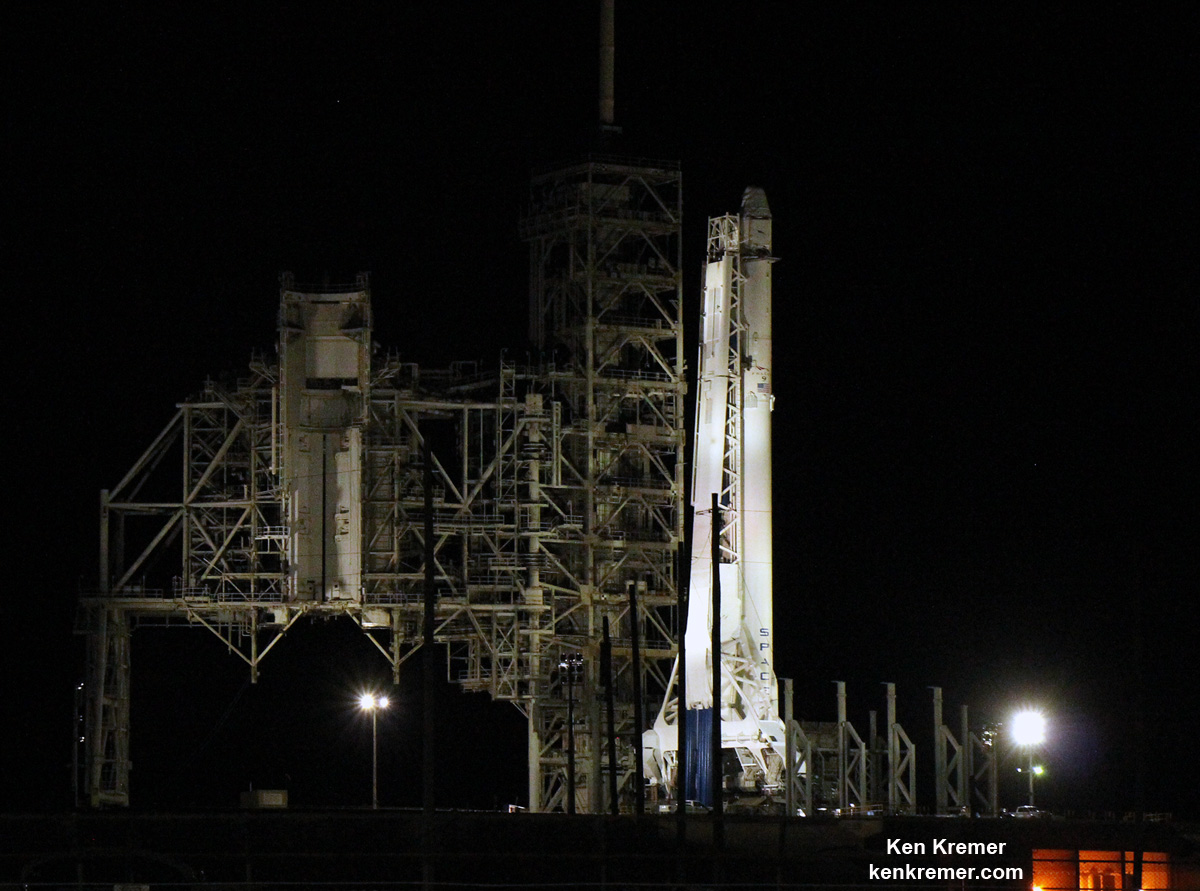
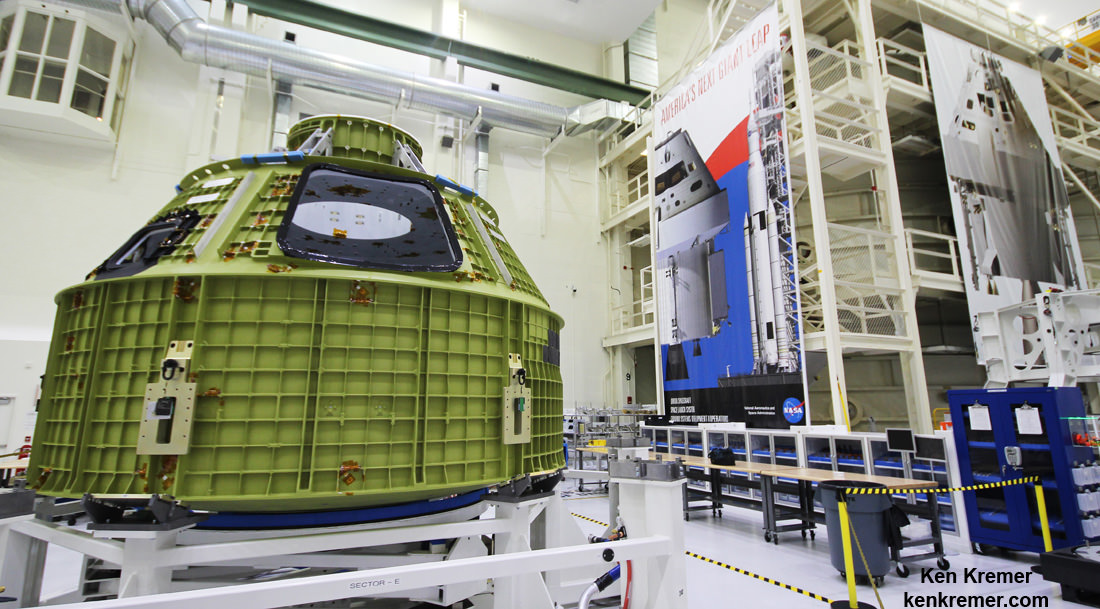
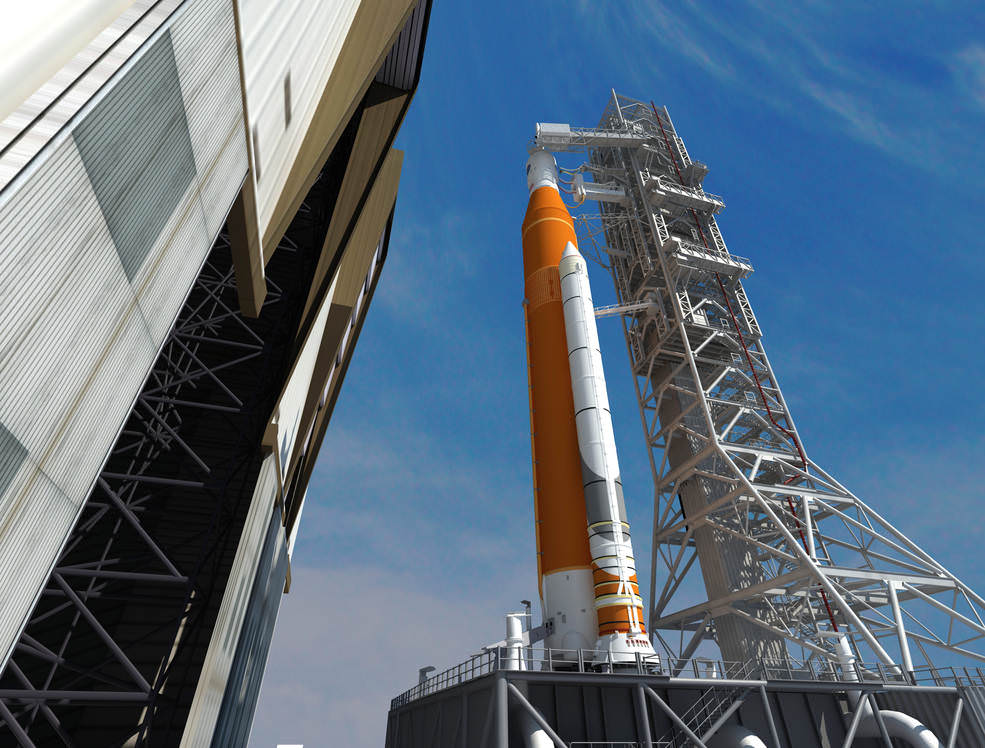
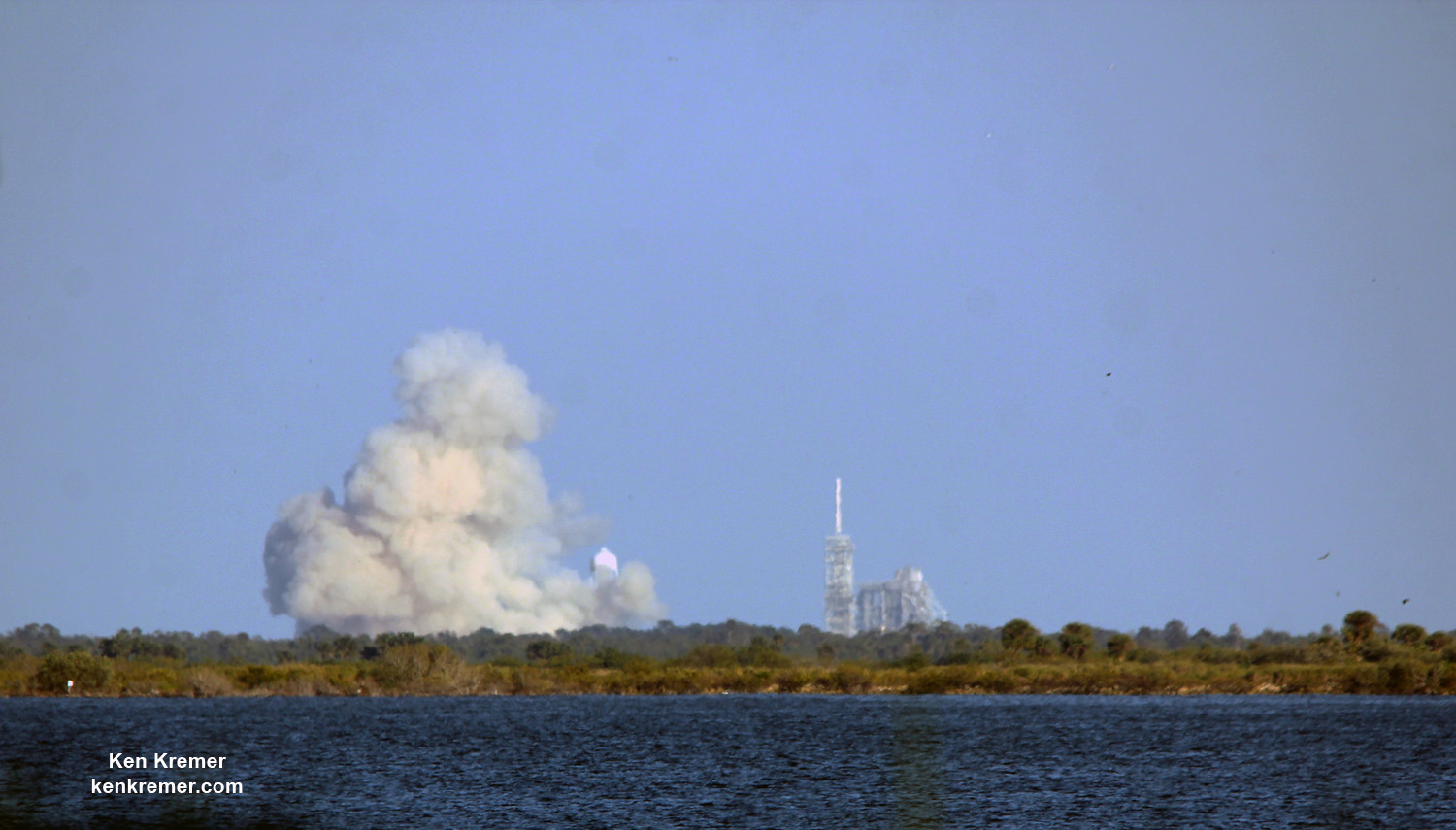
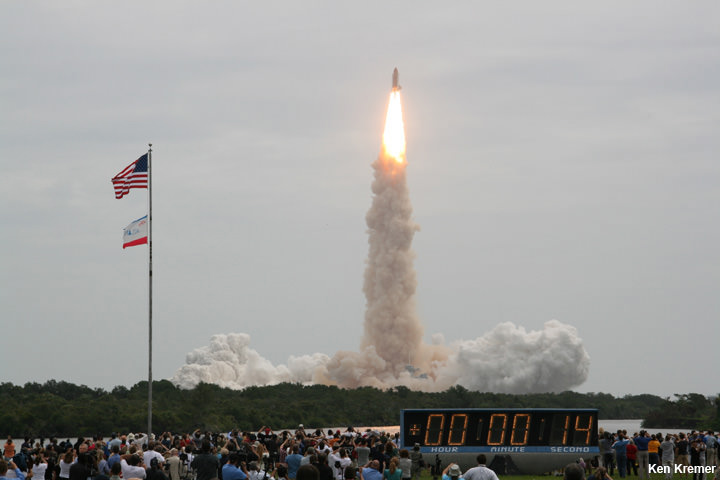
