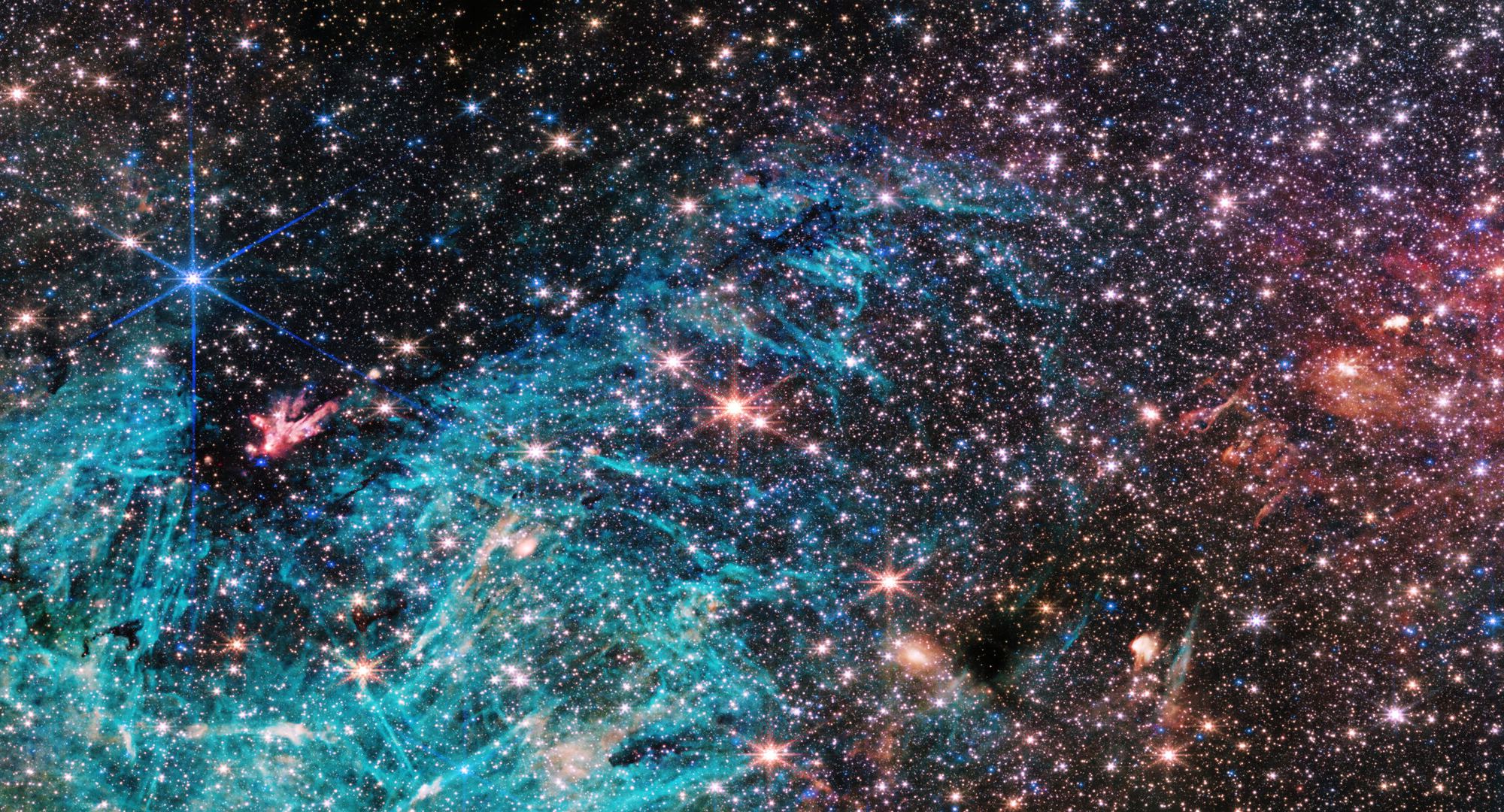
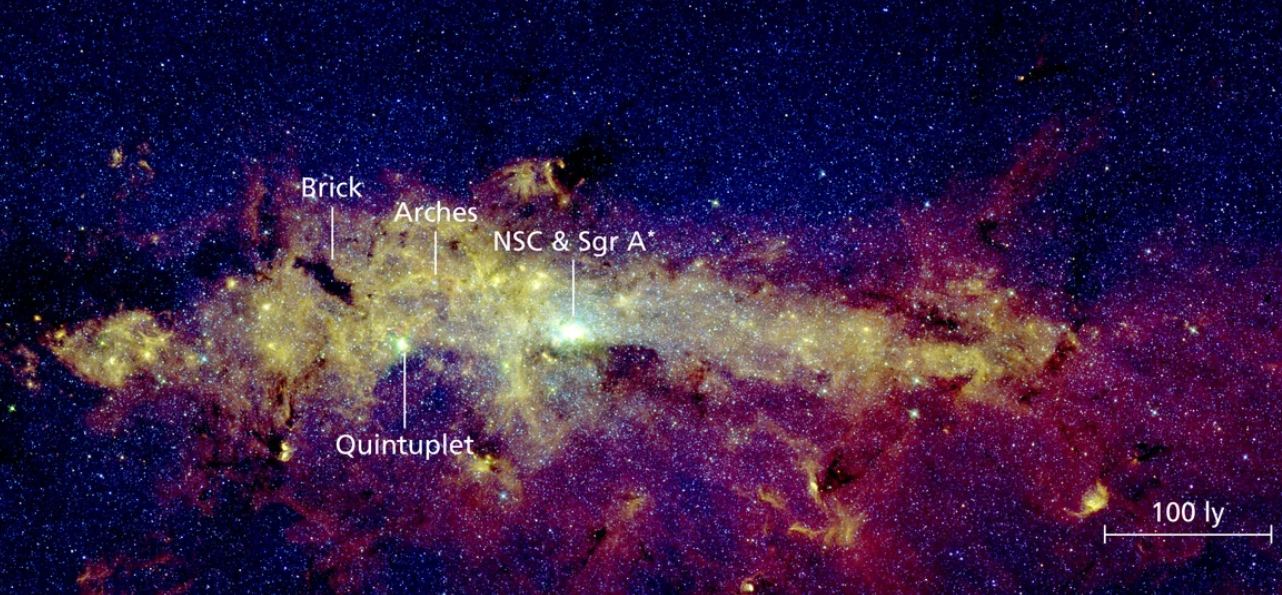
Thanks to its infrared capabilities, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) allows astronomers to peer through the gas and dust clogging the Milky Way’s center, revealing never-before-seen features. One of the biggest mysteries is the star forming region called Sagittarius C, located about 300 light-years from the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole. An estimated 500,000 stars are forming in this region that’s being blasted by radiation from the densely packed stars. How can they form in such an intense environment?
Right now, astronomers can’t explain it.
Continue reading “Gaze Into the Heart of the Milky Way in This Latest JWST Image”