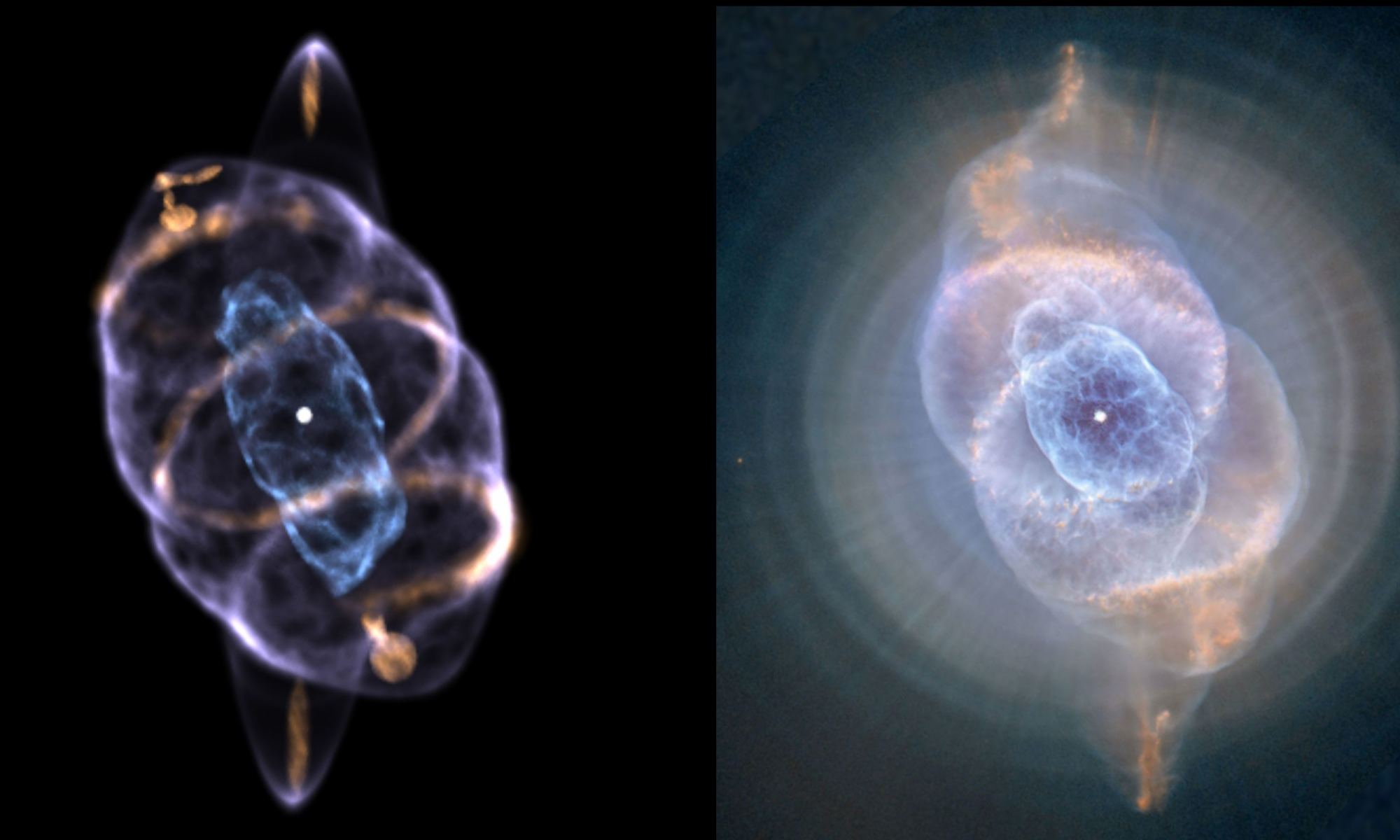
In a recent study published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, an international team of researchers led by Stanford University have produced the first computer-generated 3D model of the Cat’s Eye Nebula, which unveiled a symmetric pair of rings that enclose the outer shell of the nebula. This study holds the potential for helping us better understanding the nebula’s makeup and how it formed, as the symmetric rings provides clues that they were formed from a precessing jet, which produces strong confirmation that a binary star exists at the nebula’s center.
