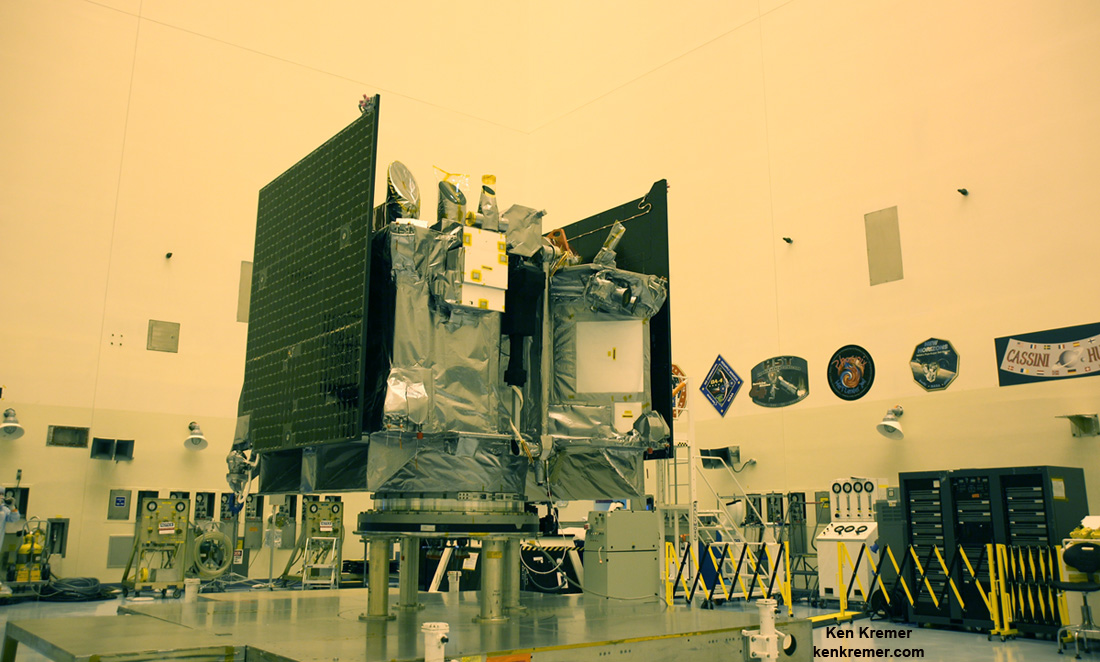
NASA’s newest planetary probe, the OSIRIS-REx asteroid sampling spacecraft, is merrily snapping its ‘First-Light’ images following the successful power up and health check of all of the probes science instruments, barely three weeks after a stunning sunset launch from the Florida Space Coast – as it is outbound to asteroid Bennu.
“The spacecraft has passed its initial instrument check with flying colors as it speeds toward a 2018 rendezvous with the asteroid Bennu,” NASA officials reported in a mission update.
All five of the Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft science instruments and one of its navigational instruments were powered on, starting last week on September 19.
NASA says they are all fully healthy for the groundbreaking mission whose purpose is to visit the carbon rich asteroid Bennu, snatch samples from the black as coal surface and return them to Earth in 2023 inside a Sample Return Capsule that will soft land by parachute in the Utah desert.
The seven year roundtrip mission to Bennu and back could potentially bring back samples infused with the organic chemicals like amino acids that are the building blocks of life as we know it.
“The data received from the checkout indicate that the spacecraft and its instruments are all healthy.”
