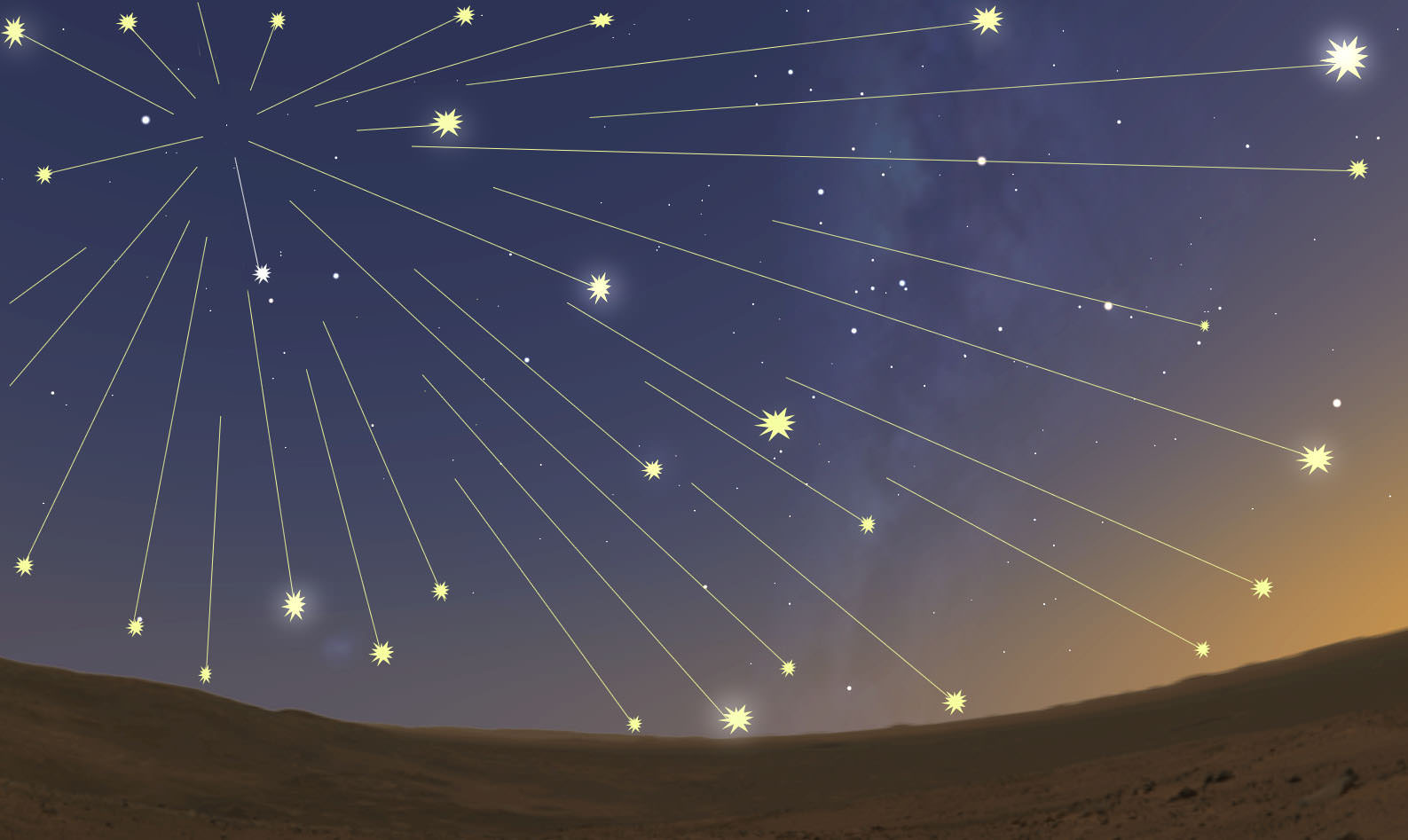
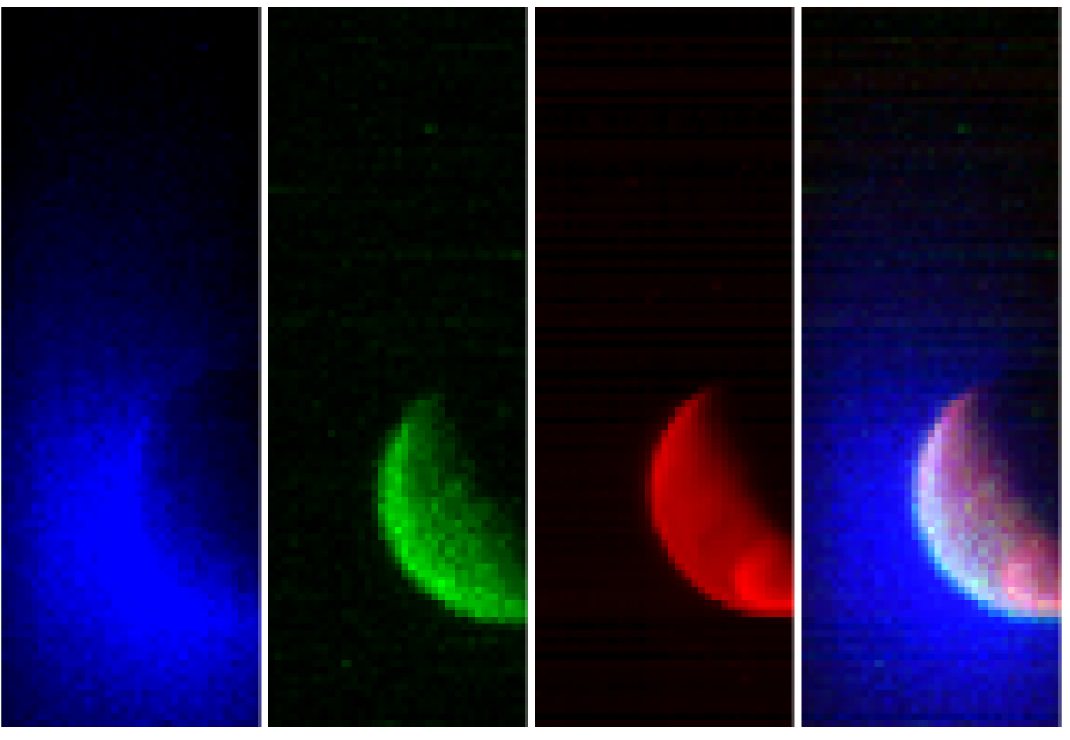
“Thousands of meteors per hour would have been visible — truly astounding to the human eye.” That’s Nick Schneider’s description of what you and I would have seen standing on Mars during Comet Siding Spring’s close flyby last month. “It would have been really mind-blowing,” he added. Schneider is instrument lead for MAVEN’s Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph (IUVS).
He and a group of scientists who work as lead investigators for instruments on the MAVEN and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) spacecraft shared the latest results from the comet flyby during a media teleconference earlier today. There were many surprises. Would we expect anything less from a comet?
Here’s a summary of the results:
A very dusty ice ball – The comet’s dust tail and the amount of dust in its coma were much larger than expected, prompting Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division in Washington, to remark: “It makes me very happy we hid them (the spacecraft) on the backside of Mars. That really saved them.” Siding Spring dumped several tons of fine dust into the Martian atmosphere prompting a spectacular meteor shower and possibly causing a yellow, twilight afterglow above the Curiosity landing site from vaporizing sodium atoms contained in the minerals. That, and dust in the mid-levels of the atmosphere at the time contributed to the rover’s difficulty in getting good photos of the comet itself. Scientists are still examining the images.