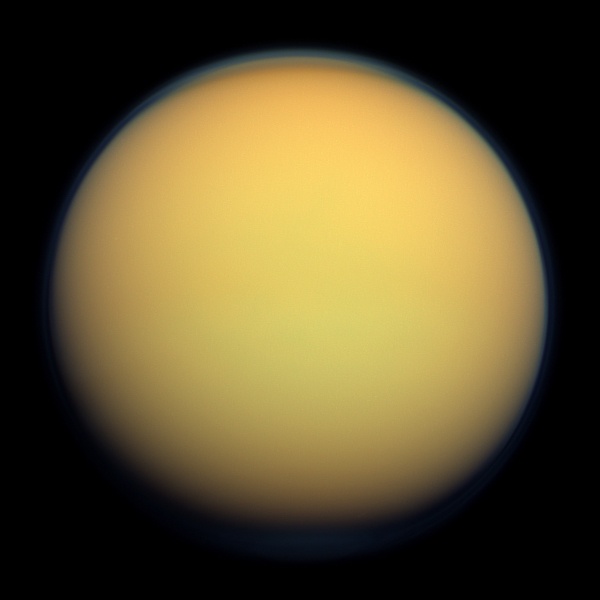
Continue reading “Astronomers Simulate the Cat’s Eye Nebula in 3D”Will Titan finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’
We recently examined how and why Jupiter’s moon, Europa, could answer the longstanding question: Are we alone? While this small icy world gives plenty of reasons to believe why we could—and should—find life within its watery depths, it turns out our solar system is home to a myriad of places where we might find life. Much like how the Voyager missions gave us the first hints of an interior ocean swirling beneath Europa’s outer icy shell, it was only fitting that Voyager 1 also gave us the first hints of the potential for life on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, as well.
Continue reading “Will Titan finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’”Mysterious Europa Gets an Extreme Closeup From NASA’s Juno Probe

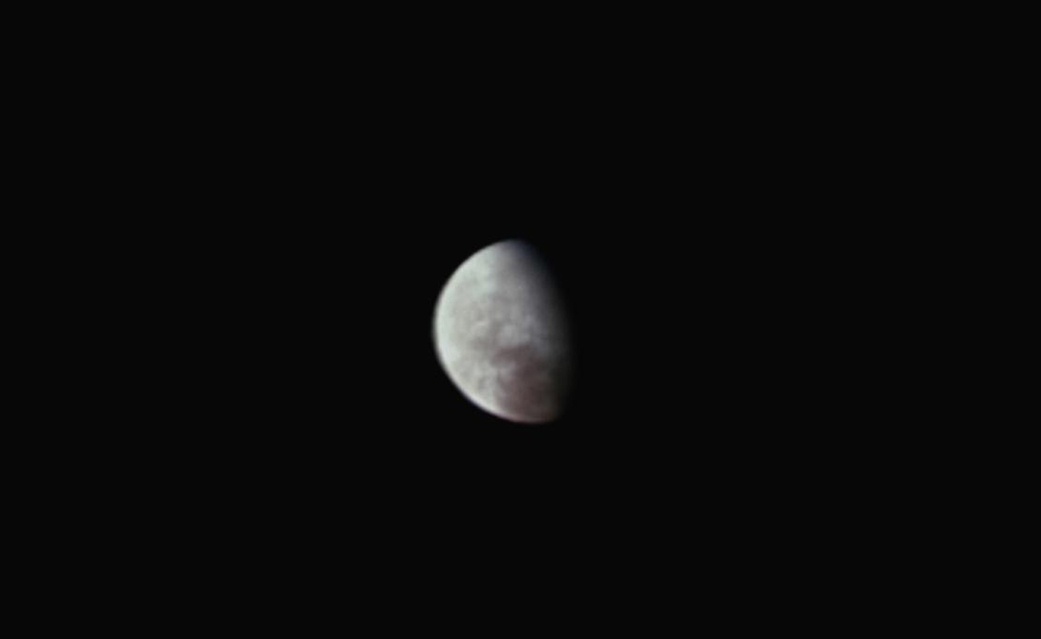
Over the course of a brief two-hour opportunity, NASA’s Juno spacecraft captured a rare close look at Europa, an ice-covered moon of Jupiter that’s thought to harbor a hidden ocean — and perhaps an extraterrestrial strain of marine life.
Juno has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, but this week brought the best opportunity to look at Europa, which is the prime target for investigation by NASA’s Europa Clipper probe in the 2030s. On Sept. 29, the orbiter buzzed over the moon’s surface at a velocity in excess of 52,000 mph (23.6 km per second), and at an altitude of 352 kilometers (219 miles).
That’s as close as any spacecraft has come to Europa since the Galileo orbiter’s 218-mile flyby in 2000.