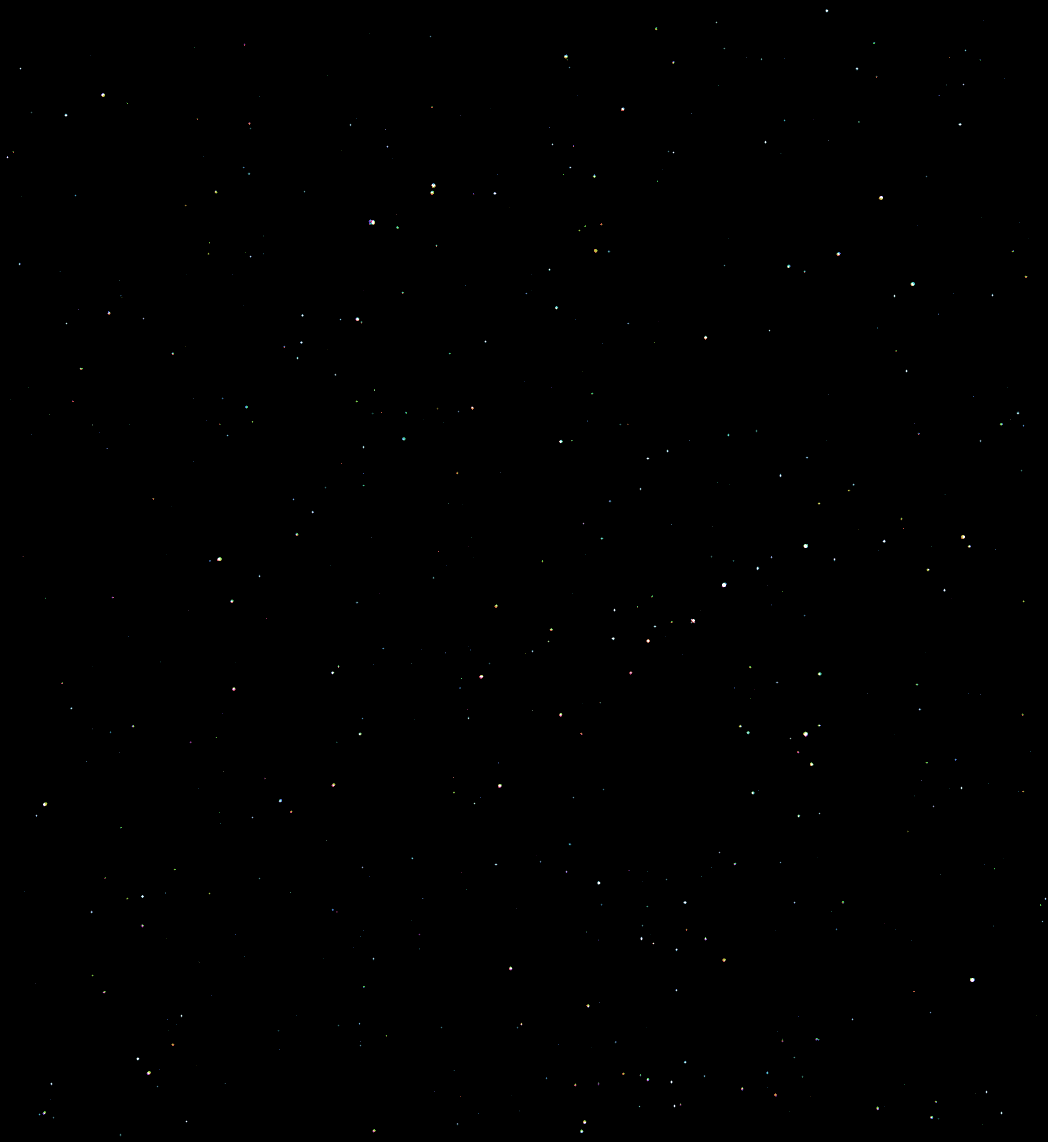
The ‘First-Light’ image shown above was taken on Sept. 19, 2016 by the probes OCAMS MapCam camera and recorded a star field in Taurus, north of the constellation Orion along with Orion’s bright red star Betelgeuse.
“MapCam’s first color image is a composite of three of its four color filters, roughly corresponding to blue, green, and red wavelengths. The three images are processed to remove noise, co-registered, and enhanced to emphasize dimmer stars,” researchers said.
The OSIRIS-REx Camera Suite (OCAMS) was the first of the five science instrument to be tested and checlked out perfectly with “no issues.” It was provided by the University of Arizona and is comprised of three cameras which will image and map Bennu in high resolution.