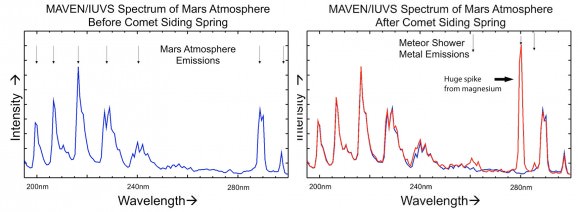
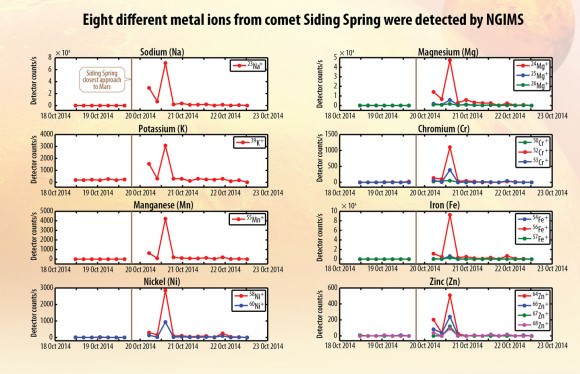
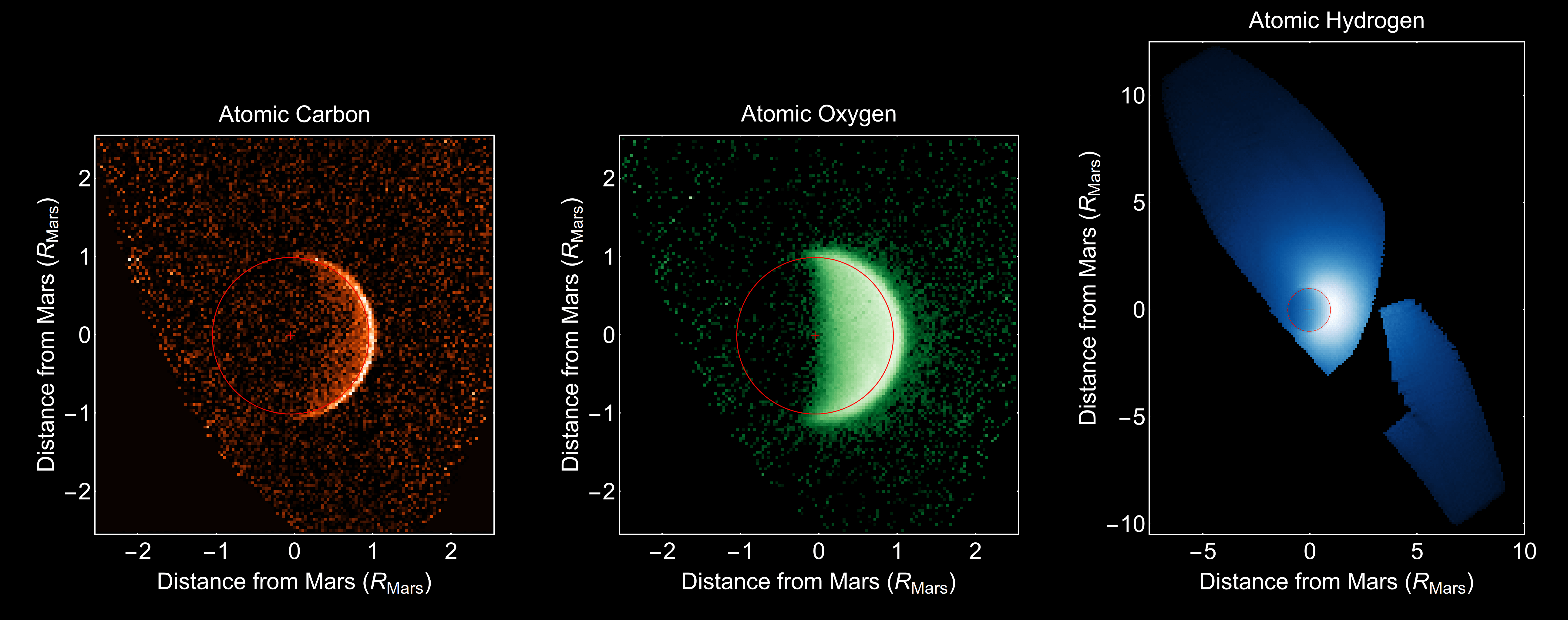
Chemistry of Mars’ atmosphere changed – Dust vaporized in the intense meteor shower produced a striking increase in the amount of magnesium, iron and others metals in Mars’ upper atmosphere. “We were pressed back in our chairs,” said Mike Schneider. The bombardment created a temporary new layer of comet-tainted air and may have acted as condensation nuclei for the formation of high-altitude clouds. MAVEN’s Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer (NGIMS) recorded huge spikes in the levels of eight different metals during the comet’s passage and then trailed off a day or so later. “They came to MAVEN as a free sample from no less than an Oort Cloud comet,” said Mehdi Benna, instrument scientist for MAVEN’s Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer.

