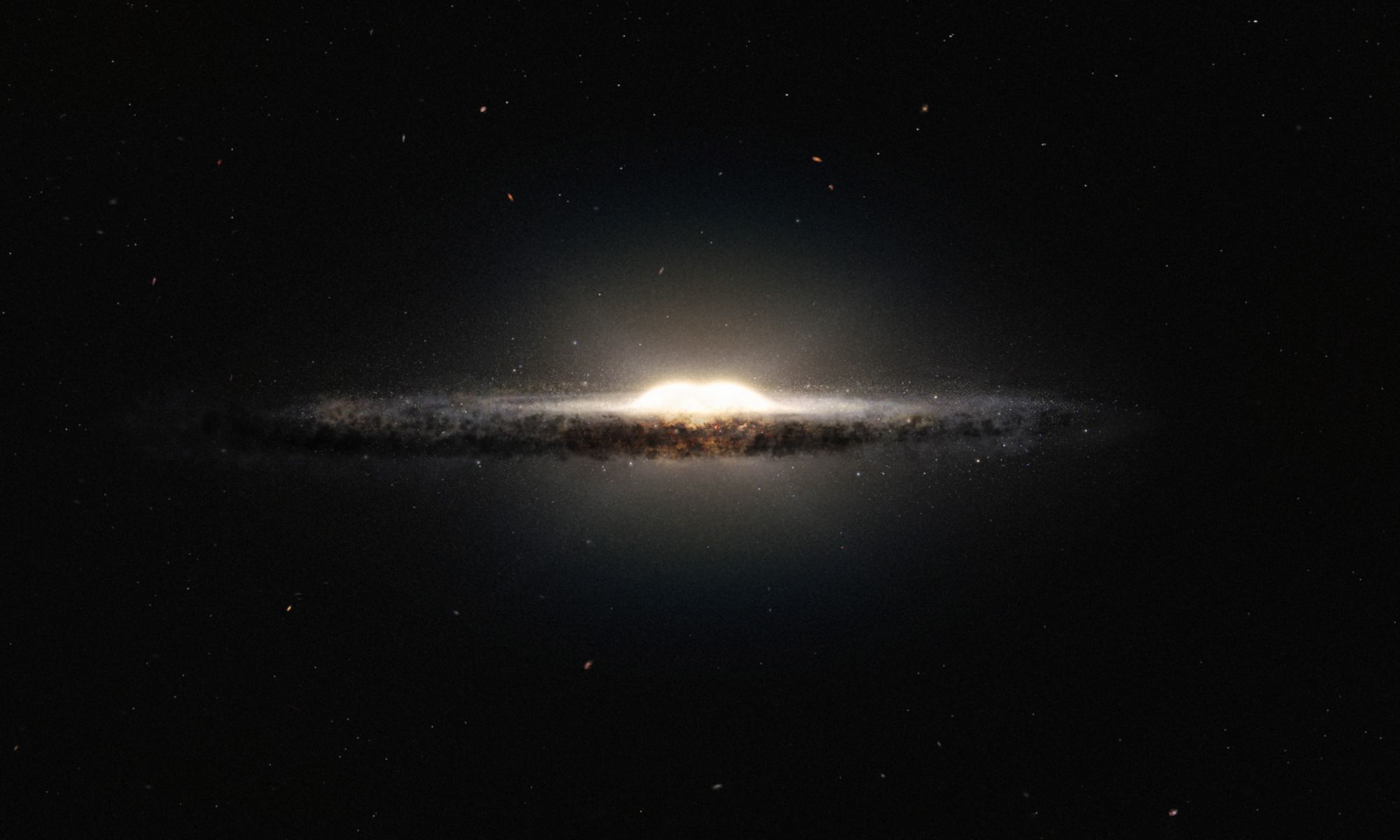
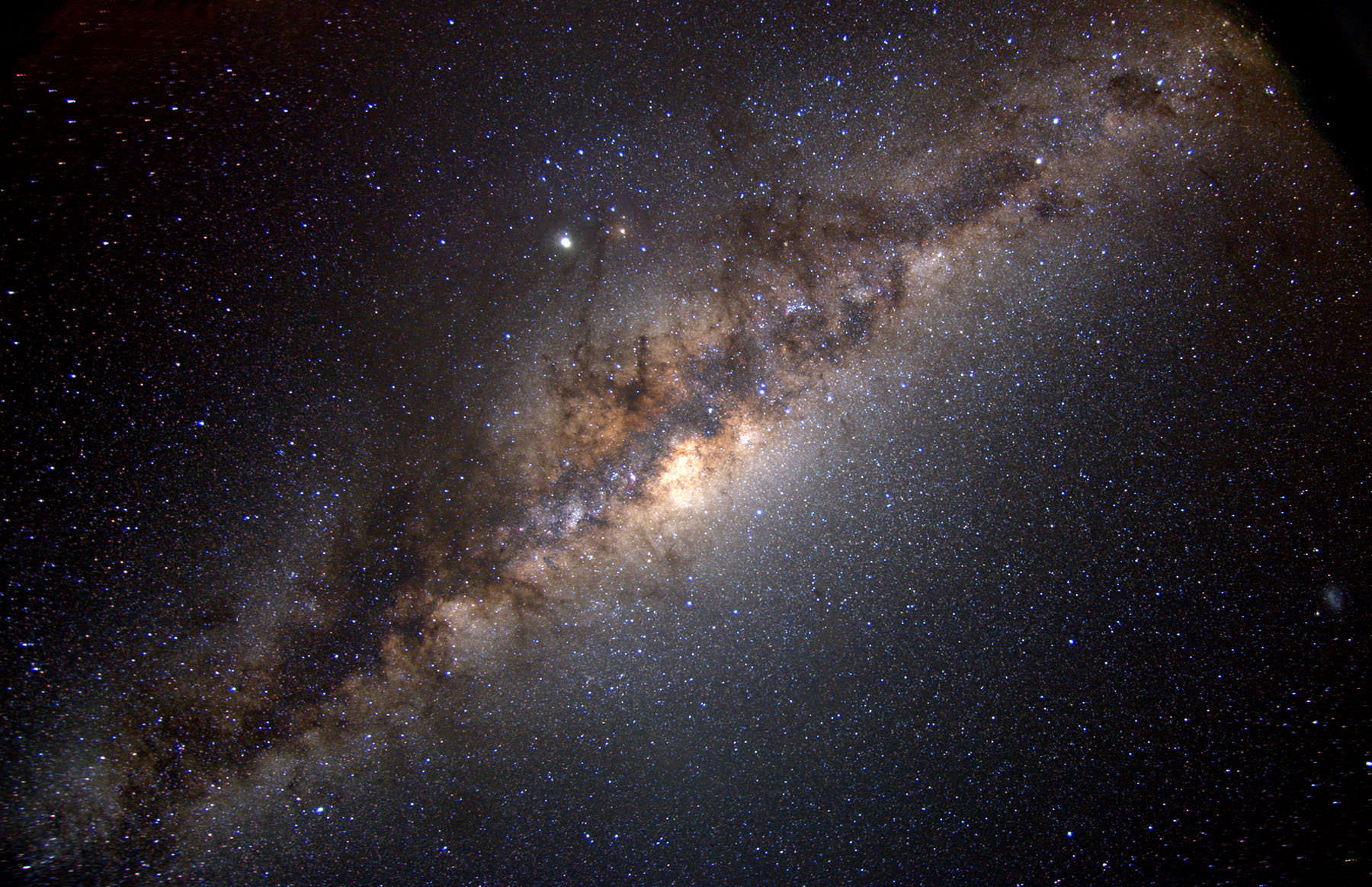
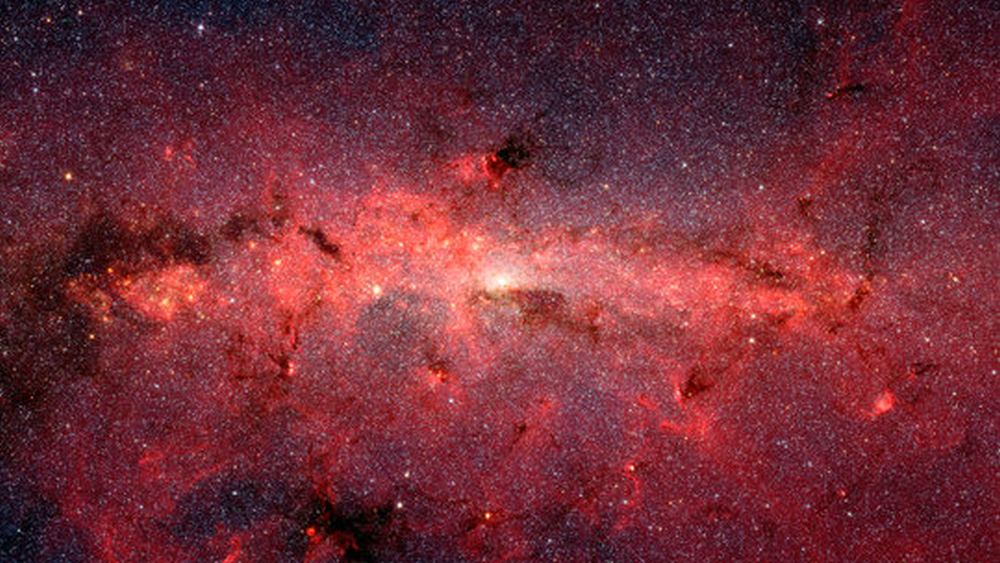
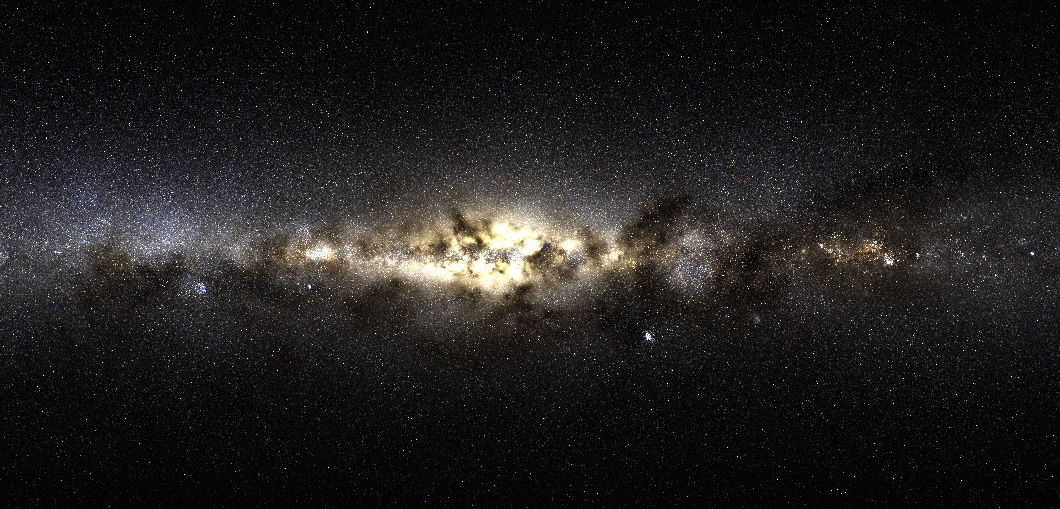
Ten billion years ago the young Milky Way survived a titanic merger with a neighboring galaxy, eventually consuming the whole thing. Now, remnants of that fossil galaxy still swim in our galaxy’s core – and astronomers have discovered that almost a third of the Milky Way’s current population came from that dismantled rival.
Continue reading “A third of the stars in the Milky Way came from a single merger 10 billion years ago”A third of the stars in the Milky Way came from a single merger 10 billion years ago