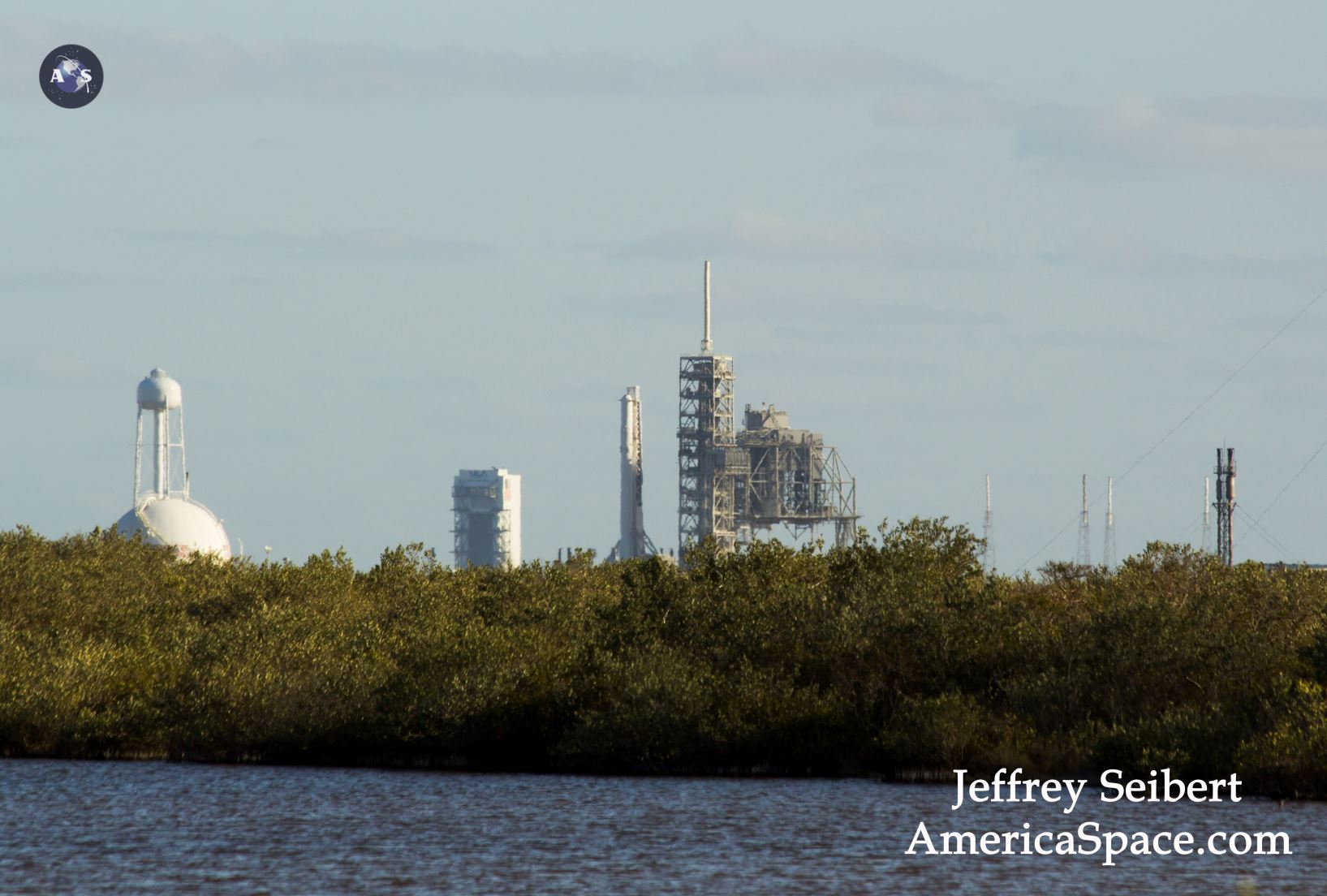
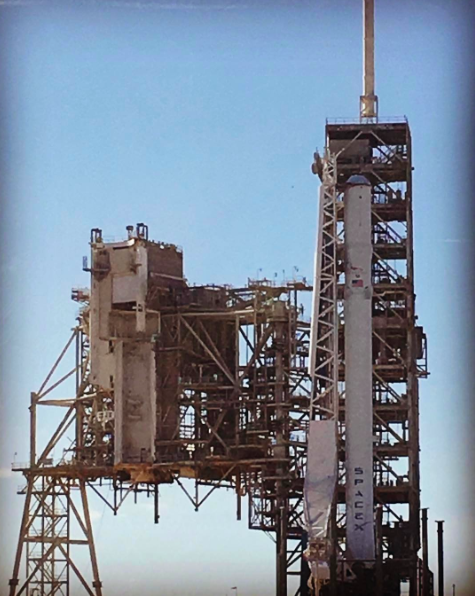
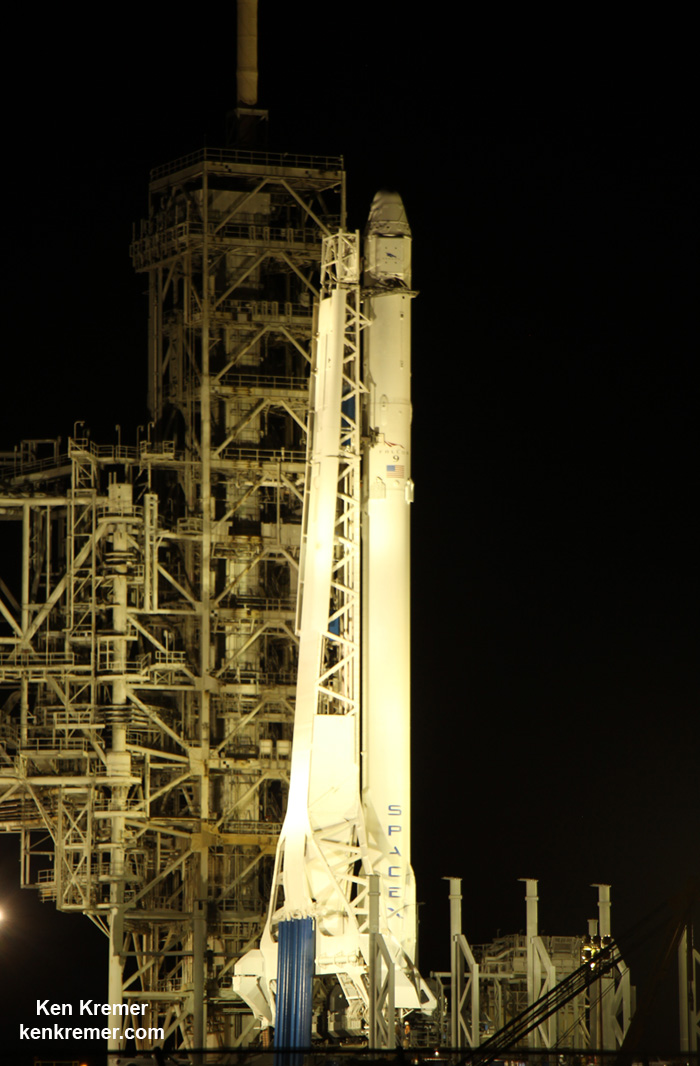
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – Just hours before blastoff, the first ever SpaceX Falcon 9 set to soar to the space station from historic pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC), the rocket went vertical below delightfully dark skies on the Florida Space Coast.