Continue reading “Mysterious Europa Gets an Extreme Closeup From NASA’s Juno Probe”NASA and SpaceX Will Study Low-Cost Plan to Give Hubble a Boost
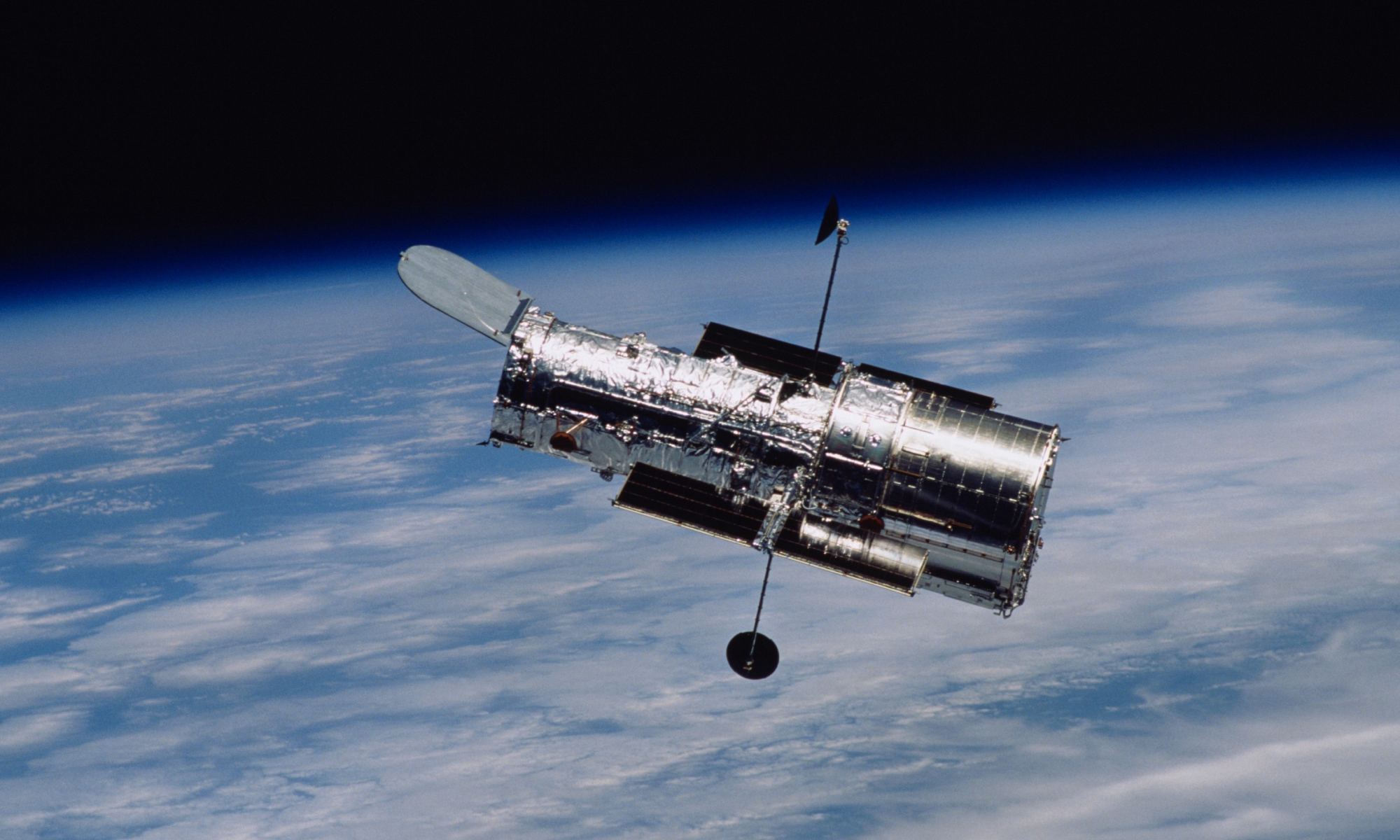

NASA and SpaceX say they’ll conduct a feasibility study into a plan to reboost the 32-year-old Hubble Space Telescope to a more sustainable orbit, potentially at little or no cost to NASA.
The plan could follow the model set by last year’s Inspiration4 mission, an orbital trip that was facilitated by SpaceX and paid for by tech billionaire Jared Isaacman as a philanthropic venture. Isaacman, who is now spearheading a privately funded space program called Polaris in cooperation with SpaceX, says he’ll participate in the feasibility study.
