Boeing has officially and publicly rejected a bid by Aerojet Rocketdyne to buy rocket maker United Launch Alliance (ULA), which the firm co-owns with rival aerospace giant Lockheed Martin. Furthermore Boeing affirmed support for ULA’s new next generation Vulcan rocket now under development, a spokesperson confirmed to Universe Today.
Aerojet Rocketdyne, which supplies critical rocket engines powering ULA’s fleet of Atlas and Delta rockets, recently made an unsolicited offer to buy ULA for approximately $2 Billion in cash, as Universe Today reported last week.
The Vulcan is planned to replace all of ULA’s existing rockets – which are significantly more costly than those from rival launch provider SpaceX, founded by billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk.
Boeing never “seriously entertained” the Aerojet-Rocketdyne buyout offer, Universe Today confirmed with Boeing spokesperson Cindy Anderson.
Meanwhile in stark contrast to Boeing, Lockheed Martin has “no comment” regarding the Aerojet-Rocketdyne offer to buy ULA, Universe Today confirmed with Lockheed Martin Director External Communications Matt Kramer.
Furthermore Lockheed Martin is not only noncommittal about the future of ULA but is also “currently assessing our options” concerning the development of ULA’s Vulcan rocket, Kramer told me.
“With regard to reports of an unsolicited proposal for ULA, it is not something we seriously entertained for a number of reasons,” Boeing spokesperson Anderson told Universe Today.
“Regarding Aerojet and ULA, as a matter of policy Lockheed Martin does not have a comment,” Lockheed Martin spokesman Kramer told Universe Today.