UPDATE- The launch was scrubbed until Feb. 19 after a hold was called to deal with a thrust vector control issue. Story updated
Packed with over a thousand pounds of research experiments and science instruments probing the human body and our home planet from the heavens above, the Falcon 9 rocket is poised for liftoff at 9:38 a.m., Sunday morning, Feb. 19, from Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) at KSC.
Everything is on track for Sunday’s launch of the 229 foot tall (70 meter) SpaceX Falcon 9 on the NASA contracted SpaceX CRS-10 resupply mission for NASA to the million pound orbiting lab complex.
And the weather looks promising at this time.
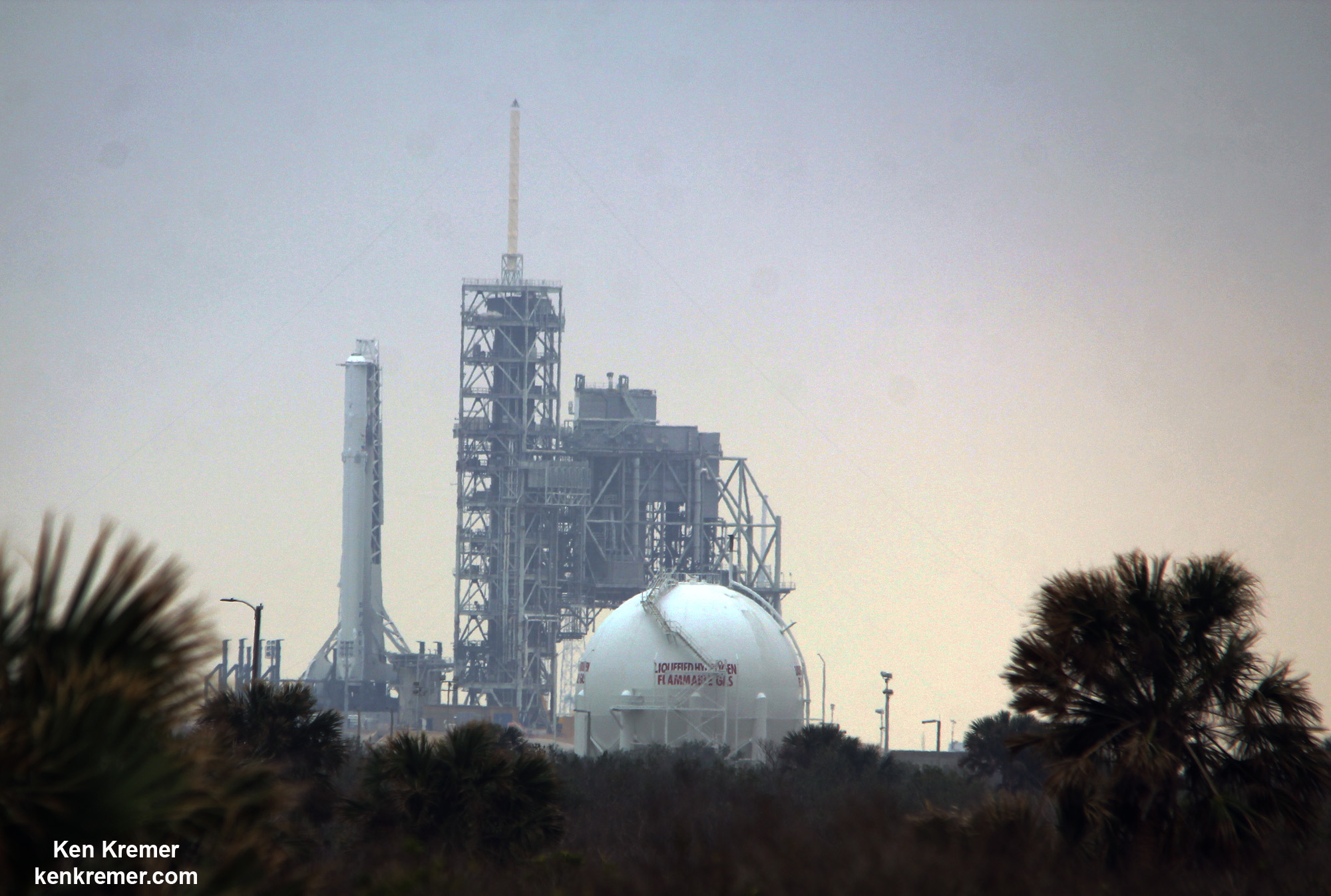
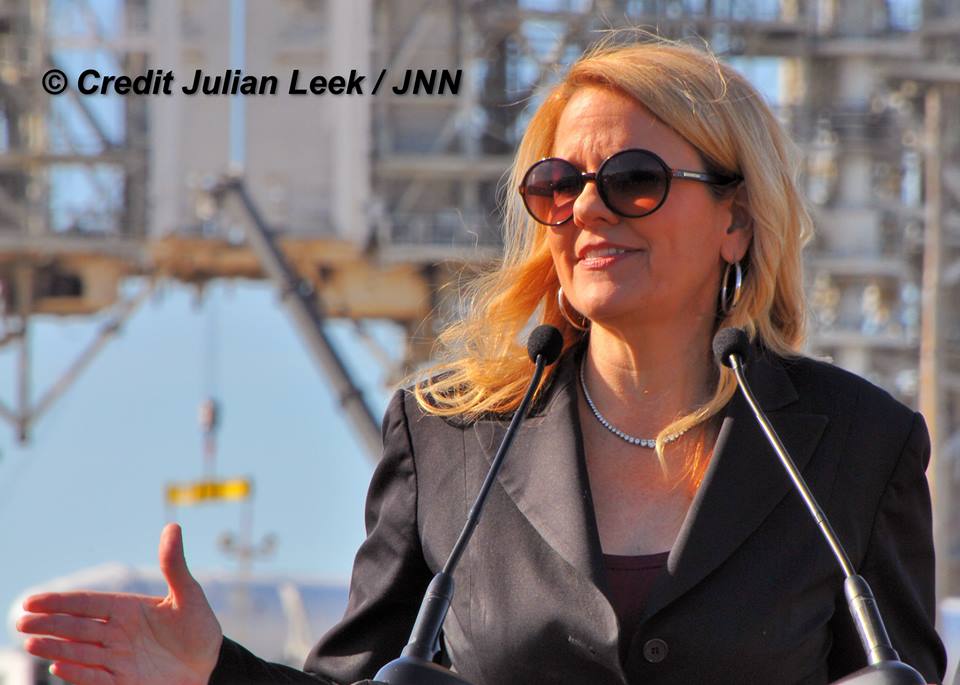
At a meeting with reporters at pad 39A on Friday, Feb. 17, SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell confirmed the success of the static fire test of the two stage rocket and all nine first stage Merlin 1D engines conducted on Sunday afternoon, Feb. 12 – minus the SpaceX Dragon cargo freighter payload.

