This week we welcome back to the show Dr. David Warmflash. Since he was last with us, David has been named as Co-Principal Investigator and Medical Director for a new NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBRI) Phase I study titled “Mixed-Reality Holographic Training System to Enable High-Value Surgical and Complex Medical Procedures by Astronauts.” This study, managed by the New Jersey-based Mgenuity Corporation with collaboration from Oregon Health Sciences University (OHSU), aims to develop a system to guide astronauts through surgical and medical procedures on Exploration Class missions.
Continue reading “Weekly Space Hangout: October 7, 2020, Dr. David Warmflash Discusses Mixed-Reality Surgical System”InSight’s Mole Is In!
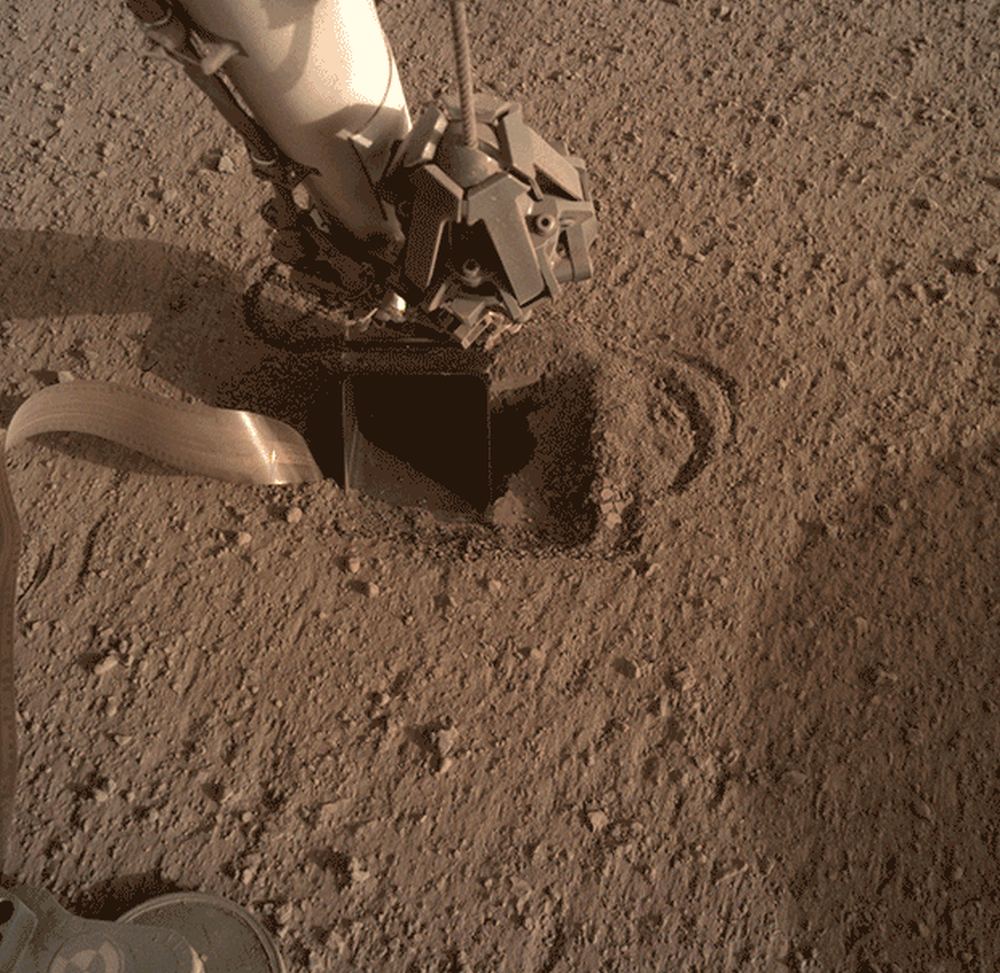
The InSight lander is making progress on Mars. After many months of struggle and careful adaptation, the InSight lander’s ‘Mole’ is finally into the ground. There’s still more delicate work to be done, and they’re not at operating depth yet. But after such a long, arduous affair, this feels like a victory.
