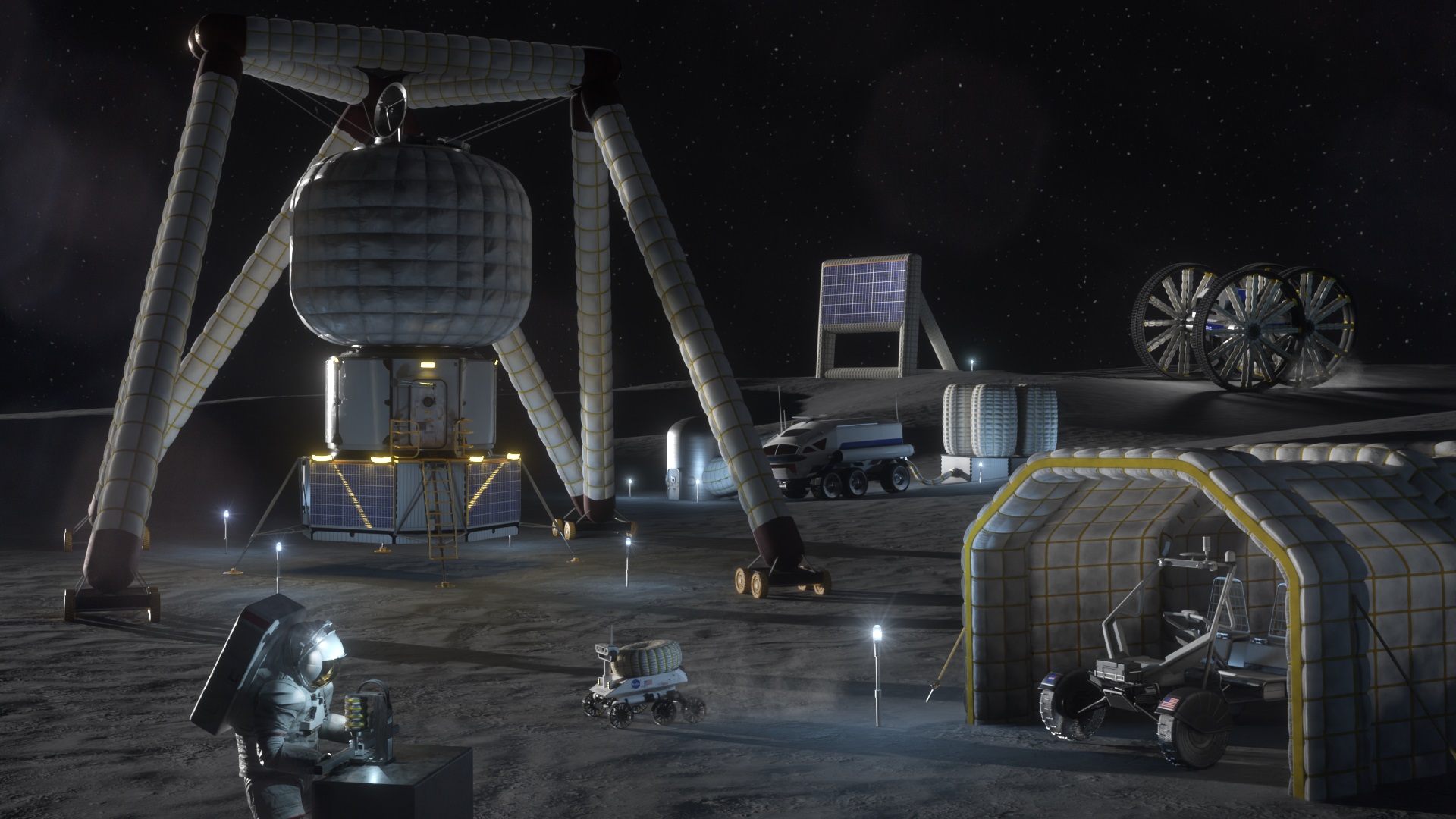
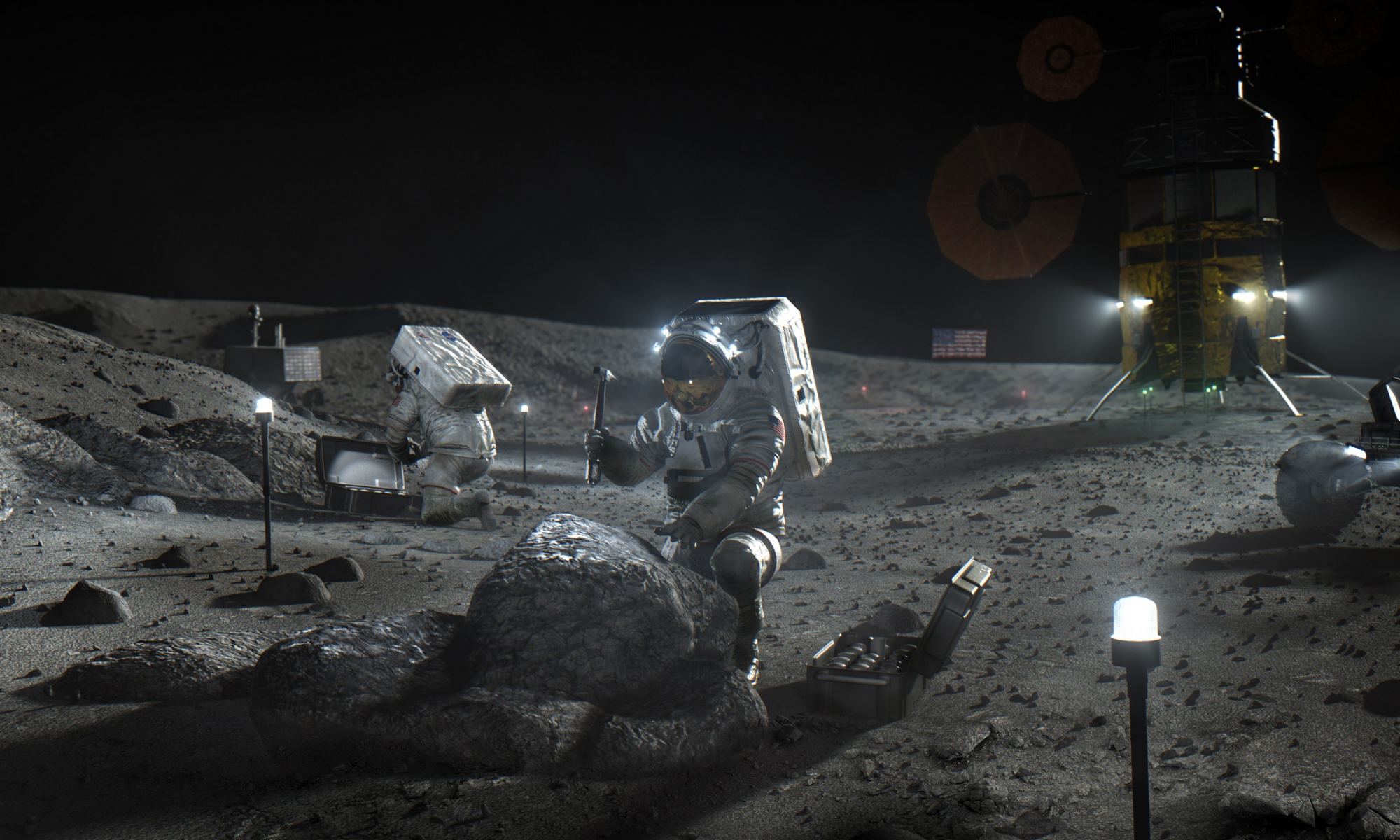
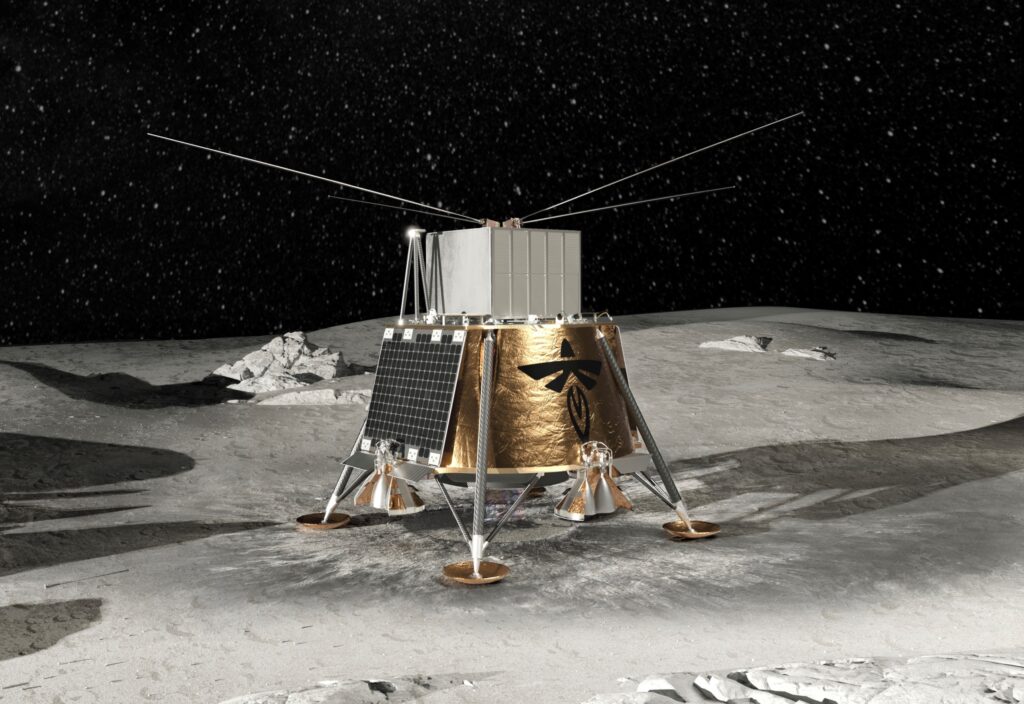
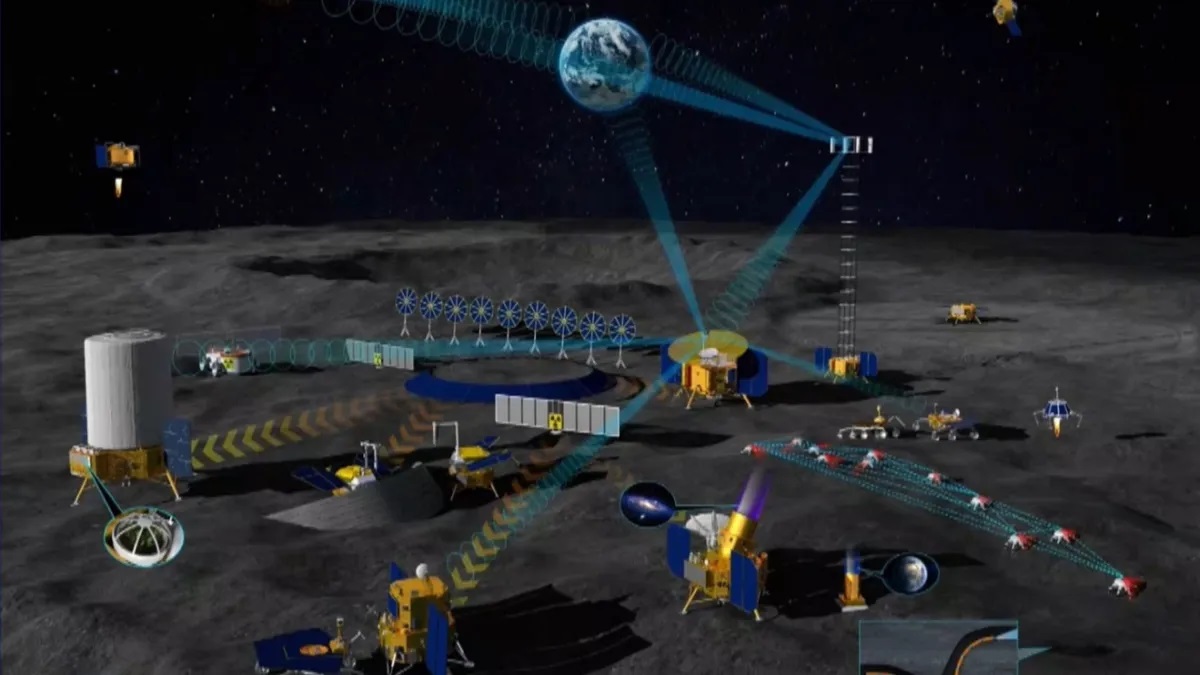
Every year, NASA’s Breakthrough, Innovative, and Game-Changing (BIG) Idea Challenge invites student innovators to build and demonstrate concepts that can benefit future human missions to the Moon and beyond. This year’s theme is “Inflatable Systems for Lunar Operations,” which could greatly reduce the mass and stowed volume of payloads sent to the Moon. This is critical for the Artemis Program as it returns astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era over fifty years ago. It will also reduce the costs of sending payloads to the Moon, Mars, and other deep-space destinations.
Continue reading “Balloon Animals and Bouncy Castles on the Moon. The Case for Inflatable Habitats”Balloon Animals and Bouncy Castles on the Moon. The Case for Inflatable Habitats