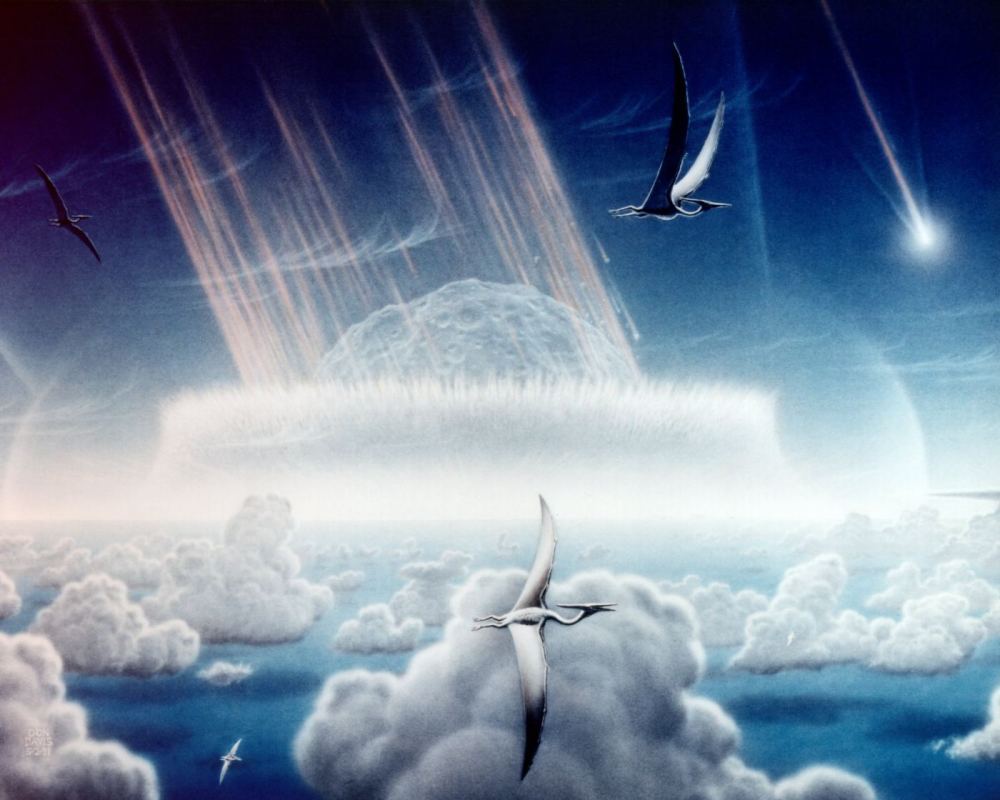
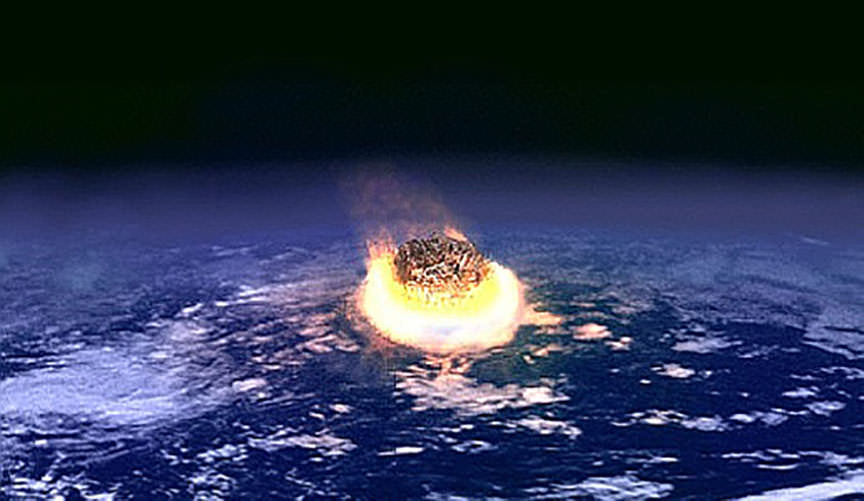
Sixty-six million years ago, an asteroid struck Earth in what is now the Yucatan Peninsula in southern Mexico. This event, known as the Chicxulub asteroid impact, measured 9 km in diameter and caused extreme global cooling and drought. This led to a mass extinction, which not only claimed the lives of the dinosaurs, but also wiped out about 75% of all land and sea animals on Earth.