ULA was formed in 2006 as a 50:50 joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing that combined their existing expendable rocket fleet families – the Atlas V and Delta IV – under one roof.
Who owns ULA is indeed of significance to all Americans – although most have never head of the company – because ULA holds a virtual monopoly on launches of vital US government national security payloads and the nation’s most critical super secret spy satellites that safeguard our national defense 24/7. ULA’s rocket fleet also launched scores of NASA’s most valuable science satellites including the Curiosity Mars rover, Dawn and New Horizons Pluto planetary probe.
Since 2006 ULA has enjoyed phenomenal launch success with its venerable fleet of Atlas V and Delta IV rockets.
“ULA is a huge part of our strategic portfolio going forward along with our satellites and manned space business. This bid we’ve really not spent much time on it at all because we’re focusing on a totally different direction,” said Chris Chadwick, president and chief executive of Boeing Defense, Space & Security, on Sept. 16 at the Air Force Association’s annual technology expo in National Harbor, Maryland – according to a report by Space News.
Boeing offered strong support for ULA and the Vulcan rocket.
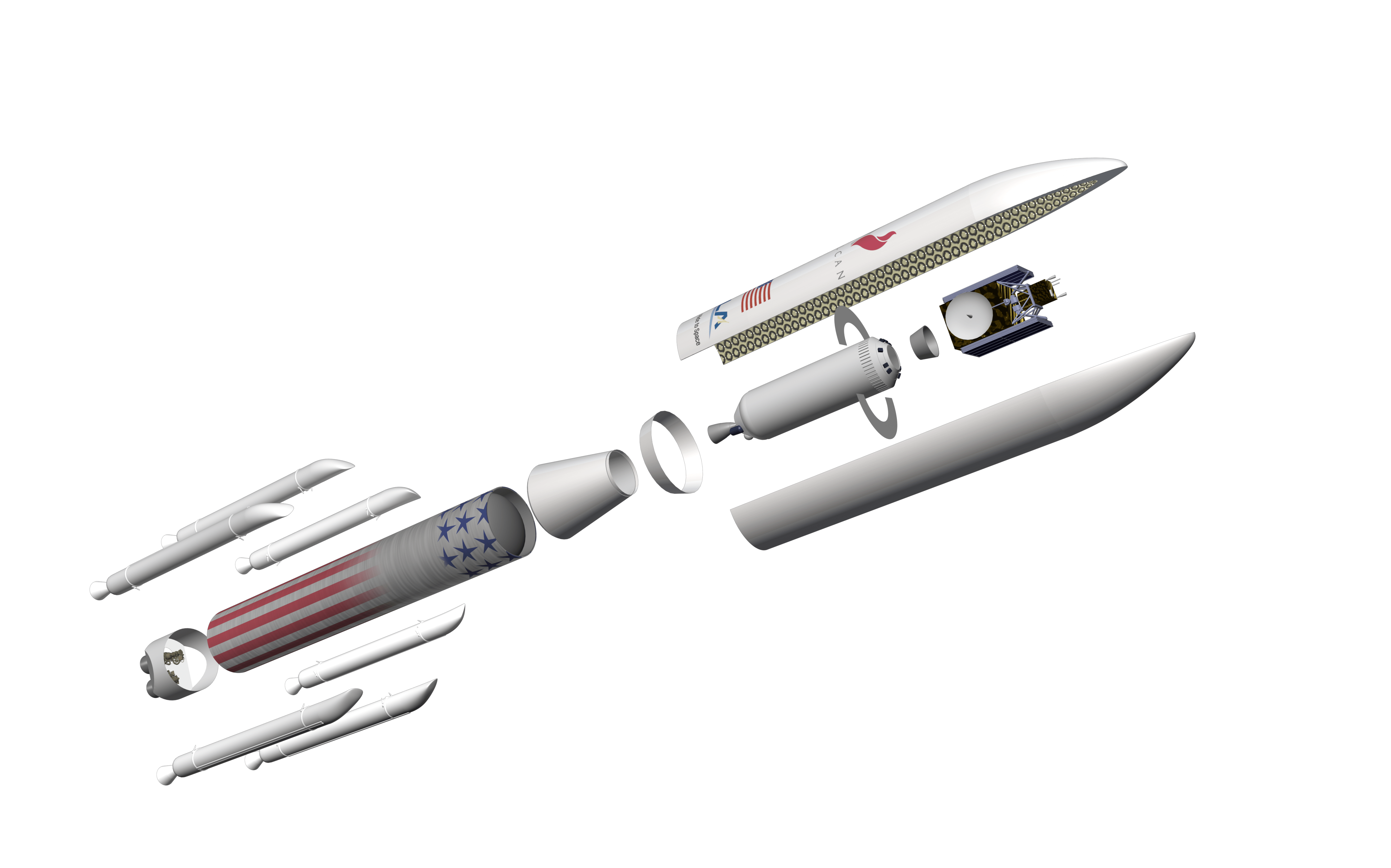
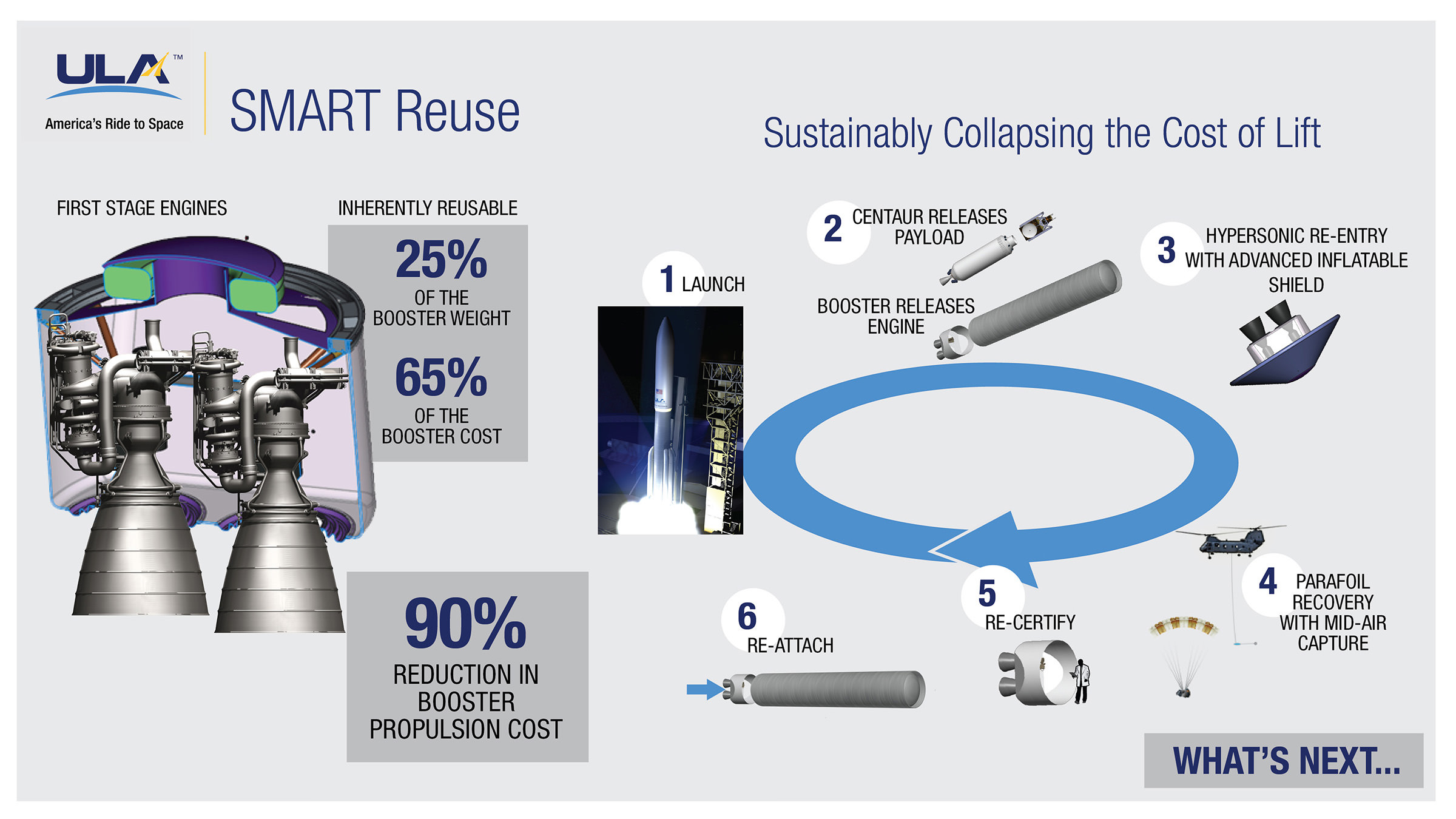
Vulcan is ULA’s next generation rocket to space that can propel payloads to low Earth orbit as well as throughout the solar system – including Pluto. It is slated for an inaugural liftoff in 2019.