The successful test firing of the engines cleared the path to orbit for liftoff of Dragon on a critical cargo flight for NASA to deliver over two and a half tons of supplies and science on the CRS-10 resupply mission to the six person crew living and working aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
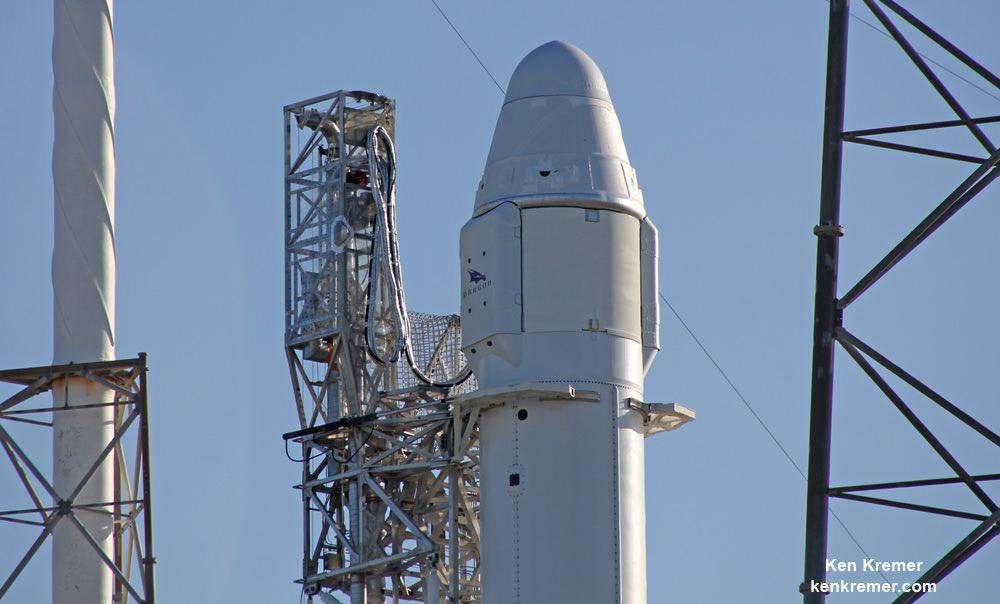
Shotwell then said technicians integrated with the unmanned Dragon CRS-10 cargo freighter with the Falcon 9 rocket.

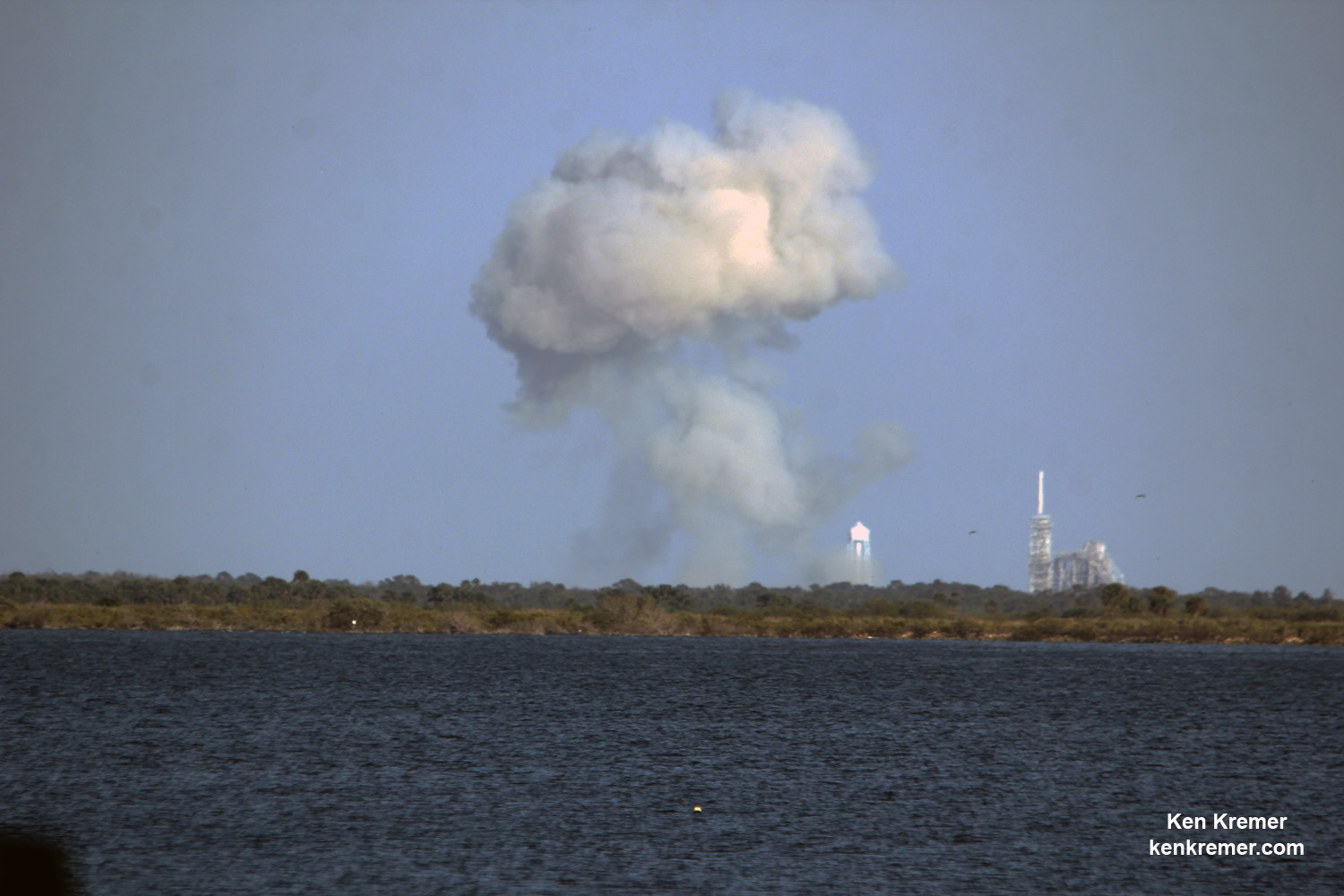
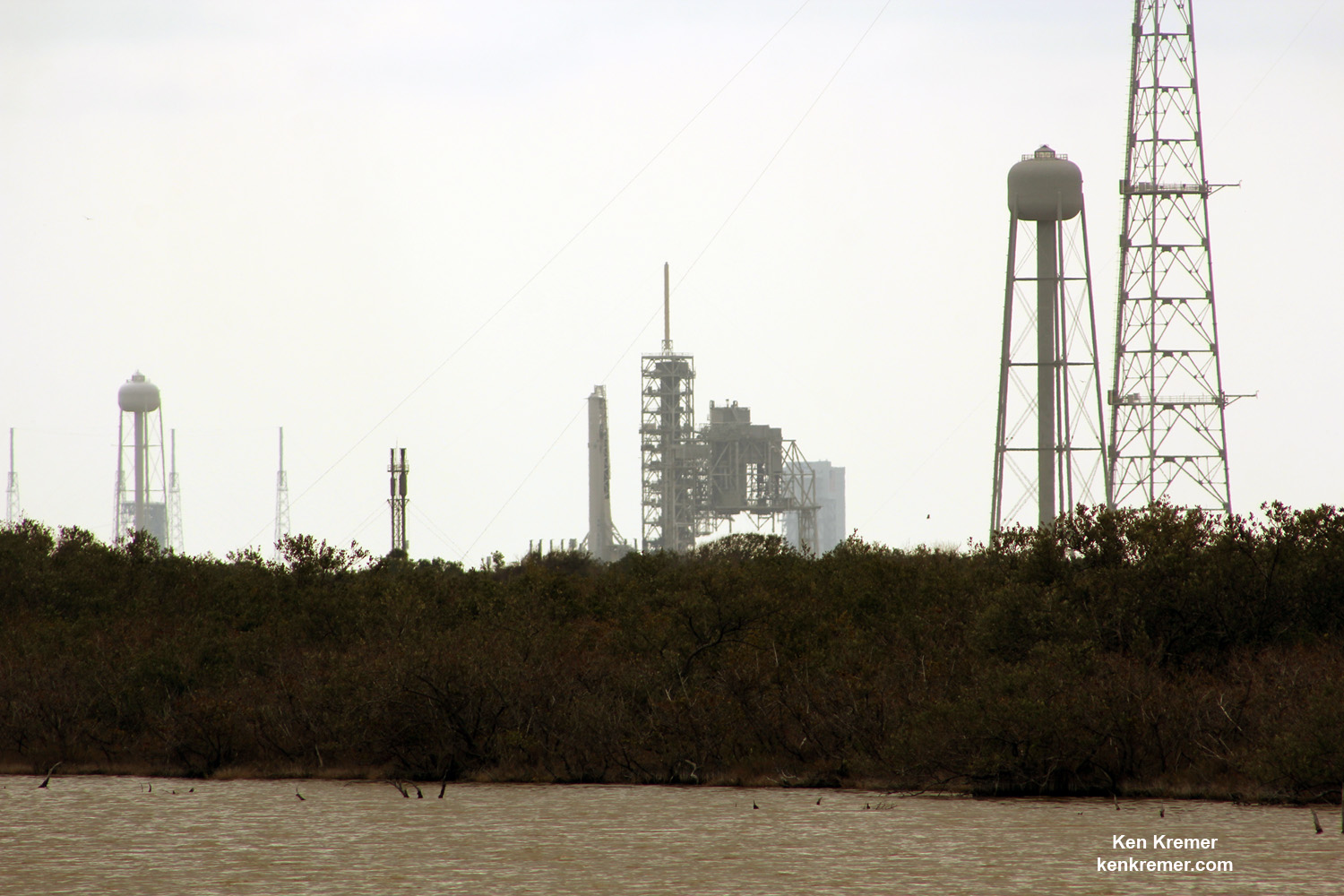
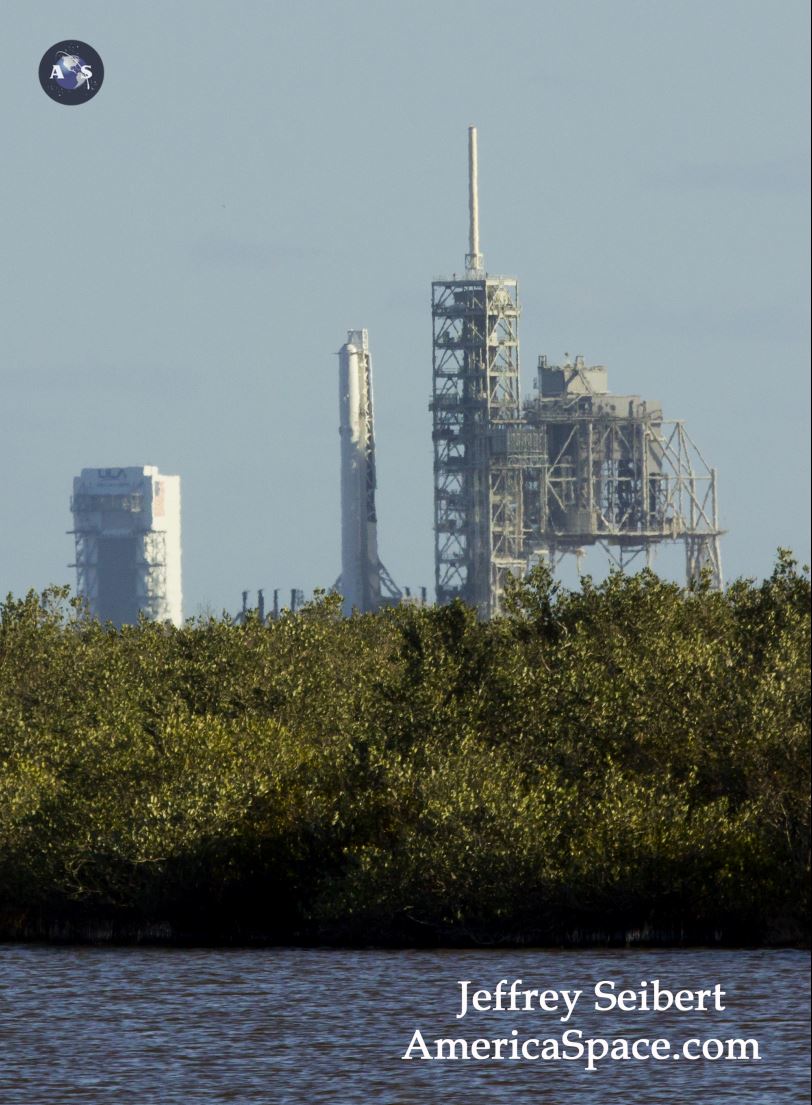
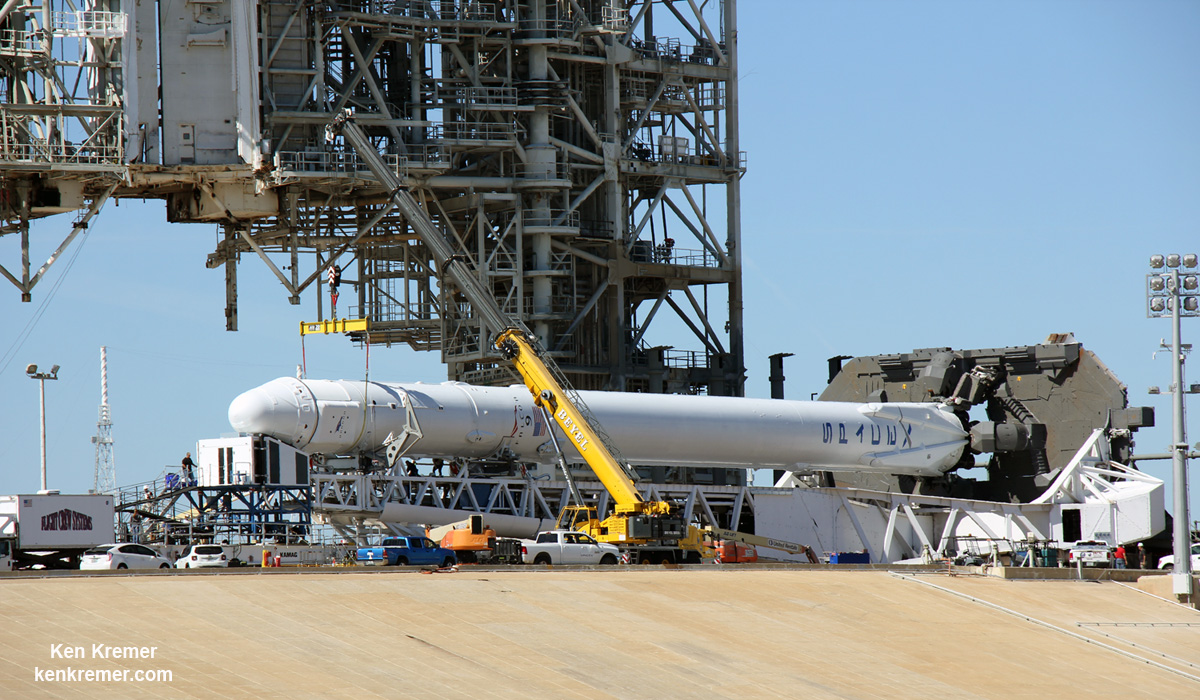
The 22 story tall rocket rolled out of the SpaceX processing hangar at the perimeter fence and then up the incline to the top of pad 39A on Thursday morning using a dedicated transporter-erector, so ground crews could begin final preparations for the Saturday morning blastoff. Now reset to Sunday.

Thousands and thousands of spectators from across the globe, local residents, media and scientists and engineers and their families have flocked to the Florida Space Coast, filling area hotels to witness the historic maiden blastoff of a Falcon 9 from seaside pad 39A at KSC at 9:38 a.m. EST Sunday, Feb. 19.