Continue reading “InSight’s Mole Is In!”Instead of Going Straight to Mars, Astronauts Should Make a Slingshot Past Venus First

Every 26 months, the orbits of both Earth and Mars conspire to make travel between the two planets shorter. Launching in one of these windows means the travel time can be reduced to only six months. Our robotic missions to the Martian surface, and missions that place satellites in Martian orbit, launch during these windows.
But are there other alternatives to this mission architecture?
One group of researchers says that crewed missions to Mars shouldn’t go directly to their destination; they should slingshot past Venus first.
Continue reading “Instead of Going Straight to Mars, Astronauts Should Make a Slingshot Past Venus First”How Would We Do Surgery in Space?
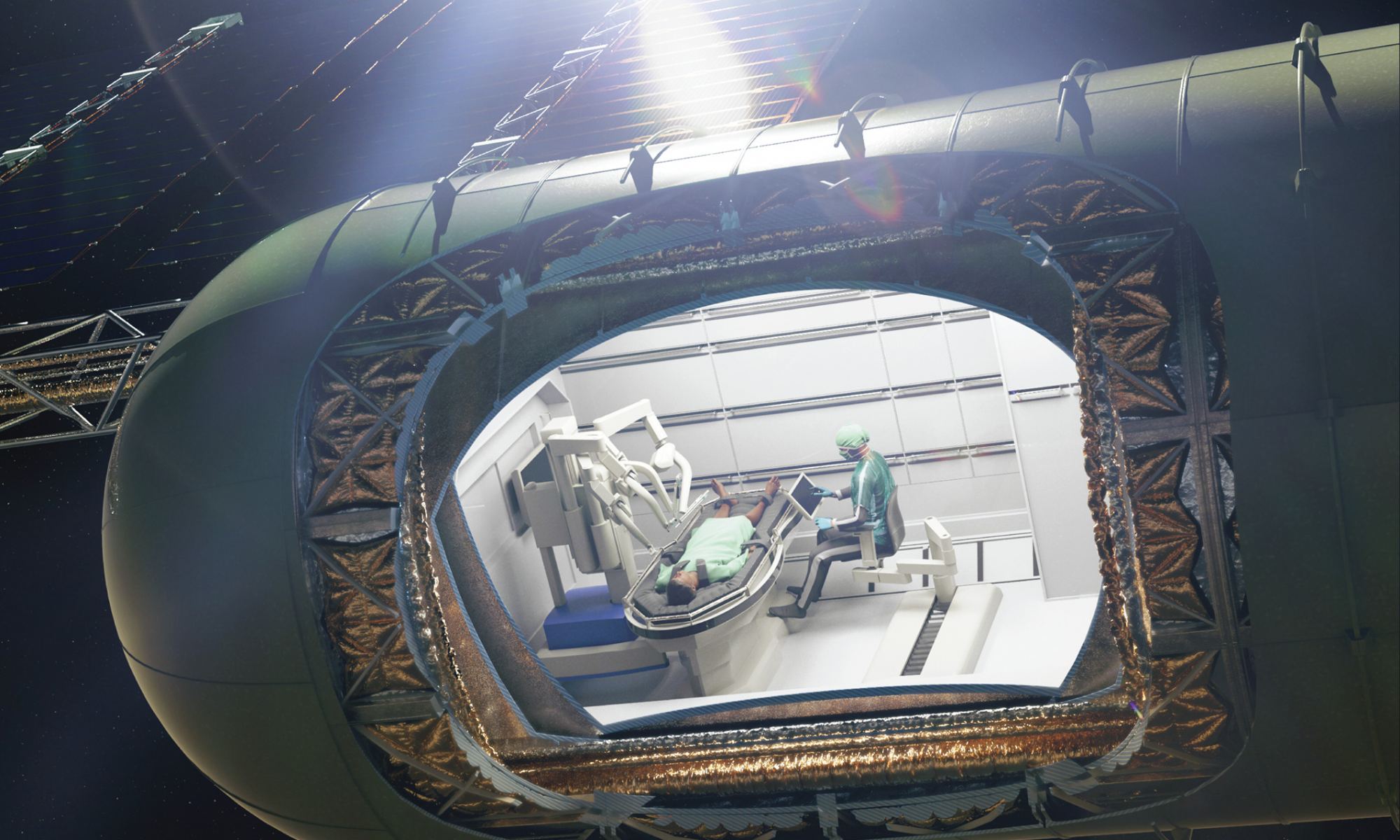

Any mission to Mars requires deeper planning than missions to the ISS or the Moon. Based purely on the length of the mission, contingencies branch outwards in complex logistical pathways. What if there’s an accident? What if someone’s appendix bursts?