Vulcan’s continued development is being funded by Lockheed Martin and Boeing, but only on a quarterly basis.
The key selling point of Vulcan is that it will be an all American built rocket and it will dramatically reduce launch costs to compete toe to toe with the SpaceX Falcon rocket family.
“To be successful and survive ULA needs to transform to be more of a competitive company in a competitive environment,” ULA VP Dr. George Sowers told Universe Today in a wide ranging interview regarding the rationale and goals of the Vulcan rocket.
And there is a heated competition on which of two companies will provide the new American built first stage engine that will replace the Russian-built RD-180 that currently powers the ULA Atlas V.
Vulcan’s first stage will most likely be powered by the BE-4 engine being developed by the secretive Blue Origin aerospace firm owned by billionaire Jeff Bezos.
This week ULA announced an expanded research agreement with Blue Origin about using the BE-4.
But ULA is also evaluating the AR-1 liquid fueled engine being developed by Aerojet-Rocketdyne – the company that wants to buy ULA.
The Atlas V dependence on Russia’s RD-180’s landed at the center of controversy after Russia invaded Crimea in the spring of 2014, raising the ire of Congress and enactment of a ban on their use several years in the future.
ULA is expected to make a final decision on which first stage engine to use between Blue Origin and Aerojet-Rocketdyne, sometime in 2016.
The engine choice would clearly be impacted if Aerojet-Rocketdyne buys ULA.
Boeing for its part says they strongly support ULA and continued development of the Vulcan.
“Boeing is committed to ULA and its business, and to continued leadership in all aspects of space, as evidenced by the recent announcement of an agreement with Blue Origin,” Boeing spokesperson Anderson told me.
Lockheed Martin in complete contrast did not express any long term commitment to Vulcan and just remarked they were merely “actively evaluating continued investment,” as is their right as a stakeholder.
“We have made no long-term commitments on the funding of a new rocket, and are currently assessing our options. The board is actively evaluating continued investment in the new rocket program and will continue to do so,” Lockheed Director, External Communications Matt Kramer told Universe Today.
Another factor is that Aerojet-Rocketdyne has also sought to buy the rights to manufacture the Atlas V from ULA, which is currently planned to be retired several years after Vulcan is introduced, officials have told me.