SpaceX will also attempt to achieve a secondary mission goal of landing the 156 foot tall first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket on land at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Landing Zone 1, located a few miles south of launch pad 40.
If you can’t personally be here to witness the launch in Florida, you can also watch NASA’s live coverage on NASA Television and the agency’s website.
The SpaceX/Dragon CRS-10 launch coverage will be broadcast on NASA TV beginning at 8:30 a.m. EDT Saturday, Feb. 18, with additional commentary on the NASA launch blog.
SpaceX will also feature their own live webcast beginning approximately 20 minutes before launch at 9:41 a.m. EDT.
You can watch the launch live at NASA TV at – http://www.nasa.gov/nasatv
You can also watch the launch live at SpaceX Webcast at – spacex.com/webcast
The launch window is instantaneous, meaning that any delays due to weather or technical issues results in a minimum 1 day postponement.
The long awaited FAA launch license was finally granted at the last minute on Friday afternoon – less than 24 hours before launch.
The weather outlook currently is improving from earlier in the week and looks good for Saturday morning with a 70% chance of favorable condition at launch time. The concerns are for thick clouds according to Air Force meteorologists with the 45th Space Wing at Patrick Air Force Base.
In case of a scrub for any reason on Feb. 18, the backup launch opportunity is 9:38 a.m. Sunday, Feb. 19. with NASA TV coverage starting at about 8:10 a.m. EDT.
CRS-10 marks only the third time SpaceX has attempted a land landing of the 15 story tall first stage booster.
Shotwell confirmed they are attempting the secondary mission of landing the 156 foot tall first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket on land at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Landing Zone 1, located about 9 miles south of launch pad 39a.
And it won’t take long to learn the results – the ground landing at LZ -1 will take place about 9 minutes after liftoff.

