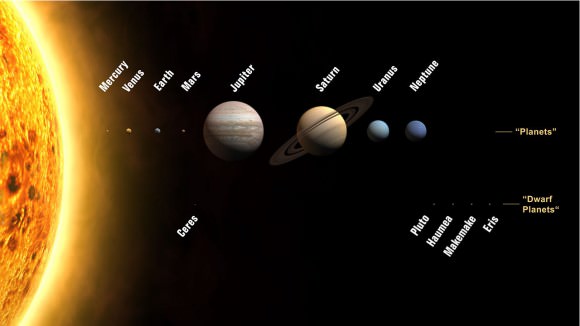
Our Solar System is an immense and amazing place. Between its eight planets, 176 moons, 5 dwarf planets (possibly hundreds more), 659,212 known asteroids, and 3,296 known comets, it has wonders to sate the most demanding of curiosities. Our Solar System is made up of different regions, which are delineated based on their distance from the Sun, but also the types of planets and bodies that can be found within them.
In the inner Solar System, we find the “Inner Planets” – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars – which are so named because they orbit closest to the Sun. In addition to their proximity, these planets have a number of key differences that set them apart from planets elsewhere in the Solar System.
For starters, the inner planets are rocky and terrestrial, composed mostly of silicates and metals, whereas the outer planets are gas giants. The inner planets are also much more closely spaced than their outer Solar System counterparts. In fact, the radius of the entire region is less than the distance between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn.
Credit: Planets2008/Wikimedia Commons
This region is also within the “frost line,” which is a little less than 5 AU (about 700 million km) from the Sun. This line represents the boundary in a system where conditions are warm enough that hydrogen compounds such as water, ammonia, and methane are able to take liquid form. Beyond the frost line, these compounds condense into ice grains.Some scientists refer to the frost line as the “Goldilocks Zone” — where conditions for life may be “just right.”
Generally, inner planets are smaller and denser than their counterparts, and have few to no moons or rings circling them. The outer planets, meanwhile, often have dozens of satellites and rings composed of particles of ice and rock.
The terrestrial inner planets are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals such as iron and nickel which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather. All of them have impact craters and tectonic surface features as well, such as rift valleys and volcanoes.
Mercury:
Of the inner planets, Mercury is the closest to our Sun and the smallest of the terrestrial planets. This small planet looks very much like the Earth’s Moon and is even a similar grayish color, and it even has many deep craters and is covered by a thin layer of tiny particle silicates.
Its magnetic field is only about 1 percent that of Earth’s, and it’s very thin atmosphere means that it is hot during the day (up to 430°C) and freezing at night (as low as -187 °C) because the atmosphere can neither keep heat in or out. It has no moons of its own and is comprised mostly of iron and nickel. Mercury is one of the densest planets in the Solar System.

Venus:
Venus, which is about the same size as Earth, has a thick toxic atmosphere that traps heat, making it the hottest planet in the Solar System. This atmosphere is composed of 96% carbon dioxide, along with nitrogen and a few other gases. Dense clouds within Venus’ atmosphere are composed of sulphuric acid and other corrosive compounds, with very litter water.
Only two spacecraft have ever penetrated Venus’s thick atmosphere, but it’s not just man-made objects that have trouble getting through. There are fewer crater impacts on Venus than other planets because all but the largest meteors don’t make it through the thick air without disintegrating. Much of Venus’ surface is marked with volcanoes and deep canyons — the biggest of which is over 6400 km (4,000 mi) long.
Venus is often called the “morning star” because, with the exception of Earth’s moon, it’s the brightest object we see in the sky. Like Mercury, Venus has no moon of its own.
Earth:
Earth is the third inner planet and the one we know best. Of the four terrestrial planets, Earth is the largest, and the only one that currently has liquid water, which is necessary for life as we know it. Earth’s atmosphere protects the planet from dangerous radiation and helps keep valuable sunlight and warmth in, which is also essential for life to survive.
Like the other terrestrial planets, Earth has a rocky surface with mountains and canyons, and a heavy metal core. Earth’s atmosphere contains water vapor, which helps to moderate daily temperatures. Like Mercury, the Earth has an internal magnetic field. And our Moon, the only one we have, is comprised of a mixture of various rocks and minerals.
Mars:
Mars is the fourth and final inner planet, and also known as the “Red Planet” due to the rust of iron-rich materials that form the planet’s surface. Mars also has some of the most interesting terrain features of any of the terrestrial planets. These include the largest mountain in the Solar System – Olympus Mons – which rises some 21,229 m (69,649 ft) above the surface, and a giant canyon called Valles Marineris. Valles Marineris is 4000 km (2500 mi) long and reaches depths of up to 7 km (4 mi)!
For comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 800 km (500 mi) long and 1.6 km (1 mi) deep. In fact, the extent of Valles Marineris is as long as the United States and it spans about 20 percent (1/5) of the entire distance around Mars. Much of the surface is very old and filled with craters, but there are geologically newer areas of the planet as well.

At the Martian poles are polar ice caps that shrink in size during the Martian spring and summer. Mars is less dense than Earth and has a smaller magnetic field, which is indicative of a solid core, rather than a liquid one.
Mars’ thin atmosphere has led some astronomers to believe that the surface water that once existed there might have actually taken liquid form, but has since evaporated into space. The planet has two small moons called Phobos and Deimos.
Beyond Mars are the four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We have written many interesting articles about the inner planets here at Universe Today. Here’s The Solar System Guide as well as The Inner and Outer Planets in Our Solar System.
For more information, check out this article from NASA on the planets of the Solar System and this article from Solstation about the inner planets.
Astronomy Cast also has episodes on all of the inner planets including this one about Mercury.