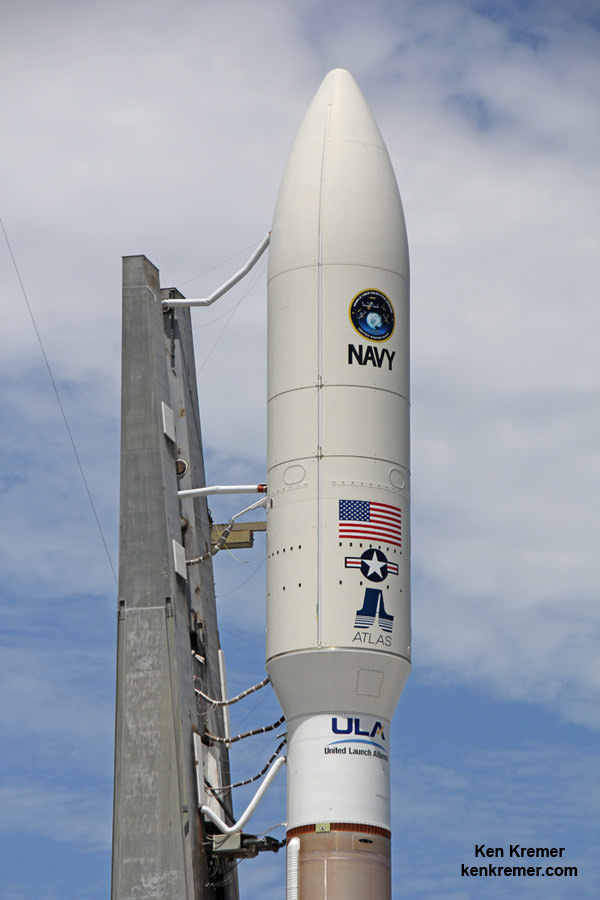
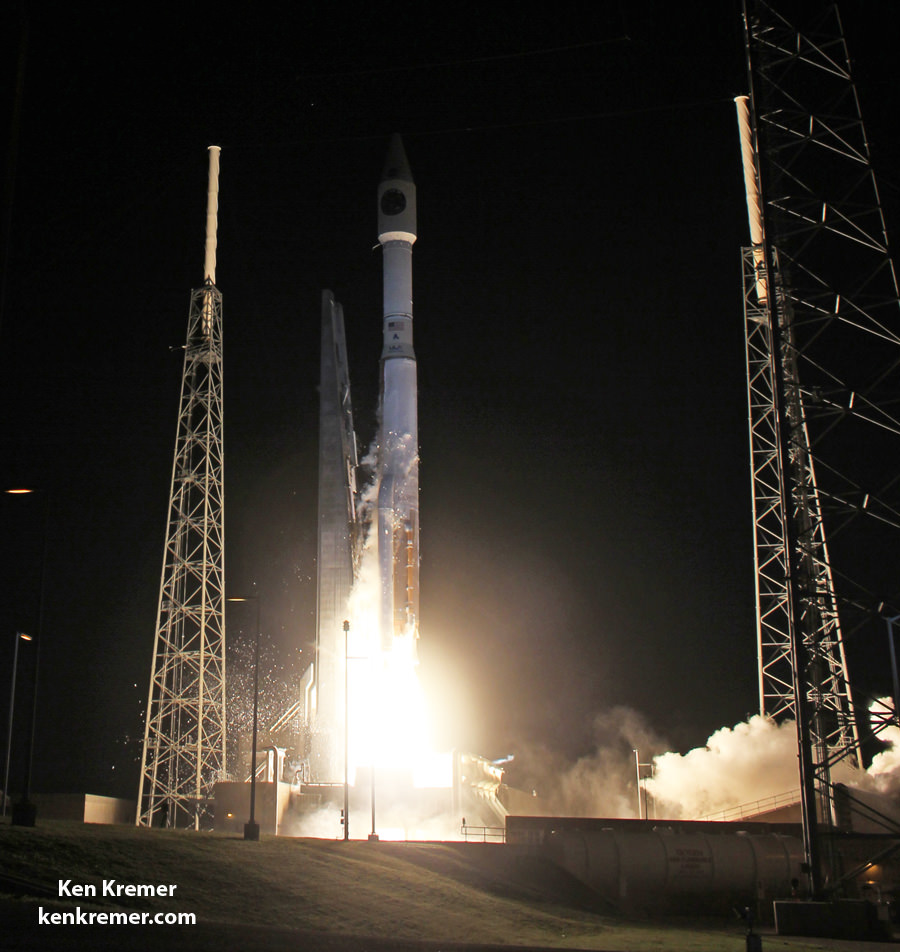
The Atlas V enjoys unparalleled success. Earlier this month on Sept. 2, ULA conducted its 99th launch with the successful blastoff of an Atlas V with the MUOS-4 military communications satellite from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for the U.S. Navy.
Boeing has also chosen the Atlas V as the launcher that will soon propel Americans astronauts riding aboard the commercially developed Boeing CST-100 ‘Starliner’ taxi to the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
Starliner will eventually blastoff atop Vulcan after the Atlas V is retired in the next decade.
Lockheed provided me this update on Vulcan and ULA on Sept 21:
“Lockheed Martin is proud of ULA’s unparalleled track record of mission success, with 99 consecutive successful launches to date. We support the important role ULA plays in providing the nation with assured access to space. ULA’s Vulcan rocket takes the best performance elements of Atlas and Delta and combines them in a new system that will be superior in reliability, cost, weight, and capability. The government is working to determine its strategy for an American-made engine and future launch services. As they make those determinations we’ll adjust our strategy to make sure we’re aligned with the government’s objectives and goals.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.