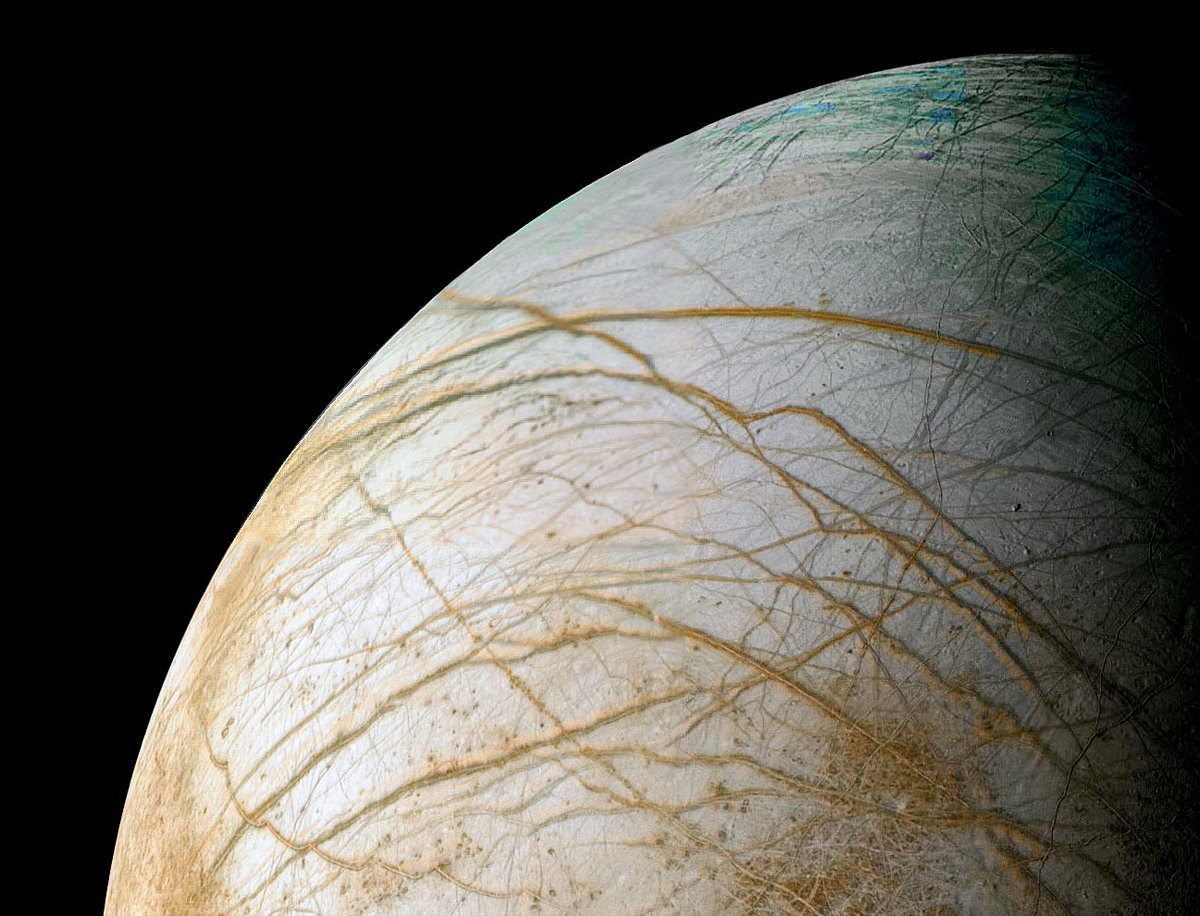
According to research by NASA astronomers using the next-generation optics of the 10-meter Keck II telescope, Jupiter’s ice-encrusted moon Europa has hydrogen peroxide across much of the surface of its leading hemisphere, a compound that could potentially provide energy for life if it has found its way into the moon’s subsurface ocean.
“Europa has the liquid water and elements, and we think that compounds like peroxide might be an important part of the energy requirement,” said JPL scientist Kevin Hand, the paper’s lead author. “The availability of oxidants like peroxide on Earth was a critical part of the rise of complex, multicellular life.”
The paper, co-authored by Mike Brown of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, analyzed data in the near-infrared range of light from Europa using the Keck II Telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, over four nights in September 2011. The highest concentration of peroxide found was on the side of Europa that always leads in its orbit around Jupiter, with a peroxide abundance of 0.12 percent relative to water. (For perspective, this is roughly 20 times more diluted than the hydrogen peroxide mixture available at drug stores.) The concentration of peroxide in Europa’s ice then drops off to nearly zero on the hemisphere of Europa that faces backward in its orbit.
Hydrogen peroxide was first detected on Europa by NASA’s Galileo mission, which explored the Jupiter system from 1995 to 2003, but Galileo observations were of a limited region. The new Keck data show that peroxide is widespread across much of the surface of Europa, and the highest concentrations are reached in regions where Europa’s ice is nearly pure water with very little sulfur contamination.

The peroxide is created by the intense radiation processing of Europa’s surface ice that comes from the moon’s location within Jupiter’s strong magnetic field.
“The Galileo measurements gave us tantalizing hints of what might be happening all over the surface of Europa, and we’ve now been able to quantify that with our Keck telescope observations,” Brown said. “What we still don’t know is how the surface and the ocean mix, which would provide a mechanism for any life to use the peroxide.”
Read more: Evidence for a Deep Ocean on Europa Might Be Found on its Surface
The scientists think hydrogen peroxide is an important factor for the habitability of the global liquid water ocean under Europa’s icy crust because hydrogen peroxide decays to oxygen when mixed into liquid water. “At Europa, abundant compounds like peroxide could help to satisfy the chemical energy requirement needed for life within the ocean, if the peroxide is mixed into the ocean,” said Hand.
(Source: NASA)
What’s notable to add, on March 26, 2013, the U.S. President signed a bill that would increase the budget for NASA’s planetary science program as well as provide $75 million for the exploration of Europa. Exactly how the funds will be used isn’t clear — perhaps for components on the proposed Europa Clipper mission? — but it’s a step in the right direction for learning more about this increasingly intriguing world. Read more on SETI’s Destination: Europa blog.