“We could be taking advantage of everything that’s been developed within the commercial space industry to execute on a mission, should the study warrant it, with little or no potential cost to the government,” Isaacman said at a news briefing.
Continue reading “NASA and SpaceX Will Study Low-Cost Plan to Give Hubble a Boost”The First Telescope Images of DART's Impact are Starting to Arrive
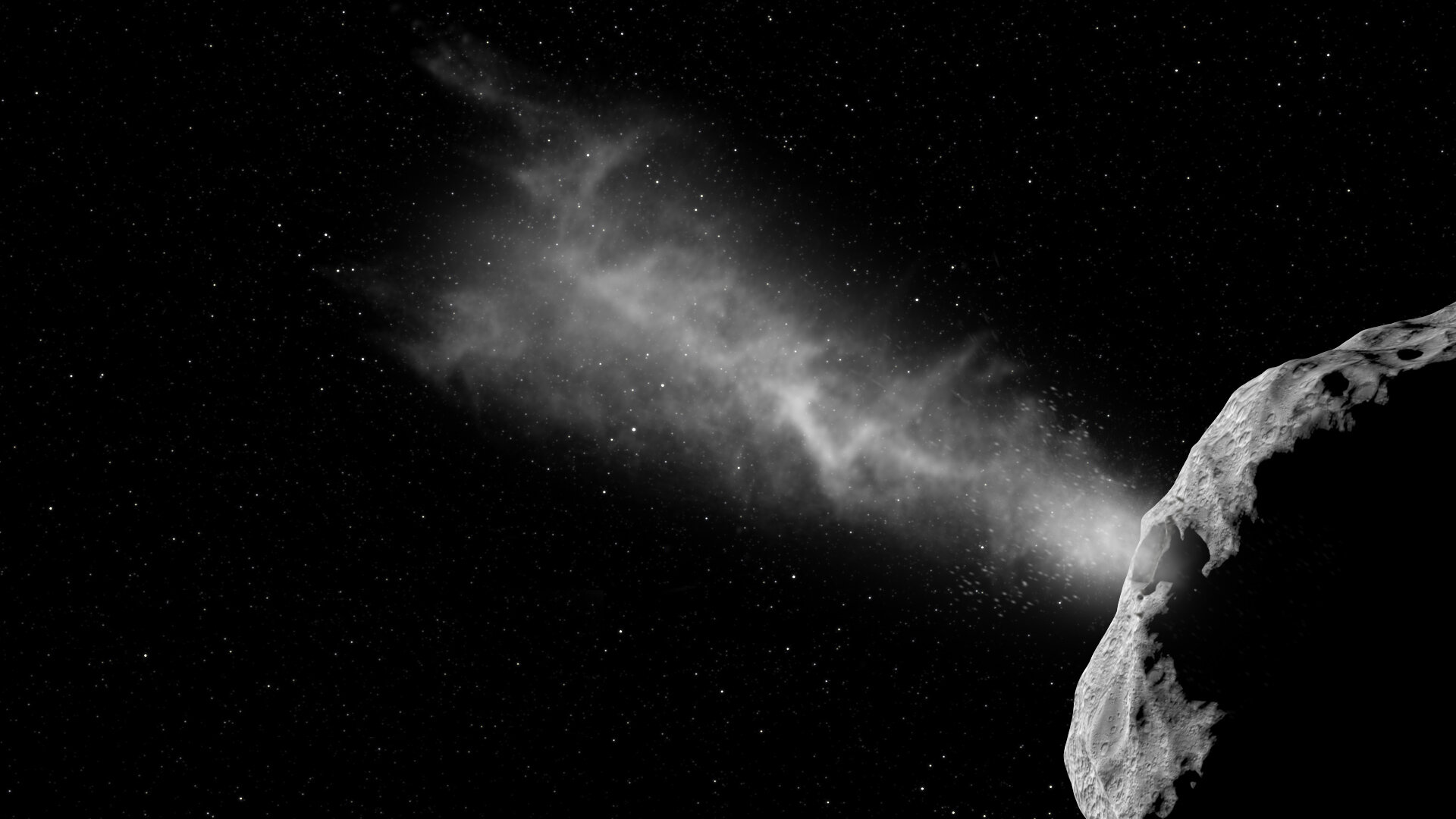
On September 26th, at 23:14 UTC (07:14 PM EST; 04:14 PM PST), NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test (DART) spacecraft successfully struck the 160-meter (525 ft) moonlet Dimorphos that orbits the larger Didymos asteroid. The event was live-streamed all around the world and showed footage from DART’s Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (DRACO) as it rapidly approached Dimorphos. In the last few seconds, DART was close enough that individual boulders could be seen on the moonlet’s surface.
