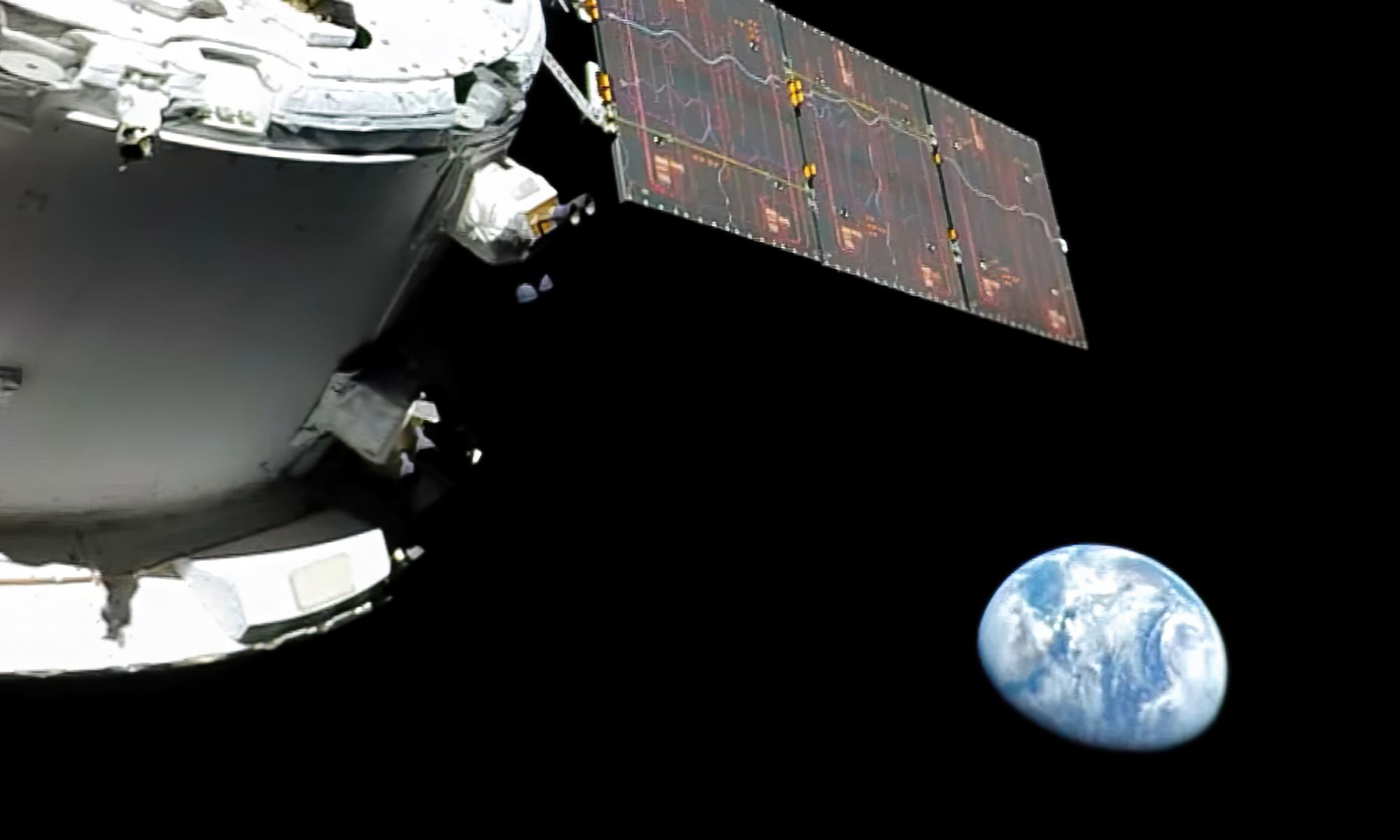
As it heads for the moon, NASA’s Orion space capsule is sending back snapshots of Earth that evoke the “blue marble” pictures taken by Apollo astronauts five decades earlier.
This time around, the photographer is basically a robot, built into the camera system for the uncrewed Artemis 1 mission. The round-the-moon odyssey got off to a spectacular start early today with the first launch of NASA’s Space Launch System, and over the next 25 days it’s due to blaze a trail for future crewed trips to the lunar surface.
Hours after liftoff, a camera mounted on one of Orion’s four solar arrays pivoted around to capture a view of the spacecraft’s European-built service module in the foreground — with our half-shadowed planet set against the black background of space.
“Orion looking back at Earth as it travels toward the moon, 57,000 miles away from the place we call home,” NASA’s Sandra Jones intoned as the imagery came down.
Continue reading “Artemis 1 Sends Back Snapshots of Earth as It Speeds Toward the Moon”