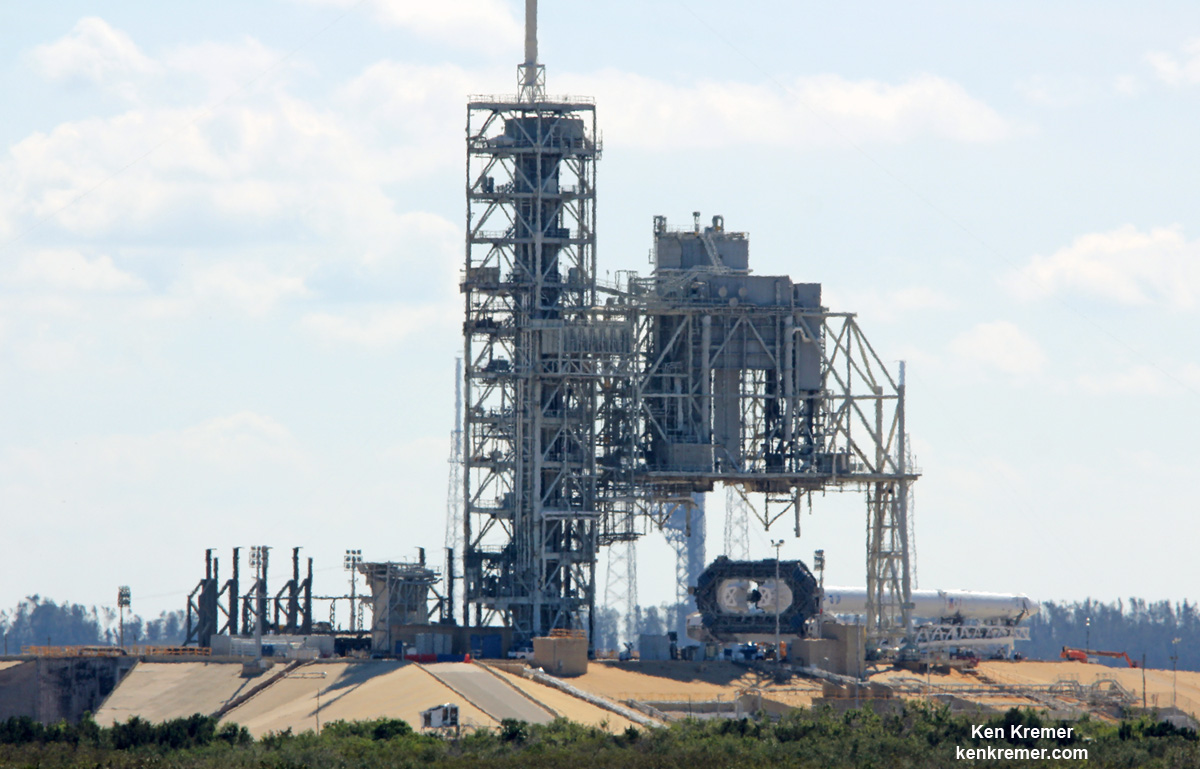
This marks the first time any fully integrated rocket has stood on pad 39A for a scheduled launch since the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttles in July 2011 on the STS-135 mission to the space station.
The historic NASA launch pad was formerly used to launch both America’s space shuttles and astronauts on Apollo/Saturn V moon landing missions as far back as the 1960s.
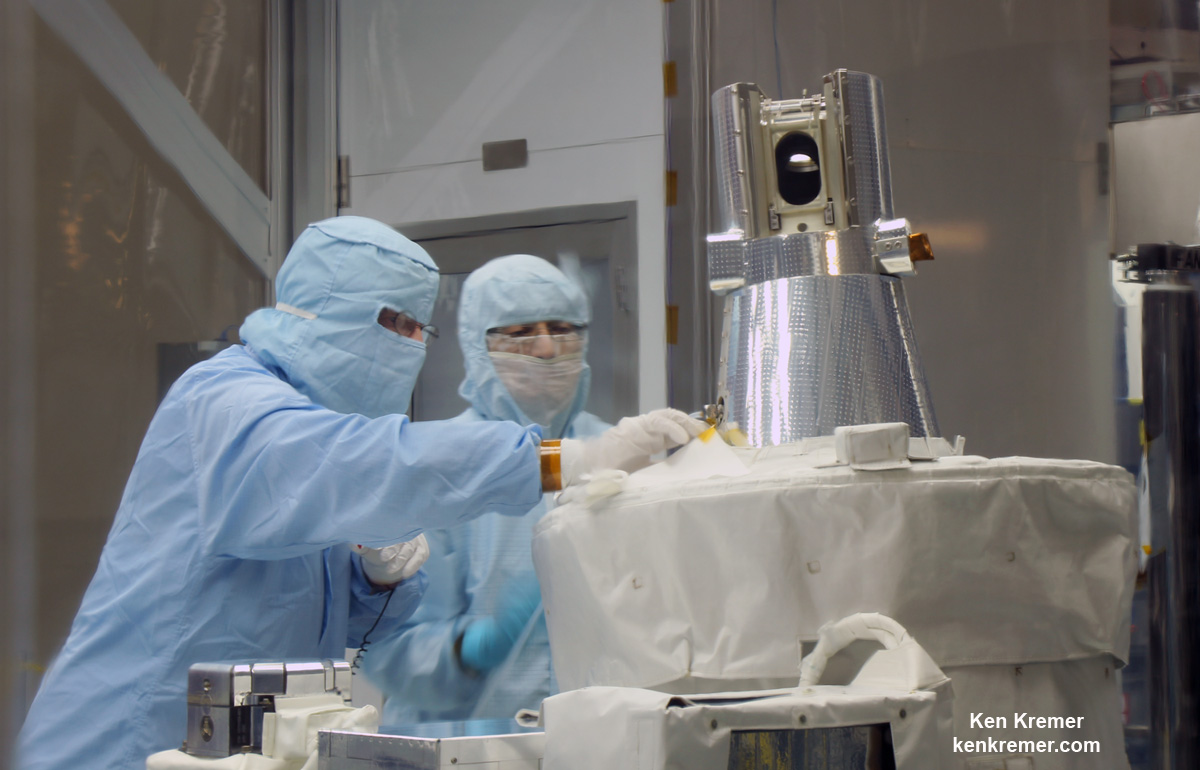
Dragon is carrying more than 5500 pounds of equipment, gear, food, crew supplies, hardware and NASA’s Stratospheric Aerosol Gas Experiment III (SAGE III) ozone mapping science payload in support of the Expedition 50 and 51 crew members.
SAGE III will measure stratospheric ozone, aerosols, and other trace gases by locking onto the sun or moon and scanning a thin profile of the atmosphere.
The LIS lightning mapper will measure lightning from the altitude of the ISS. NASA’s RAVEN experiment will test autonomous docking technologies for spacecraft.
The research supplies and equipment brought up by Dragon will support over 250 scientific investigations to advance knowledge about the medical, psychological and biomedical challenges astronauts face during long-duration spaceflight.
Watch for Ken’s onsite CRS-10 mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about SpaceX CRS-10 launch to ISS, ULA SBIRS GEO 3 launch, EchoStar launch GOES-R launch, Heroes and Legends at KSCVC, OSIRIS-REx, InSight Mars lander, ULA, SpaceX and Orbital ATK missions, Juno at Jupiter, SpaceX AMOS-6, ISS, ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, Orbital ATK Cygnus, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events at Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL:
Feb 17- 19: “SpaceX CRS-10 launch to ISS, ULA Atlas SBIRS GEO 3 launch, EchoStar 19 comsat launch, GOES-R weather satellite launch, OSIRIS-Rex, SpaceX and Orbital ATK missions to the ISS, Juno at Jupiter, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings