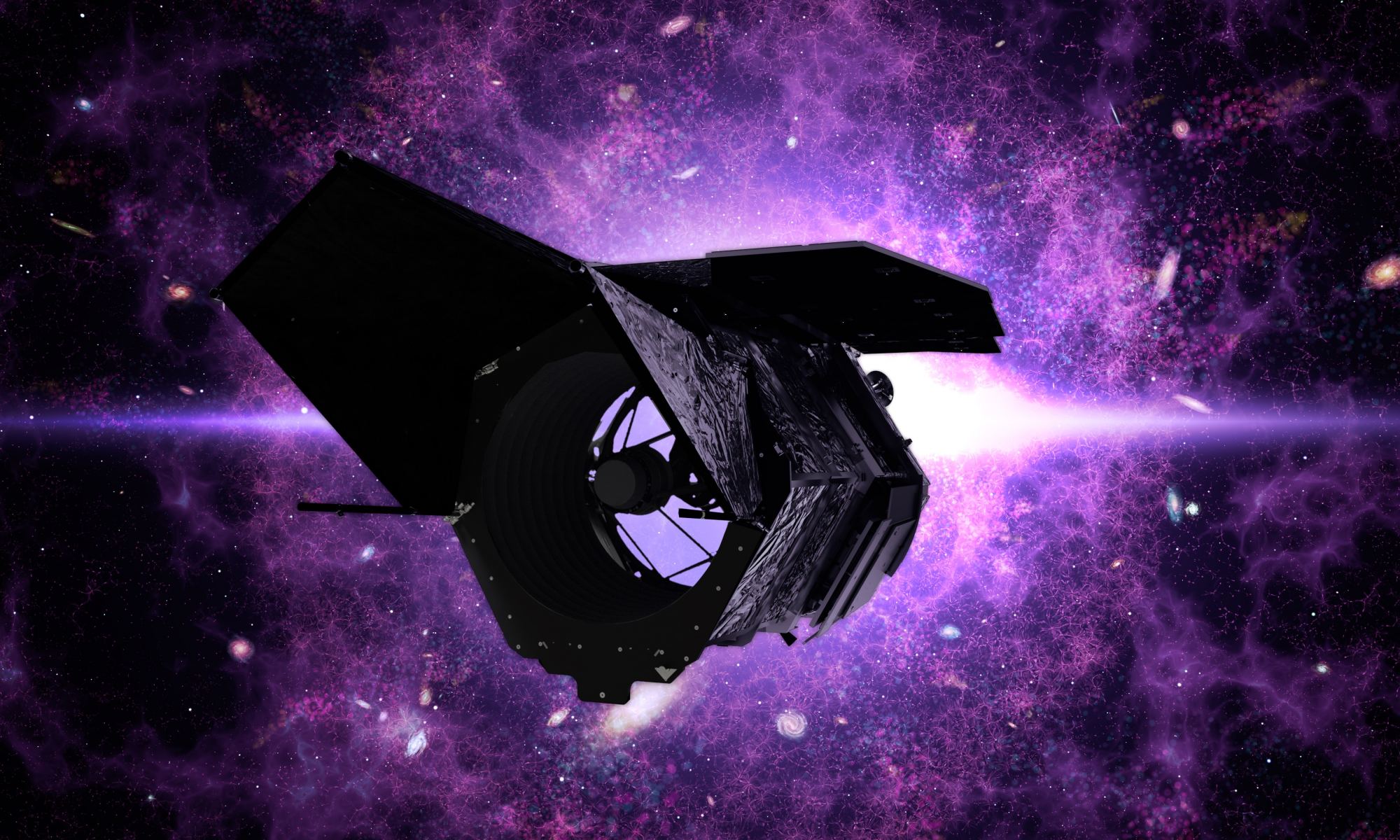
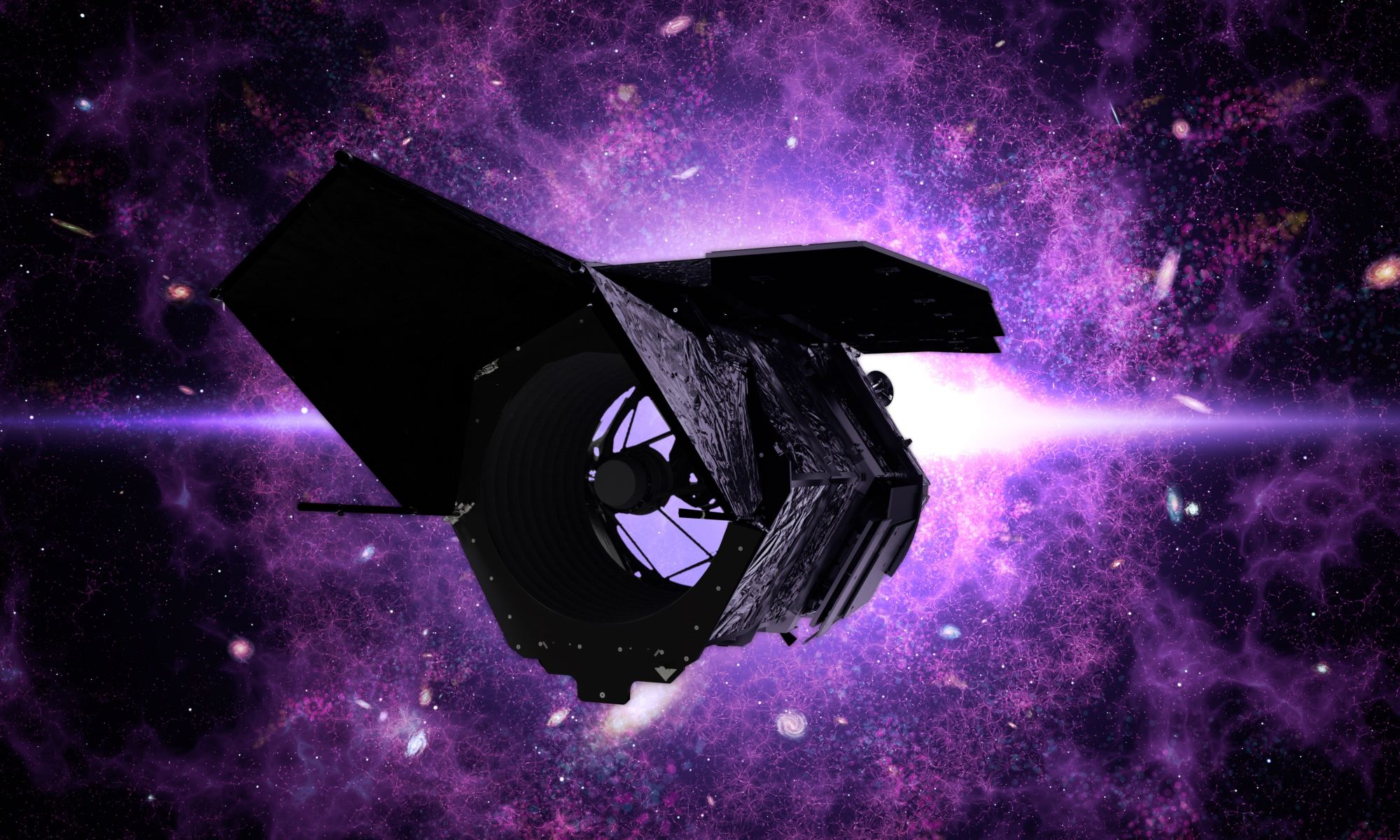
Less than a year and a half into its primary mission, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has already revolutionized astronomy as we know it. Using its advanced optics, infrared imaging, and spectrometers, the JWST has provided us with the most detailed and breathtaking images of the cosmos to date. But in the coming years, this telescope and its peers will be joined by another next-generation instrument: the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (RST). Appropriately named after “the Mother of Hubble,” Roman will pick up where Hubble left off by peering back to the beginning of time.
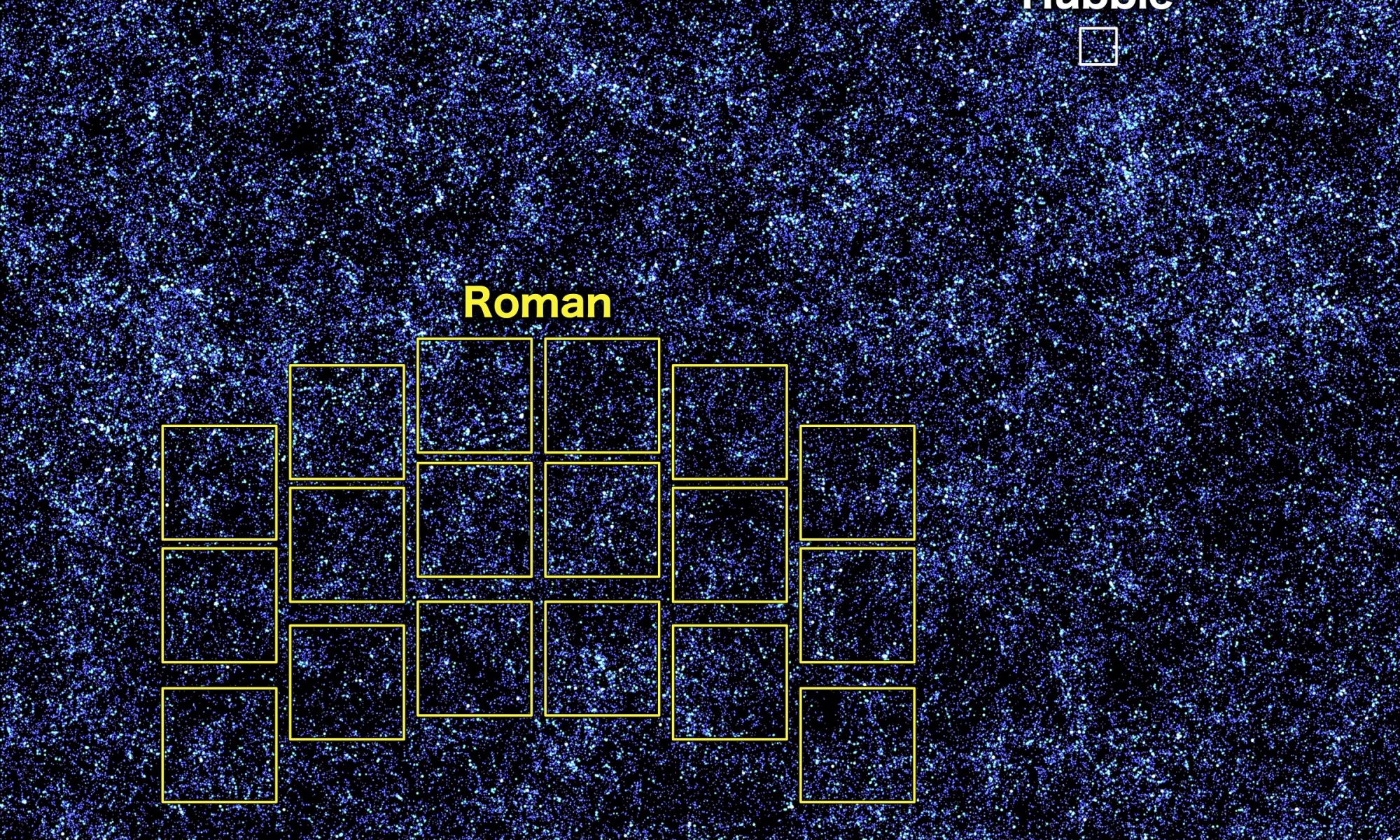
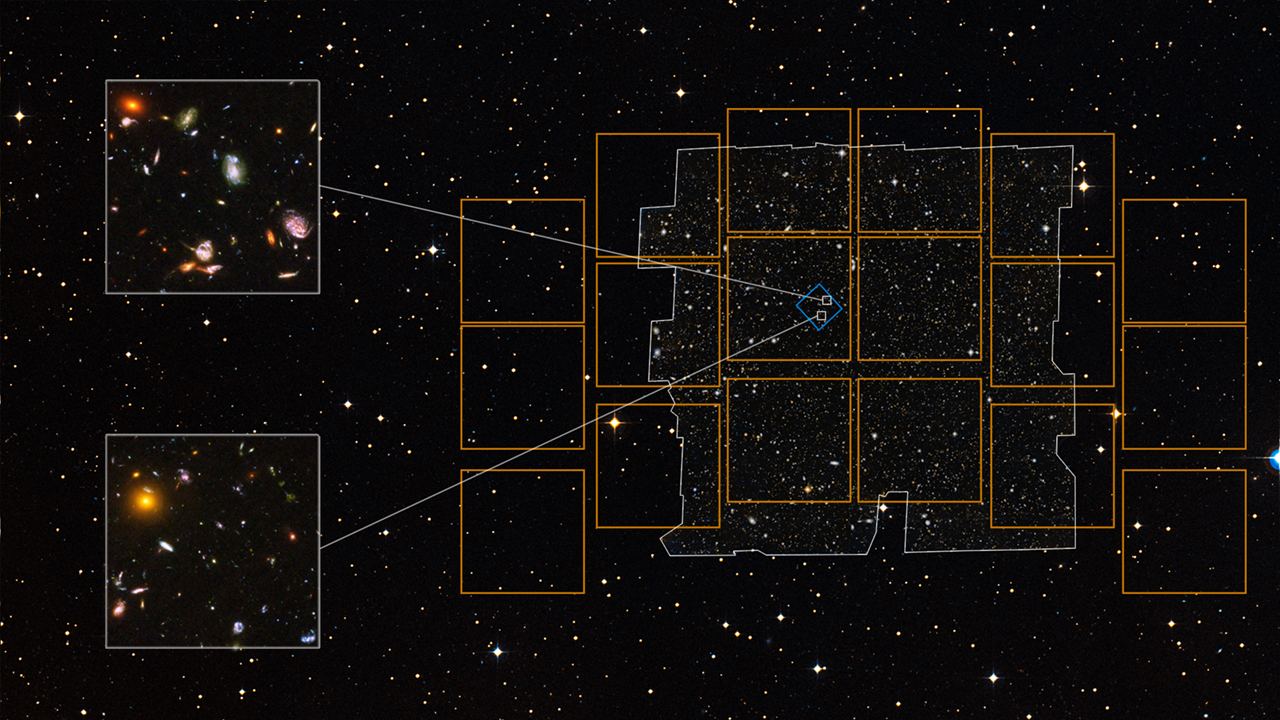
Like Hubble, the RST will have a 2.4-meter (7.9 ft) primary mirror and advanced instruments to capture images in different wavelengths. However, the RST will also have a gigantic 300-megapixel camera – the Wide Field Instrument (WFI) – that will enable a field of view two-hundred times greater than Hubble’s. In a recent study, an international team of NASA-led researchers described a simulation they created that previewed what the RST could see. The resulting data set will enable new experiments and opportunities for the RST once it takes to space in 2027.
Continue reading “It Would Take Hubble 85 Years to Match What Nancy Grace Roman Will See in 63 Days”