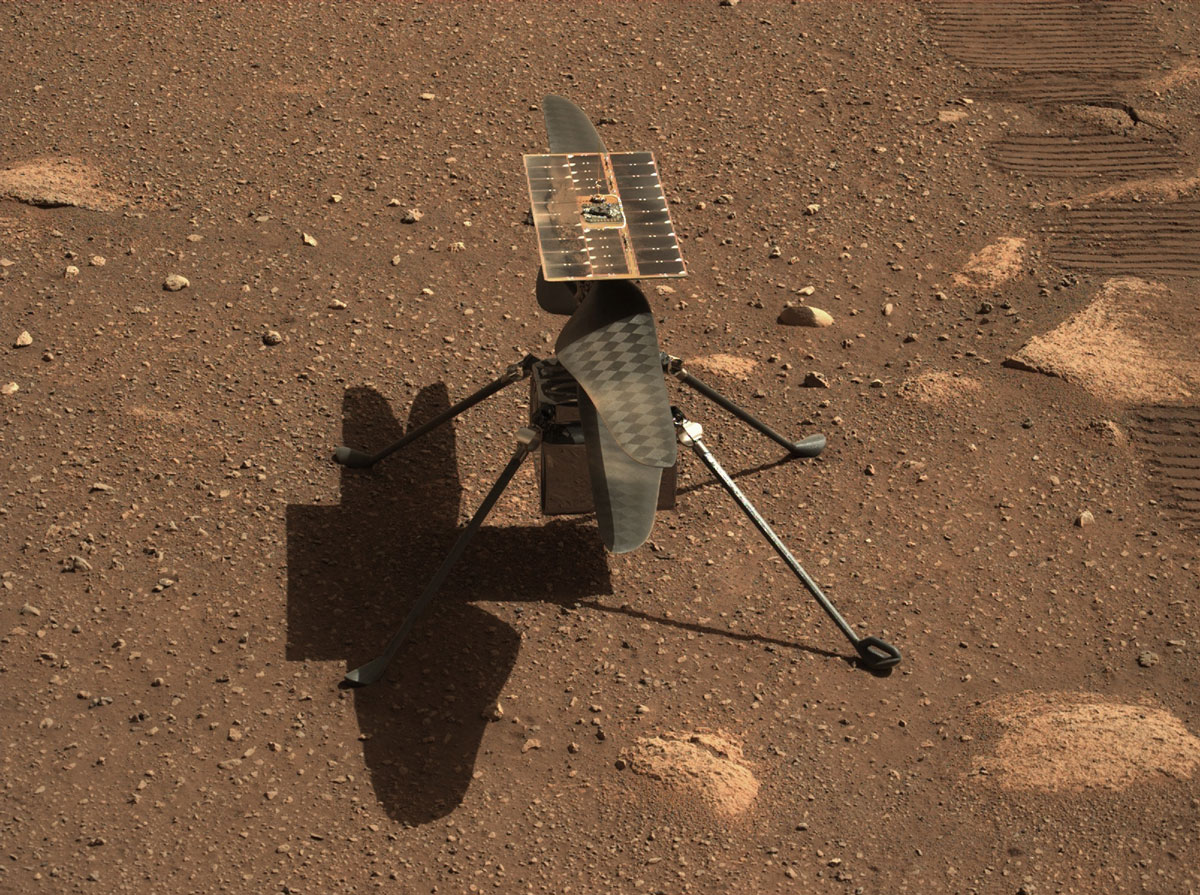
At this very moment, eleven robotic missions are operating in orbit or on the surface of Mars, more than at any point during the past sixty years. These include the many orbiters surveying the Red Planet from orbit, the handful of landers and rovers, and one helicopter (Ingenuity) studying the surface. In the coming years, many more are expected, reflecting the growing number of nations participating in the exploration process. Once there, they will join in the ongoing search for clues about the planet’s formation, evolution, and possible evidence that life once existed there.