About 38 seconds after impact, the time it took the signal to reach Earth, the live stream ended, signaling that DART had successfully impacted Dimorphos and was destroyed in the process. Meanwhile, teams of astronomers stretching from the Indian Ocean to the Arabian Peninsula watched the impact with their telescopes. One, in particular – the Les Makes Observatory on the island of Le Reunion in the Indian Ocean – captured multiple images of the impact. These were used to create a real-time video and show the asteroid brightening as it was pushed away, followed by material ejected from the surface.
Continue reading “The First Telescope Images of DART's Impact are Starting to Arrive”A Fascinating Look at Jupiter's Clouds Where the Light Intensity is Converted Into 3D
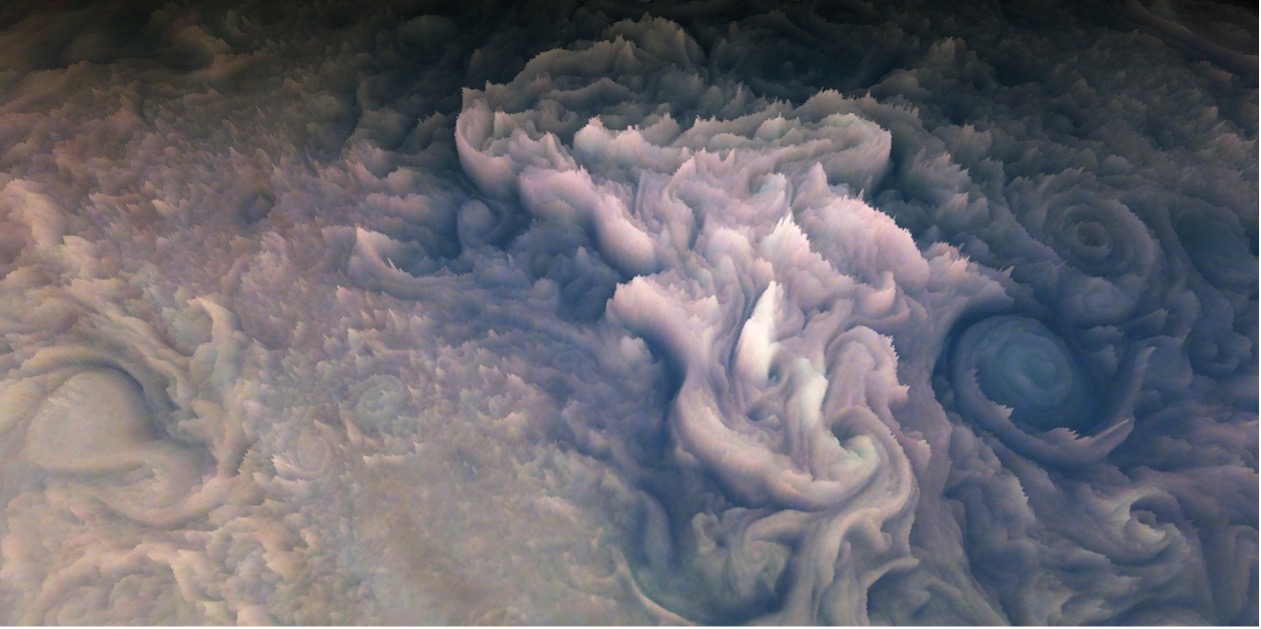

In July 2016, NASA’s Juno space probe reached Jupiter, becoming the second spacecraft in history to orbit the gas giant (the first being the Galileo probe that orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003). The data it has sent back has led to new revelations about the Jovian atmosphere, magnetosphere, gravitational field, structure, and composition. While its primary mission was intended to only last until 2018, a mission extension means that Juno will continue to orbit Jupiter’s poles (a perijove maneuver) and send back stunning images and data until 2025.
Recently, a team of citizen scientists led by mathematician and software developer Gerald Eichstädt used images taken by the probe’s visible-light camera/telescope (the JunoCam) to create a 3D animation of Jupiter’s upper atmosphere. Eichstädt’s animation was presented at the 2022 Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC), which took place from September 18 – 23 in Granada, and shows the relative heights of the cloud tops of Jupiter that reveal delicately textured swirls and peaks. Eichstädt’s work also showcased the potential for citizen science and public engagement with today’s missions.