All the other instruments were also powered on and checked out flawlessly – including the OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter (OLA) which fired its laser, the OSIRIS-REx Visible and Infrared Spectrometer (OVIRS), the OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emissions Spectrometer (OTES), and the student designed Regolith X-ray Imaging Spectrometer (REXIS).
Lastly, the Touch and Go Camera System (TAGCAMS) navigational camera was successfully powered on and tested.
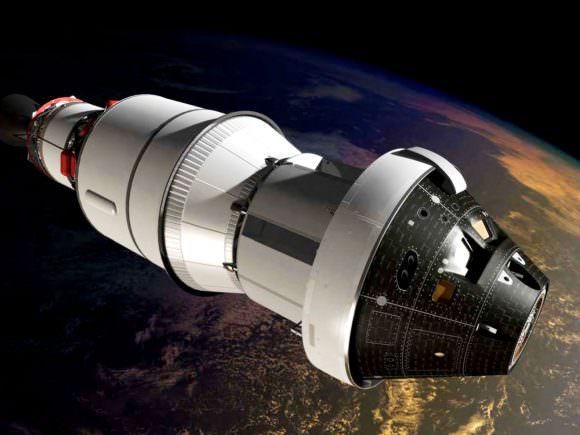
Furthermore, TAGCAMS took a dramatic image of the spacecraft’s Sample Return Capsule (below) – which is designed to bring at least a 60-gram (2.1-ounce) sample of Bennu’s surface soil and rocks back to Earth in 2023 for study by scientists using the world’s most advanced research instruments.

The capsule image was captured by the StowCam portion of TAGCAMS when it was 3.9 million miles (6.17 million km) away from Earth and traveling at a speed of 19 miles per second (30 km/s) around the Sun.
The StowCam image of the Sample Return Capsule shows it “is in perfect condition,” according to the science team.

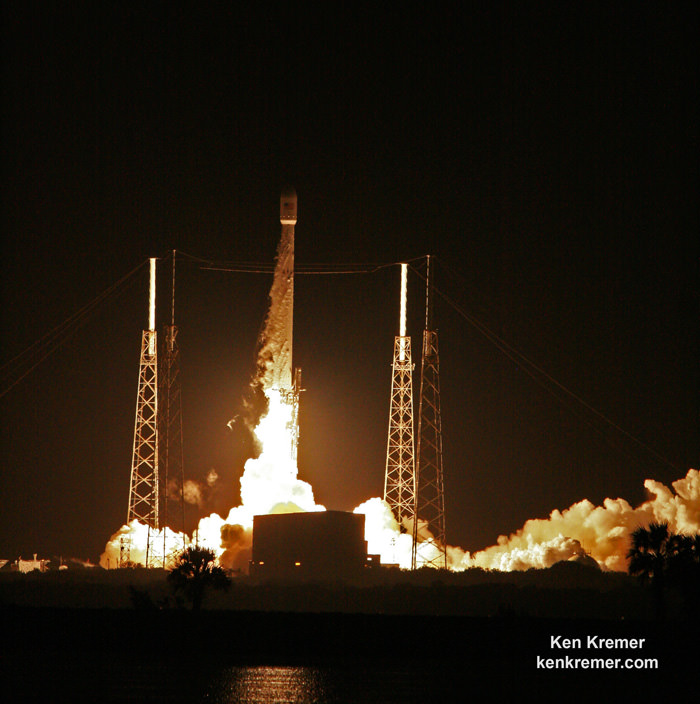
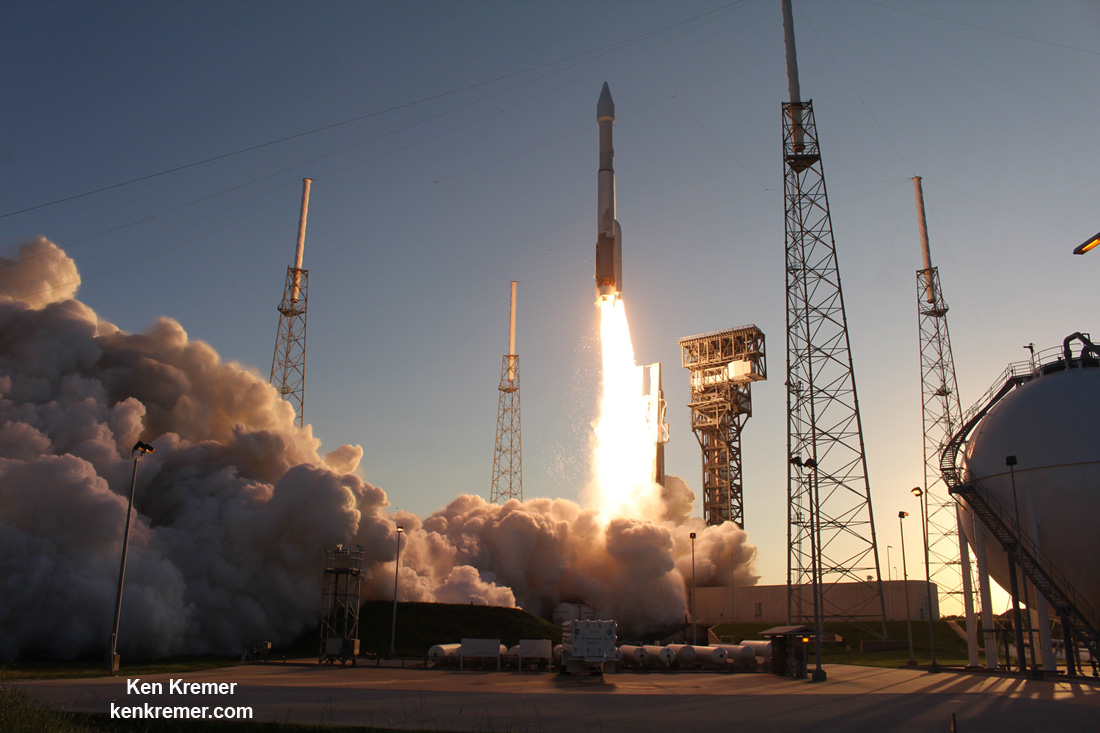
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft departed Earth with an on time engine ignition of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket under crystal clear skies on Thursday, September 8 at 7:05 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
The ULA Atlas V injected OSIRIS-Rex perfectly onto its desired trajectory.
“We got everything just exactly perfect,” said Dante Lauretta, the principal investigator for OSIRIS-REx at the University of Arizona, at the post launch briefing at the Kennedy Space Center. “We hit all our milestone within seconds of predicts.

