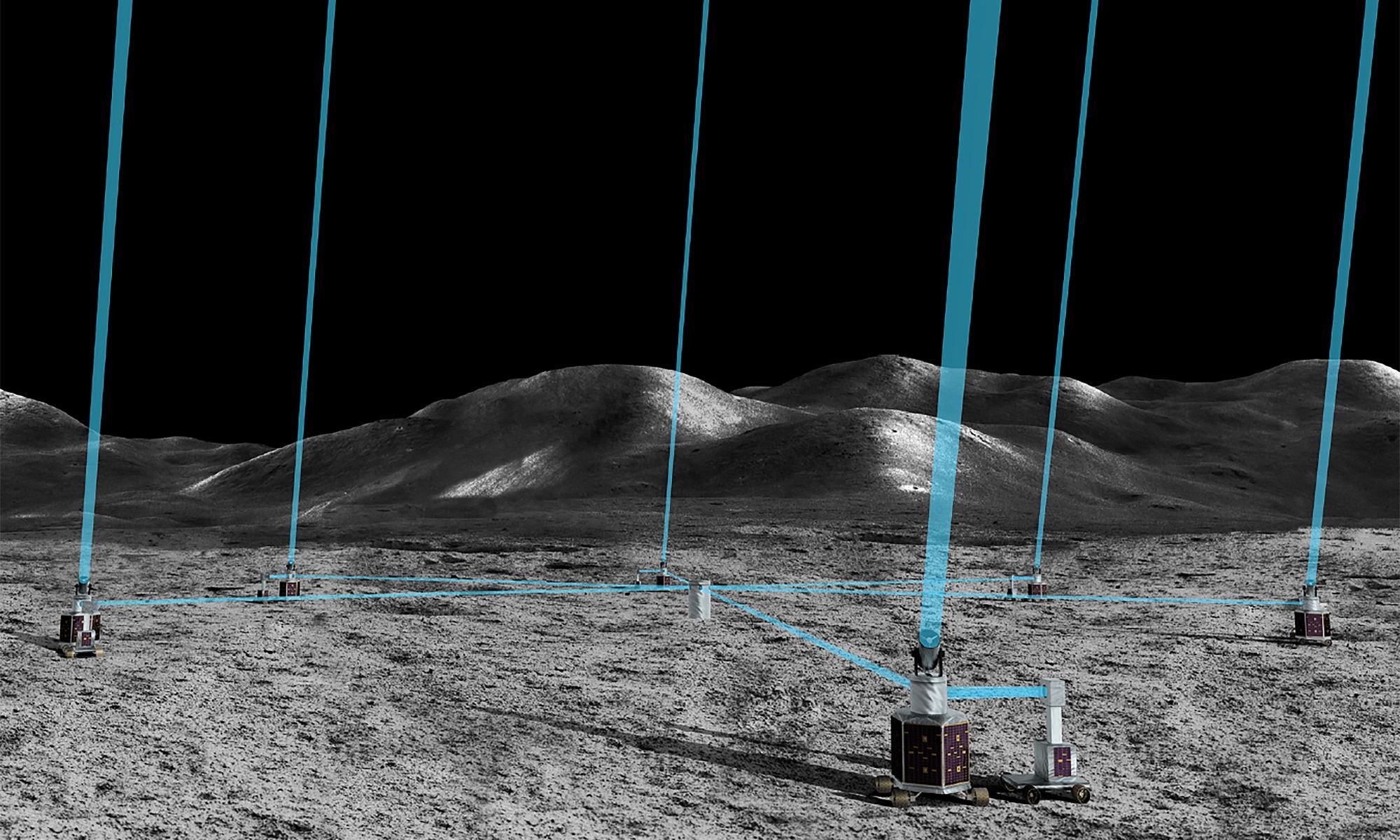
As part of the Artemis Program, NASA intends to establish all the necessary infrastructure to create a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development.” This includes the Lunar Gateway, an orbiting habitat that will enable regular trips to and from the surface, and the Artemis Base Camp, which will permit astronauts to remain there for up to two months. Multiple space agencies are also planning on creating facilities that will take advantage of the “quiet nature” of the lunar environment, which includes high-resolution telescopes.
As part of this year’s NASA Innovative Advance Concepts (NIAC) Program, a team from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center has proposed a design for a lunar Long-Baseline Optical Imaging Interferometer (LBI) for imaging at visible and ultraviolet wavelengths. Known as the Artemis-enabled Stellar Imager (AeSI), this proposed array of multiple telescopes was selected for Phase I development. With a little luck, the AeSI array could be operating on the far side of the Moon, taking detailed images of stellar surfaces and their environments.
Continue reading “NASA Wants to Put a Massive Telescope on the Moon”