And what if surgery is needed?
Continue reading “How Would We Do Surgery in Space?”Why Lava Tubes Should be Our Top Exploration Priority on Other Worlds

When magma comes out of the Earth onto the surface, it flows as lava. Those lava flows are fascinating to watch, and they leave behind some unique landforms and rocks. But a lot of what’s fascinating about these flows can be hidden underground, as lava tubes.
These lava tubes are turning out to be a very desirable target for exploration on other worlds, just as they are here on Earth.
Continue reading “Why Lava Tubes Should be Our Top Exploration Priority on Other Worlds”Rovers Will be Starting to Make Their Own Decisions About Where to Search for Life
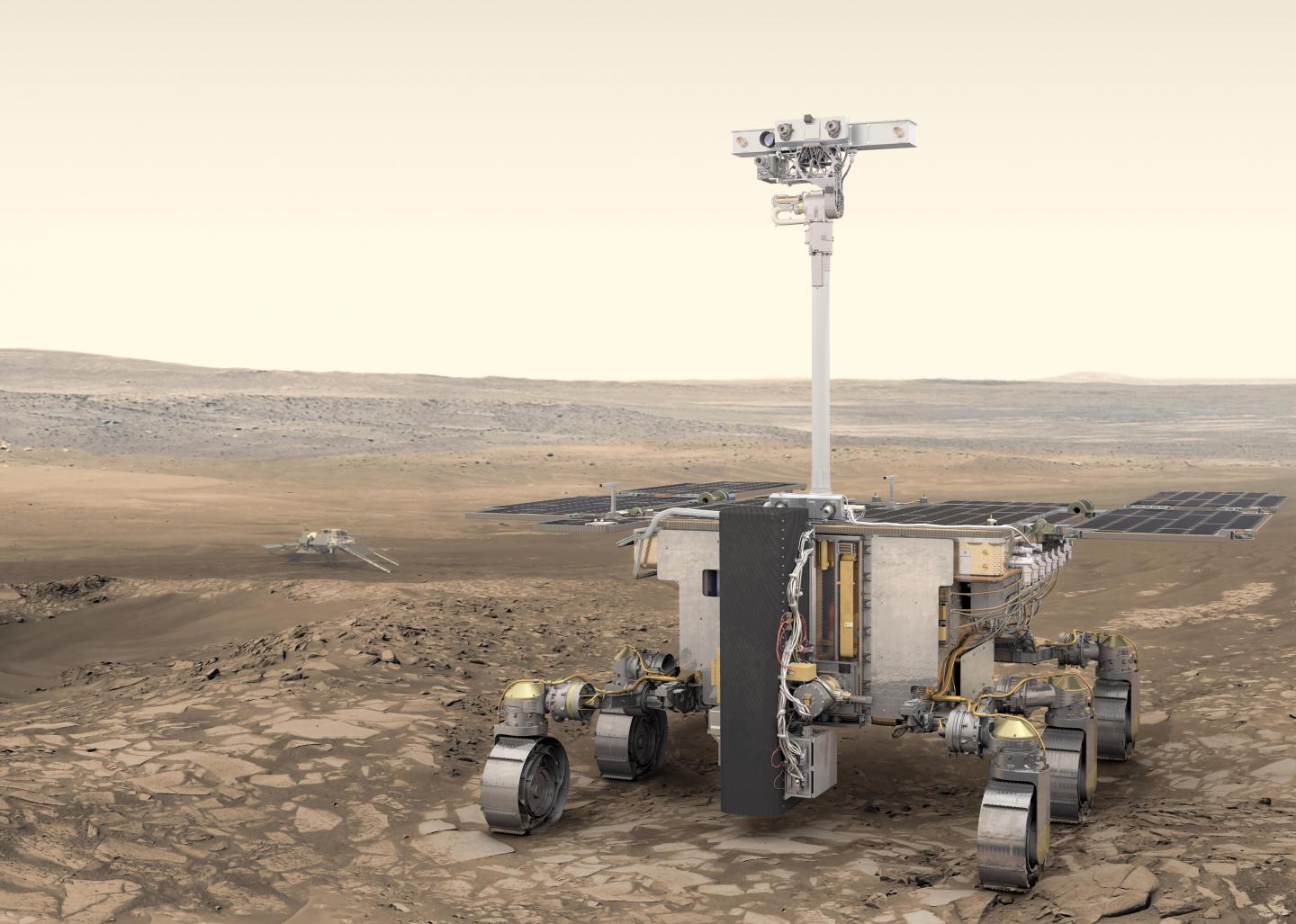
We all know how exploration by rover works. The rover is directed to a location and told to take a sample. Then it subjects that sample to analysis and sends home the results. It’s been remarkably effective.
