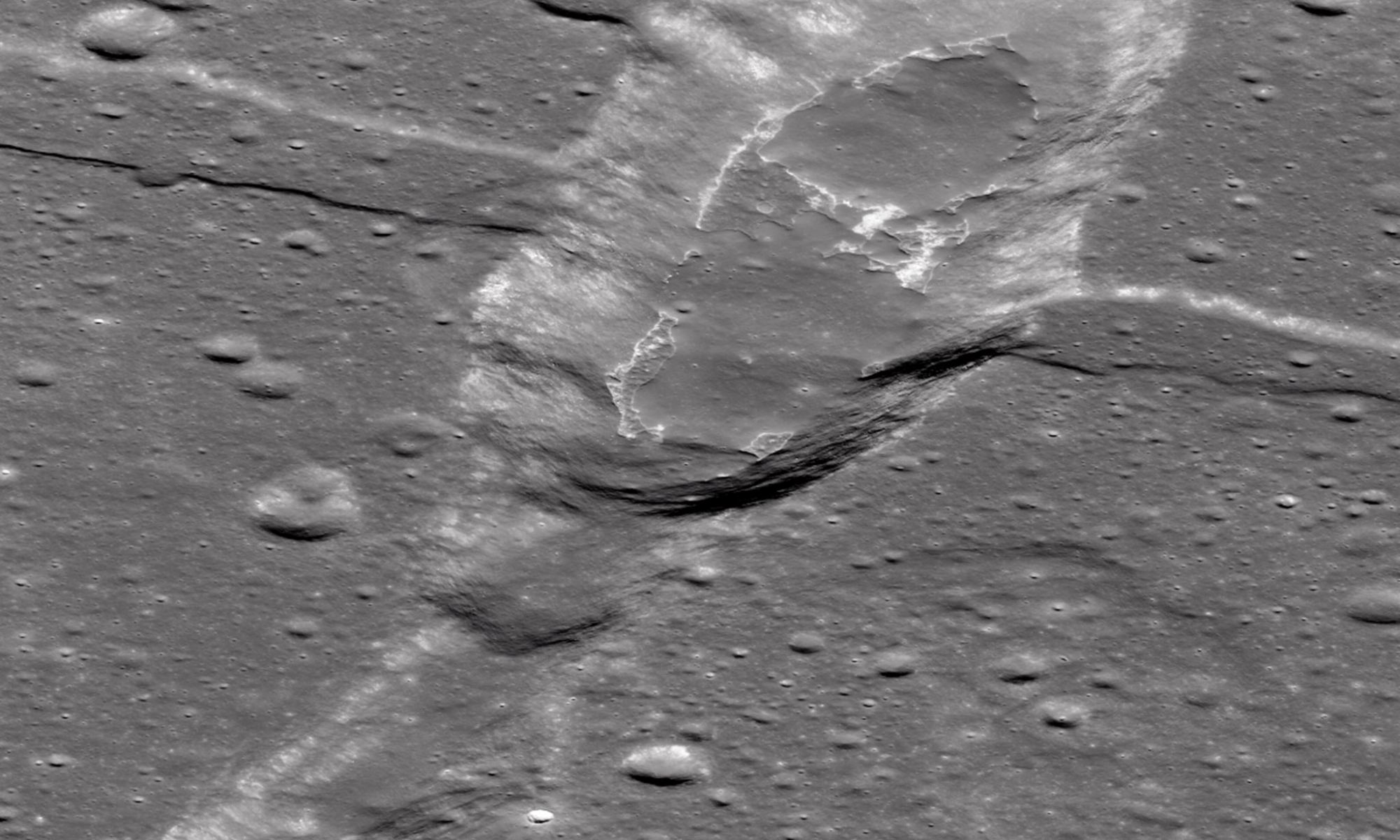
NASA recently selected a new science payload that will travel to the Moon through a series of robotic missions via the agency’s Artemis program. This instrument suite, known as the Dating an Irregular Mare Patch with a Lunar Explorer (DIMPLE), will have the task of studying the Ina Irregular Mare Patch, also known as Ina, which is a small depression that could provide insights into the Moon’s volcanic history. It was discovered using orbital images from the Apollo 15 crew, and despite several past studies, its origin remains unclear.
Continue reading “NASA Artemis DIMPLE Instrument Suite to Explore Moon’s Mysterious Volcanic Features”Volcanic Hotspot Found on the Moon

A recent study published in Nature examines a volcanic hotspot that potentially exists beneath a feature on the Moon’s farside (the side facing away from the Earth) called the Compton-Belkovich Thorium Anomaly. Researchers led by the Planetary Science Institute collected data from the hotspot region using microwave instruments onboard the China National Space Administration’s Chang’e-1 and Chang’e-2 orbiters and holds the potential to help scientists better understand the past volcanic processes on our nearest celestial neighbor, as surface evidence indicates lunar volcanic activity ceased between 3 to 4 billion years ago.
Continue reading “Volcanic Hotspot Found on the Moon”The Moon’s Ancient Volcanoes Could Have Created Ice Sheets Dozens of Meters Thick
Everyone loves looking at the Moon, especially through a telescope. To see those dark and light patches scattered across its surface brings about a sense of awe and wonder to anyone who looks up at the night sky. While our Moon might be geologically dead today, it was much more active billions of years ago when it first formed as hot lava blanketed hundreds of thousands of square kilometers of the Moon’s surface in hot lava. These lava flows are responsible for the dark patches we see when we look at the Moon, which are called mare, translated as “seas”, and are remnants of a far more active past.
In a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal, research from University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) suggests that volcanoes active billions of years ago may have left another lasting impact on the lunar surface: sheets of ice that dot the Moon’s poles and, in some places, could measure dozens or even hundreds of meters (or feet) thick.
Continue reading “The Moon’s Ancient Volcanoes Could Have Created Ice Sheets Dozens of Meters Thick”Volcanism on the Moon Ended About 2 Billion Years ago
According to the most widely accepted theories, the Moon formed about 4.5 billion years ago after a Mars-sized object (Theia) collided with Earth. After the resulting debris accreted to create the Earth-Moon system, the Moon spent many eons cooling down. This meant that a few billion years ago, lakes of lava were flowing across the surface of the Moon, which eventually hardened to form the vast dark patches (lunar maria) that are still there today.
Thanks to the samples of lunar rock brought back to Earth by China’s Chang’e 5 mission, scientists are learning more about how the Moon formed and evolved. According to a recent study led by the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (CGAS), an international team examined these samples to investigate when volcanism on the Moon ended. Their results are not only filling in the gaps of the Moon’s geological history but also of other bodies in the Solar System.
Continue reading “Volcanism on the Moon Ended About 2 Billion Years ago”