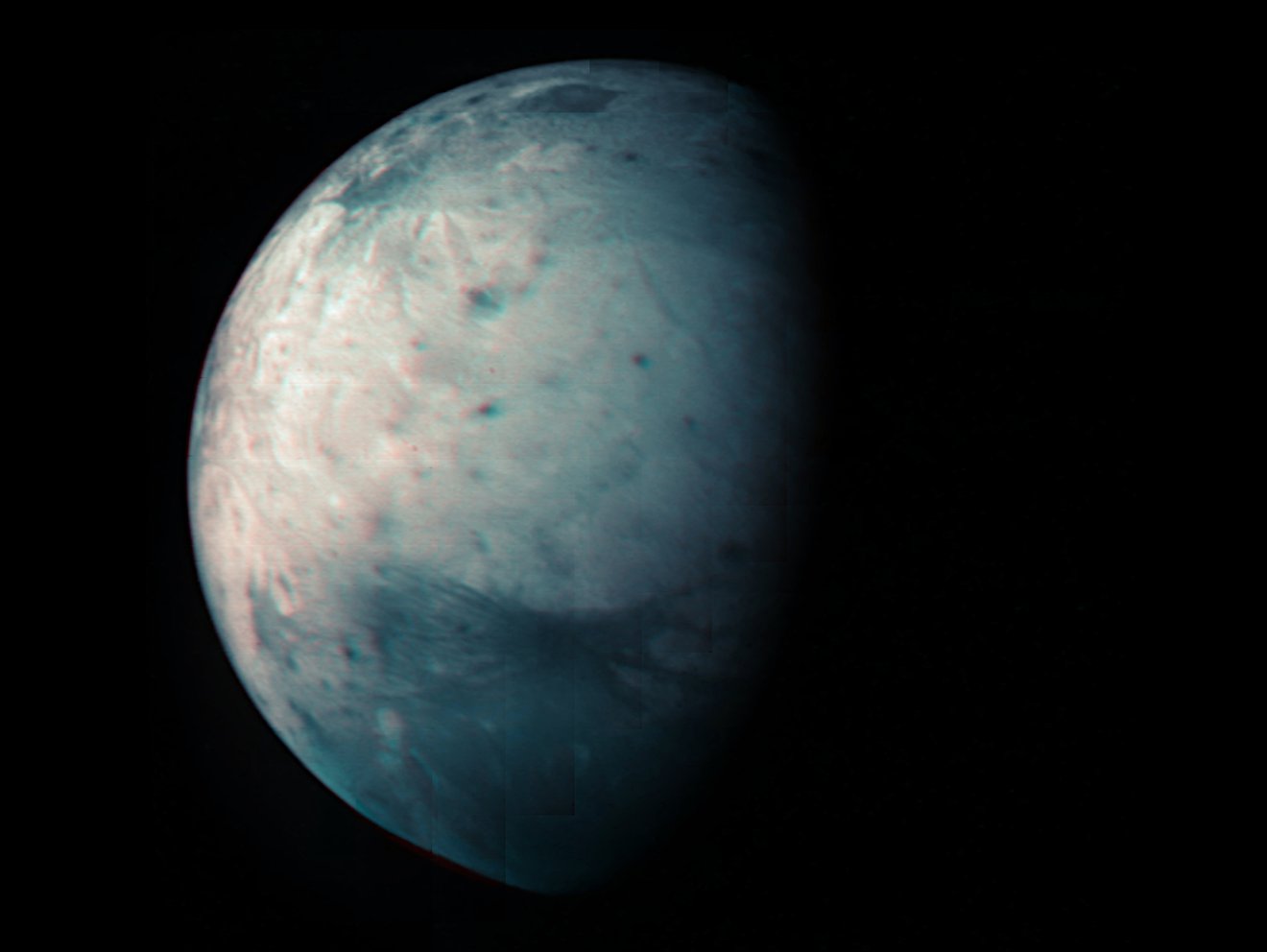
On July 20th, 2021, NASA’s Juno spacecraft conducted a flyby of Jupiter’s (and the Solar System’s) largest moon, Ganymede. This close pass was performed as part of the orbiter’s thirty-fourth orbit of the gas giant (Perijove 34), which saw the probe come within 50,109 km (31,136 mi) of the moon’s surface. The mission team took this opportunity to capture images of Ganymede’s using Juno’s Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM).
These were combined with images acquired during two previous flybys to create a new infrared map of Ganymede’s surface, which was released in honor of the mission’s tenth anniversary (which launched from Earth on Aug. 5th, 2011). This map and the JIRAM instrument could provide new information on Ganymede’s icy shell and the composition of its interior ocean, which could shed led on whether or not it could support life.
Continue reading “Ganymede in Infrared Taken During Juno’s Most Recent Flyby”