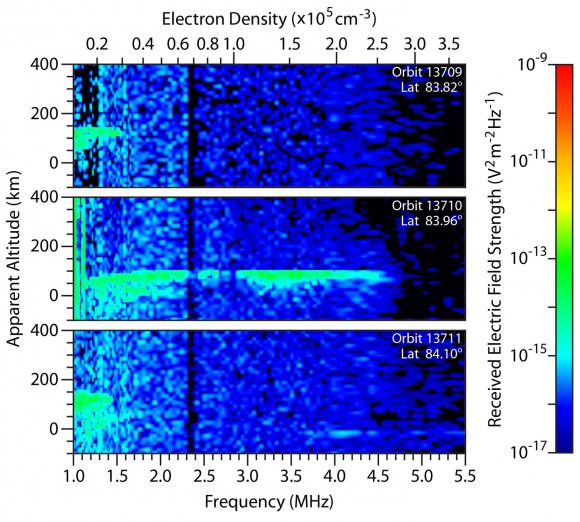
Flaming comet dust creates new ionospheric layer – Comet dust slamming into the atmosphere at 125,000 mph (56 km/sec) knocked electrons loose from atoms in the thin Martian air 50-60 miles (80-100 km) high, ionizing them and creating a very dense ionization layer in the planet’s lower ionosphere seven hours after the comet’s closest approach. Normally, Mars ionosphere is only seen on the dayside of the planet, but even when the MARSIS instrument on Mars Express beamed radio waves through the atmosphere on the nightside of the planet, it picked up a very strong signal.
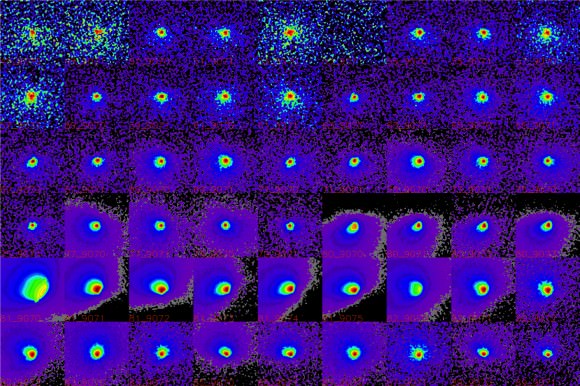

Nucleus spins once during your work day – Comet Siding Spring’s icy core spins once every 8 hours and its irregular shape causes strong variations in the comet’s brightness. The comet’s size appears less certain – at least for the moment – with estimates anywhere between a few hundred meters to 2 km (1.2 miles). More analysis on images taken by MRO’s HiRISE camera should narrow that number soon.
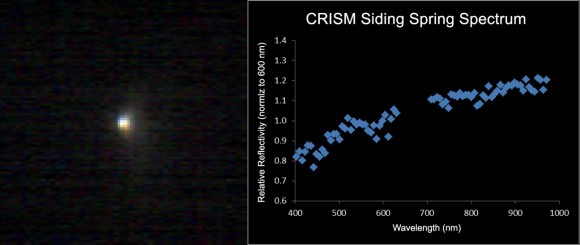
Dust motes of many sizes – Color variations across Siding Spring’s coma seen by Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) indicate it’s releasing dust particles of different sizes – big and little.
The scientists involved in the encounter couldn’t be happier with how the instruments functioned and the amount of hard data returned. Said Jim Green: “We are so lucky to observe this once-in-a-lifetime event.” How true when you consider that it takes about 8 million years for a comet from the Oort Cloud, that vast reservoir of frozen comets extending nearly a light year from the Sun, to get here in the first place. Nick Schneider put it another way:
“Not only is this a free sample of the Oort Cloud in Mars’ atmosphere, but it gives us a chance to learn more about Mars itself.”
If you’d like to listen in to the hour-long teleconference at any time, it’ll be up for the next week or so HERE.