But it’s expensive and time-consuming to send all this data home. Will this way of doing things still work? Or can it be automated?
Continue reading “Rovers Will be Starting to Make Their Own Decisions About Where to Search for Life”Well. It Looks Like James Webb is Getting Delayed Again, but it Should Still Launch in 2021
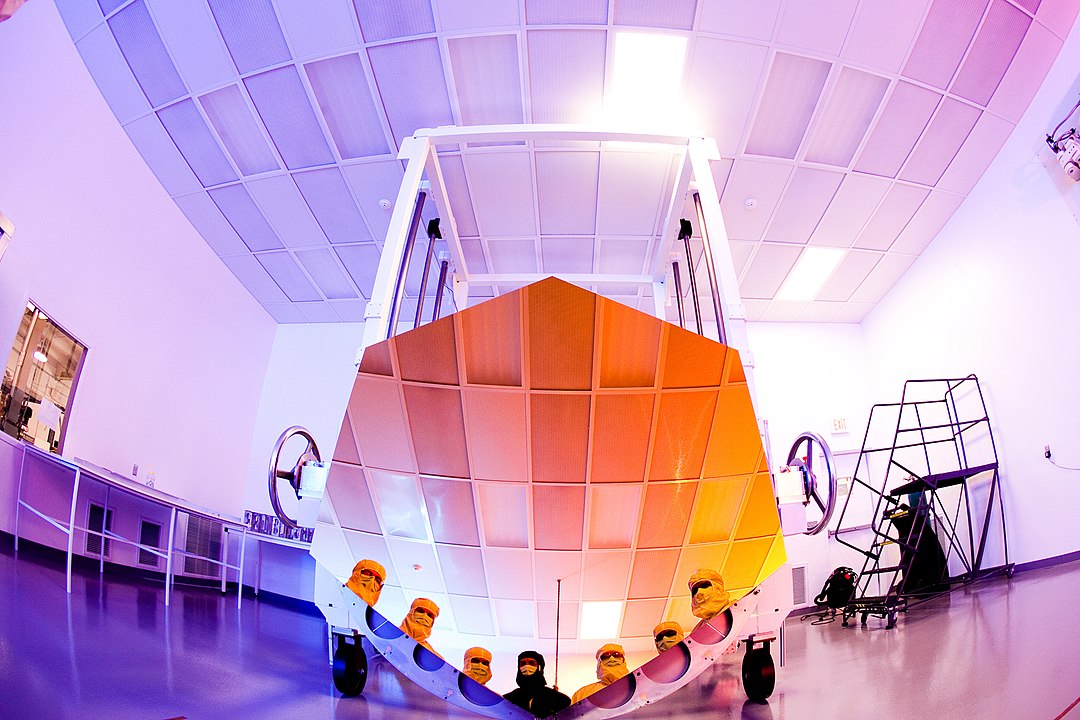

This is probably one of the least surprising announcements to come out of the coronavirus pandemic.
During a virtual meeting of the National Academies’ Space Studies Board, NASA’s associate administrator for science, Thomas Zurbuchen, made an announcement. He said there’s no way the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will meet its target launch date of March 2021.
Already on a tight timeline, work on the telescope has slowed during the pandemic.
Continue reading “Well. It Looks Like James Webb is Getting Delayed Again, but it Should Still Launch in 2021”Rocks on Bennu are Cracking Because of the Constant Day/Night Cycling

Asteroid Bennu is blanketed by rocks and huge boulders. And now that the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is taking a close look at those rocks, researchers are able to see something surprising for an airless body: the rocks have tiny cracks and fissures.