Continue reading “A Fascinating Look at Jupiter's Clouds Where the Light Intensity is Converted Into 3D”As Hurricane Ian Bears Down on Florida, NASA Decides to Roll Artemis 1 Back to the Assembly Building
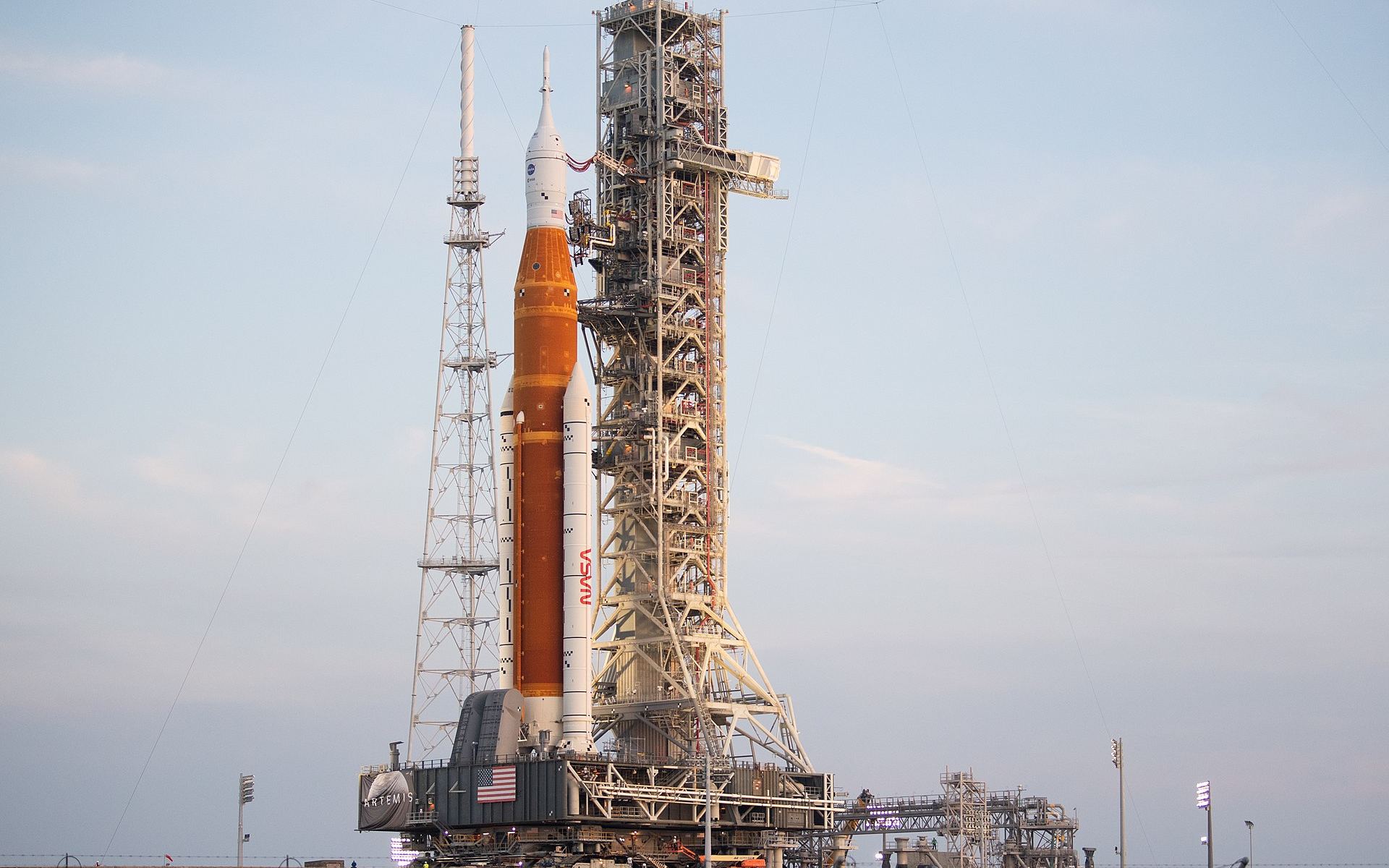
As a result of the latest weather predictions regarding Hurricane Ian, NASA managers met on the morning of September 26 and made the decision to roll Artemis 1 back into the Vehicle Assembly Building to protect the rocket from the impending storm, an operation which commenced at 11 pm EDT that evening.
