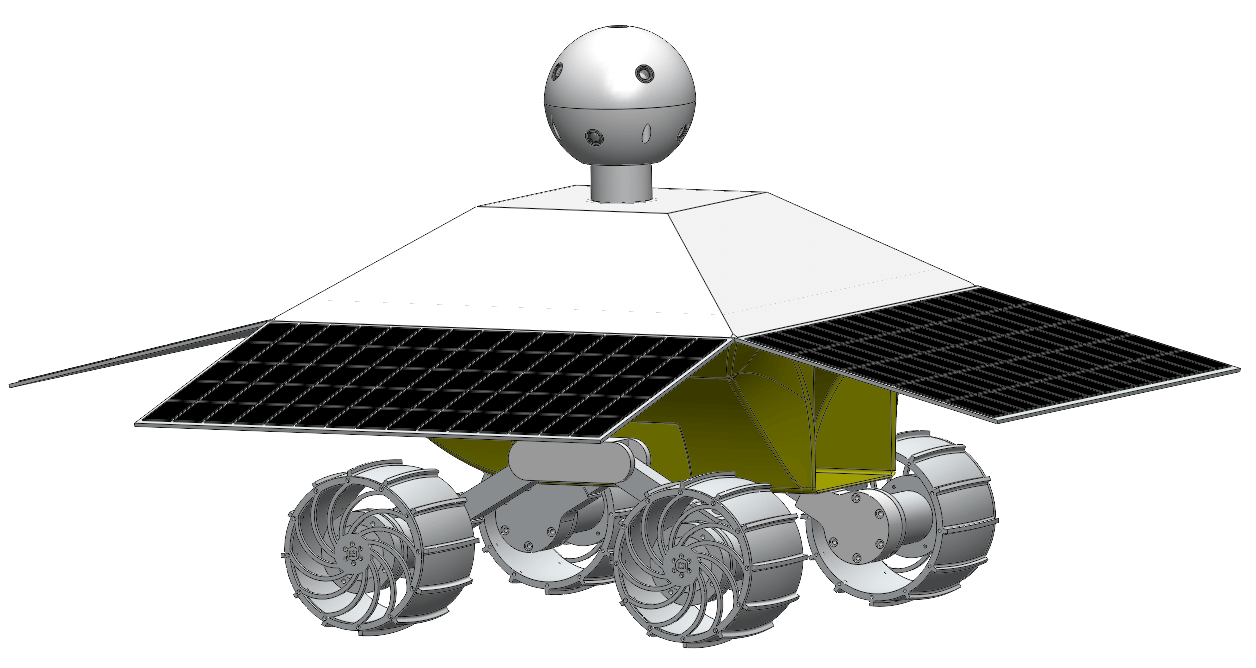
Omega Envoy, the non-profit research lab Earthrise Space, Inc.’s team competing for the Google Lunar X PRIZE, has launched a Kickstarter project to help fund a 4-axis CNC milling machine needed to continue development on their proposed lunar rover. CNC machines don’t come cheap, but in typical Kickstarter fashion Earthrise Space is offering incremental rewards to anyone who donates to their project — from mentions on their site to t-shirts, Moon globes and facility tours (and even 5-gallon tubs of duck sauce) and, if you’re lucky enough to have deep pockets and a desire to help a student training ground get their designs off the ground, you can even have your DNA sent to the Moon!
From the Google Lunar X PRIZE article:
For the first time in human history, individuals will have the opportunity to send a sample of their DNA to the lunar surface. For a pledged donation of $10,000 or more, ESI will collect your DNA sample, package it into a storage container mounted on the company’s Lunar Descent Vehicle and fly it to the surface of the moon where it will be preserved for all time.
“We are excited to be exploring new approaches for fundraising and for public engagement, including through the crowdsourcing Kickstarter platform,” said ESI’s Chief Operating Officer (COO) Joseph Palaia. “We are hopeful that this Kickstarter project helps us to make significant progress towards our near-term fundraising goals, while also providing some incredible rewards for our supporters.”
With the Google Lunar X PRIZE, a total of $30 million in prize money is available to the first privately funded team to safely land a robot on the surface of the Moon, have that robot travel 500 meters over the surface, and send HD video, images and data back to Earth.
Of the 26 teams in the competition, ESI is one of only six teams which have been selected for a NASA Innovative Lunar Demonstrations Data contract worth up to $10M. But the contract is awarded incrementally and a multi-axis CNC machine is needed to take their designs to the next level (and meet upcoming contract goals.) Donate to their Kickstarter project here.
At whatever level you contribute, know that you are helping students build real spacecraft, and you’re going to be getting some pretty amazing rewards as well! The students appreciate your support!
— Omega Envoy team, ESI
Find out more about ESI’s project on the Earthrise Space Inc. website, and check out the other Google Lunar X PRIZE competitors here.
Source: Google Lunar X PRIZE blog