The space rock measures about the size of a small mountain at about a third of a mile in diameter.
“The primary objective of the OSIRIS-Rex mission is to bring back pristine material from the surface of the carbonaceous asteroid Bennu, OSIRIS-Rex Principal Investigator Dante Lauretta told Universe Today in a prelaunch interview in the KSC cleanroom with the spacecraft as the probe was undergoing final preparations for shipment to the launch pad.
“We are interested in that material because it is a time capsule from the earliest stages of solar system formation.”
“It records the very first material that formed from the earliest stages of solar system formation. And we are really interested in the evolution of carbon during that phase. Particularly the key prebiotic molecules like amino acids, nucleic acids, phosphates and sugars that build up. These are basically the biomolecules for all of life.”
The asteroid is 1,614-foot (500 m) in diameter and crosses Earth’s orbit around the sun every six years.
After a two year flight through space, including an Earth swing by for a gravity assisted speed boost in 2017, OSIRIS-REx will reach Bennu in Fall 2018 to begin about 2 years of study in orbit to determine the physical and chemical properties of the asteroid in extremely high resolution.
Watch my up close launch video captured directly at the pad with the sights and sounds of the fury of blastoff:
Video Caption: ULA Atlas V rocket lifts off on September 8, 2016 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying NASA’s OSIRIS-REx asteroid sampling spacecraft, in this remote camera view taken from inside the launch pad perimeter. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Watch for Ken’s continuing OSIRIS-REx mission reporting. He reported on the spacecraft and launch from on site at the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.