Continue reading “As Hurricane Ian Bears Down on Florida, NASA Decides to Roll Artemis 1 Back to the Assembly Building”TESS Finds a Super-Earth and two Mini-Neptunes in a Single System
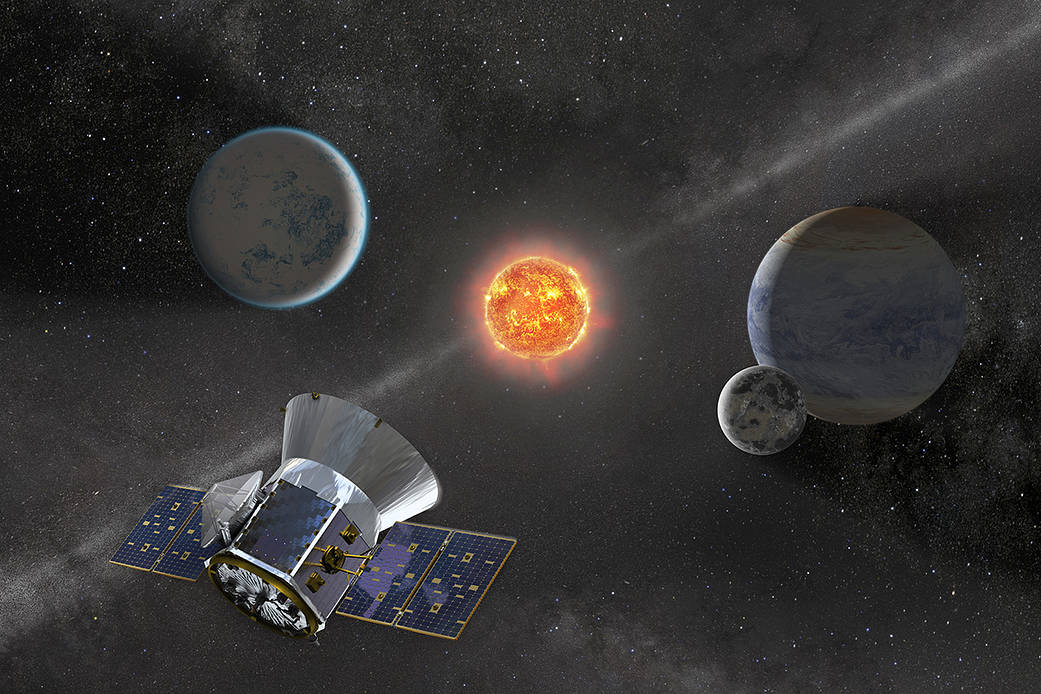

The field of extrasolar planet studies continues to grow by leaps and bounds. Currently, 5,090 exoplanets have been confirmed in 3,816 systems, and another 8,933 candidates are awaiting confirmation. The majority of these have been Neptune-like gas giants (1,779), gas giants comparable to Jupiter or Saturn (1,536), and rocky planets many times the size of Earth (1,582). The most effective means for finding exoplanets has been the Transit Method (aka. Transit Photometry), where periodic dips in a star’s brightness are seen as an indication of a planet passing in front of its star (transiting) relative to the observer.
Using data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has discovered a three-planet system orbiting a Sun-like star (HD 22946, or TOI 11) located about 205.5 light-years. Based on size estimates yielded from their transits, the team theorizes that these exoplanets consist of a rocky planet several times the size of Earth (a Super-Earth) and two gas giants smaller than Neptune. Given its proximity, this system could be ideal for follow-up studies and characterization with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
Continue reading “TESS Finds a Super-Earth and two Mini-Neptunes in a Single System”NASA’s Juno To Skim the Surface of Jupiter’s Icy Moon Europa
This next week will mark a scientifically valuable achievement for NASA’s Juno mission, as the pioneering spacecraft is slated to fly within 358 kilometers (222 miles) of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa on September 29 at 5:36 a.m. EDT (2:36 a.m. PDT) as part of its extended mission to explore the Jupiter system. A flyby this close to Europa’s surface will allow Juno to acquire some of the highest-resolution images ever taken of the icy moon. For context, the last mission to explore Europa in depth was NASA’s Galileo spacecraft, which got within 351 kilometers (218 miles) of the surface on January 3, 2000.