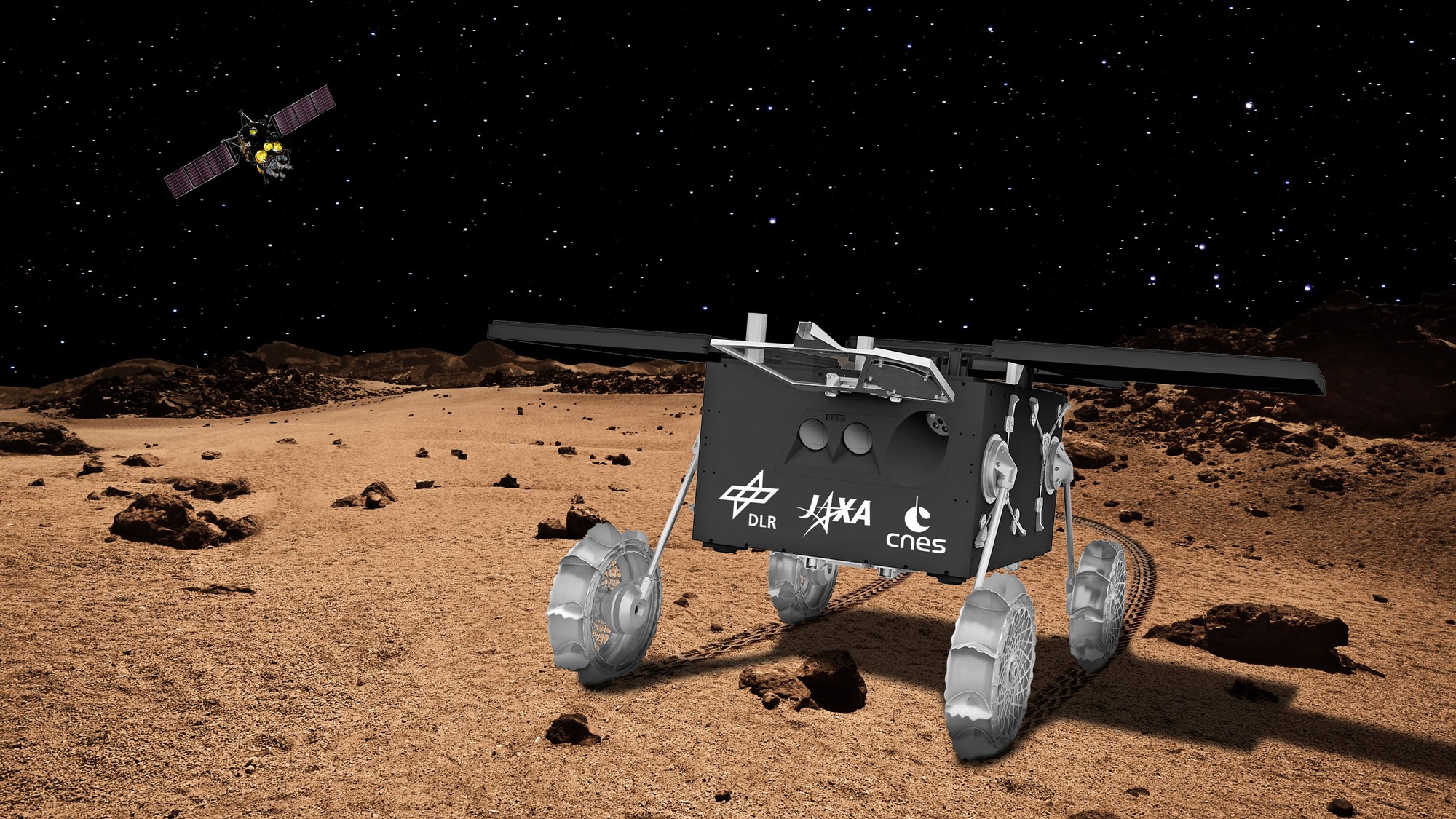
However, there’s also the mystery concerning the origin of Phobos and Deimos, Mars’ two satellites. While scientists have long suspected that these two moons began as asteroids kicked from the Main Belt that were captured by Mars’ gravity, there is no scientific consensus on this point. This is the purpose of the Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission currently under development by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), which will explore both moons with the help of a Phobos rover provided by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES).
Continue reading “Germany is Building a Tiny Rover That Will Roam the Surface of Phobos”