Astronomers have known for years that galaxies are cannibalistic. Massive galaxies like our own Milky Way have gained mass by absorbing smaller neighbours.
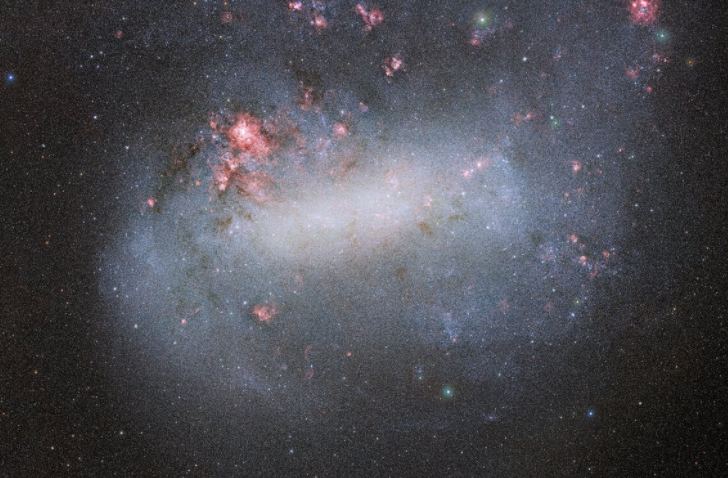
Now it looks like smaller galaxies like the Large Magellanic Cloud have also feasted on smaller neighbours.
Continue reading “The Large Magellanic Cloud Stole one of its Globular Clusters”