Continue reading “NASA’s Juno To Skim the Surface of Jupiter’s Icy Moon Europa”Axiom’s Next Trip to the ISS Will Carry the First Saudi Woman in Space
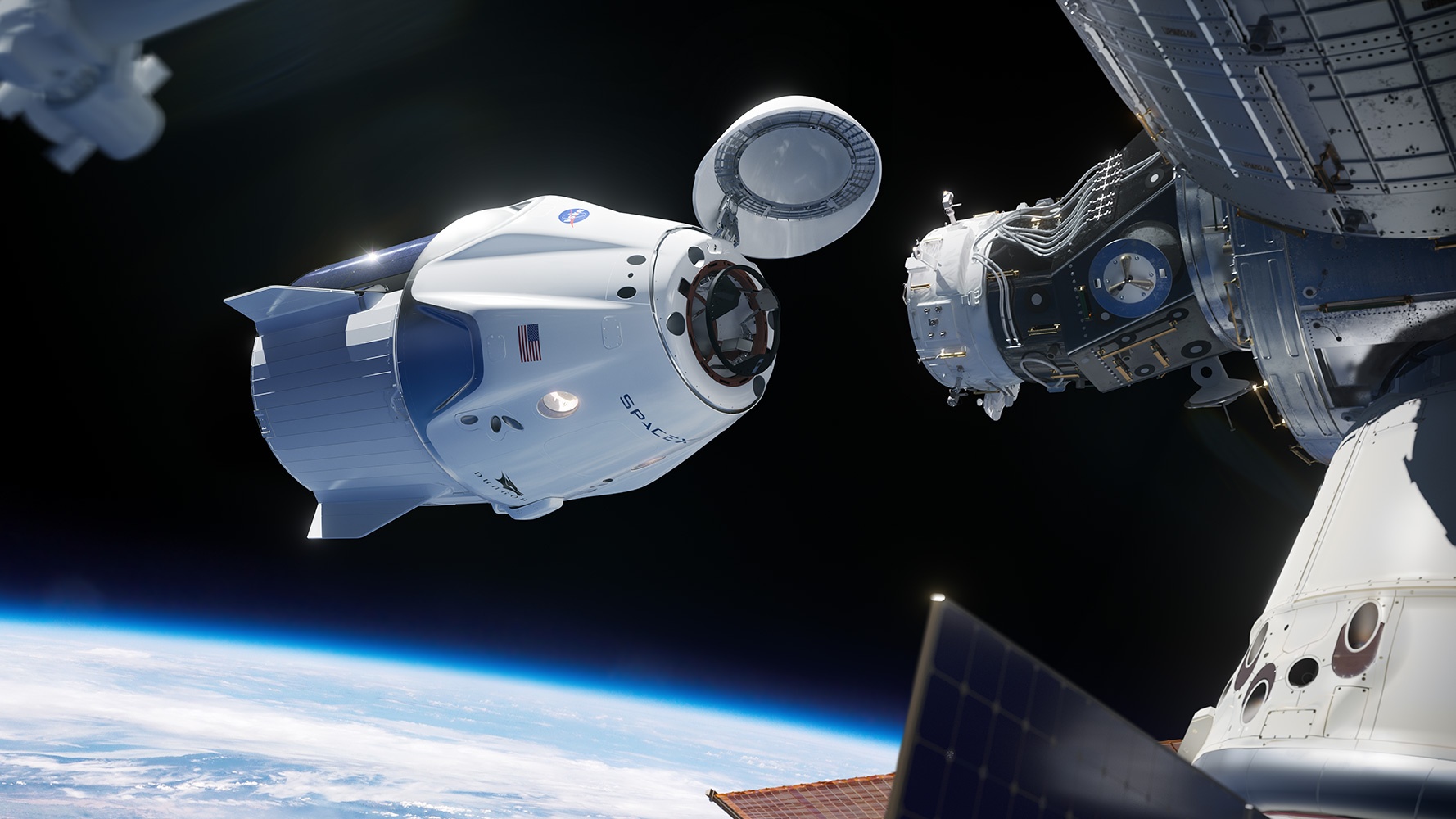

Axiom Space says it’s working with the Saudi Space Commission to send two spacefliers from the Arab kingdom, including the first Saudi woman to go into orbit, to the International Space Station as early as next year.
The inclusion of a female astronaut is particularly notable for Saudi Arabia — where women were forbidden to drive motor vehicles until 2018, and where the status of women is still a controversial subject.
Continue reading “Axiom’s Next Trip to the ISS Will Carry the First Saudi Woman in Space”