The cause?
Continue reading “Rocks on Bennu are Cracking Because of the Constant Day/Night Cycling”Finally! Mars InSight’s Mole is Now Underground
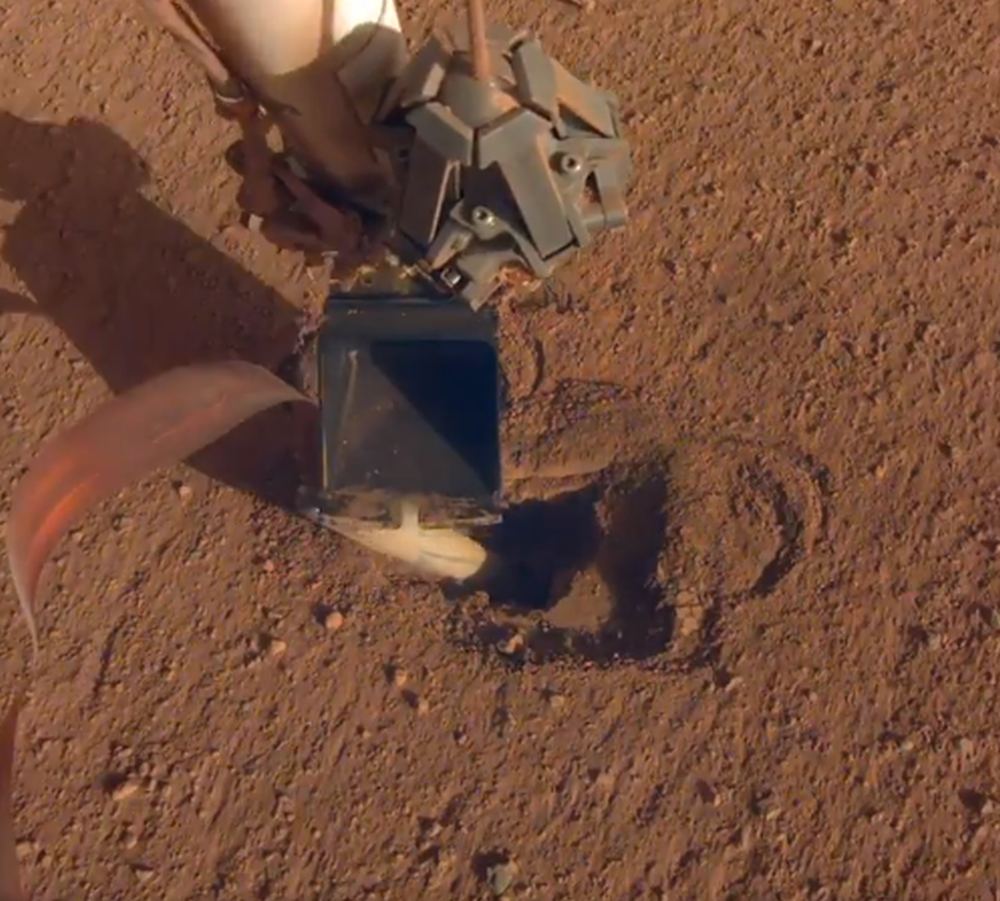
It looks like the InSight Lander’s Mole instrument is making some progress. After months of perseverance, the team operating the instrument has succeeded in getting the Mole at least some distance into the ground.
That’s a victory in itself, considering all the setbacks there’ve been. But it’s too soon to celebrate: there’s quite a ways to go before the Mole can deliver any science.
Continue reading “Finally! Mars InSight’s Mole is Now Underground”Tiny Cardboard Aircraft Could Fly in the Skies of Mars

What would be the best method for exploring planetary atmospheres, such as at Mars, Venus or even Earth? One group of researchers are developing tiny, levitating “nanocardboard” aircraft that could hover in alien skies. They would fly like dust floating in beams of sunlight – but intelligently, and with a purpose.
“It’s exciting because it’s essentially a new mechanism of flight,” said Igor Bargatin from the University of Pennsylvania. “We’re talking about a structure half an inch in size that can fly around without any moving parts.”
Continue reading “Tiny Cardboard Aircraft Could Fly in the Skies of Mars”