However, had this asteroid impacted somewhere else on the planet, things could have turned out very differently. According to a new study produced by a team of Japanese researchers, the destruction caused by this asteroid was due in large part to where it impacted. Had the Chicxulub asteroid landed somewhere else on the planet, they argue, the fallout would not have been nearly as severe.
The study, which recently appeared in the journal Scientific Reports, is titled “Site of asteroid impact changed the history of life on Earth: the low probability of mass extinction“, and was conducted by and considered how geological conditions in the Yucatan region were intrinsic to mass extinction that happened 66 million years ago.
Dr. Kaiho and Dr. Oshima began by considering recent studies that have shown how the Chicxulub impact heated the hydrocarbon and sulfur content of rocks in the region. This is what led to the formation of stratospheric soot and sulfate aerosols which caused the extreme global cooling and drought that followed. As they state in their study, it was this (not the impact and the detritus it threw up alone) that ensured the mass extinction that followed:
“Blocking of sunlight by dust and sulfate aerosols ejected from the rocks at the site of the impact (impact target rocks) was proposed as a mechanism to explain how the physical processes of the impact drove the extinction; these effects are short-lived and therefore could not have driven the extinction. However, small fractions of stratospheric sulfate (SO4) aerosols were also produced, which may have contributed to the cooling of the Earth’s surface.“
Another issue they considered was the source of the soot aerosols, which previous research has indicated were quite prevalent in the stratosphere during the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary (ca. 65 million years ago). This soot is believed to coincide with the asteroid impact since microfossil and fossil pollen studies of this period also indicate the presence of iridium, which has been traced to the Chicxulub asteroid.
Previously, this soot was believed to be the result of wildfires that raged in the Yucatan as a result of the asteroid impact. However, Kaiho and Oshima determined that these fires could not have resulted in stratospheric soot; instead positing that they could only be produced by the burning and ejecting of hyrdocarbon material from rocks in the impact target area.

The presence of these hydrocarbons in the rocks indicate the presence of both oil and coal, but also plenty of carbonate minerals. Here too, the geology of the Yucatan was key, since the larger geological formation known as the Yucatan Platform is known to be composed of carbonate and soluble rocks – particularly limestone, dolomite and evaporites.
To test just how important the local geology was to the mass extinction that followed, Kaiho and Oshima conducted a computer simulation that took into account where the asteroid struck and how much aerosols and soot would be produced by an impact. Ultimately, they found that the resulting ejecta would have been sufficient to trigger global cooling and drought; and hence, an Extinction Level Event (ELE).
This sulfur and carbon-rich geology, however, is not something the Yucatan Peninsula shares with most regions on the planet. As they state in their study:
“Here we show that the probability of significant global cooling, mass extinction, and the subsequent appearance of mammals was quite low after an asteroid impact on the Earth’s surface. This significant event could have occurred if the asteroid hit the hydrocarbon-rich areas occupying approximately 13% of the Earth’s surface. The site of asteroid impact, therefore, changed the history of life on Earth.”
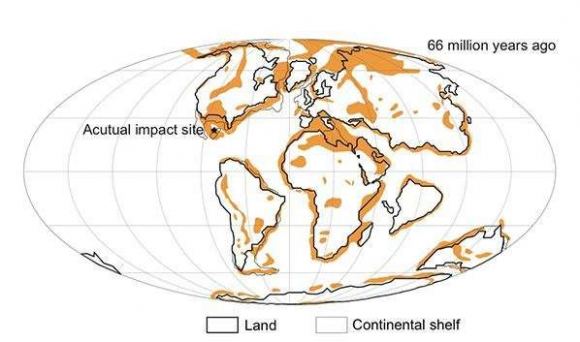
Basically, Kaiho and Oshima determined that 87% of Earth would not have been able to produce enough sulfate aerosols and soot to trigger a mass extinction. So if the Chicxulub asteroid struck just about anywhere else on the planet, the dinosaurs and most of the world’s animals would have likely survived, and the resulting macroevolution of mammals probably would not have taken place.
In short, modern hominids may very well owe their existence to the fact that the Chicxulub asteroid landed where it did. Granted, the majority of life in the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K–Pg) was wiped out as a result, but ancient mammals and their progeny appear to have lucked out. The study is therefore immensely significant in terms of our understanding of how asteroid impacts affect climatological and biological evolution.
It is also significant when it comes to anticipating future impacts and how they might affect our planet. Whereas a large impact in a sulfur and carbon-rich geological region could lead to another mass extinction, an impact anywhere else could very well be containable. Still, this should not prevent us from developing appropriate countermeasures to ensure that large impacts don’t happen at all!
Further Reading: Science Reports









