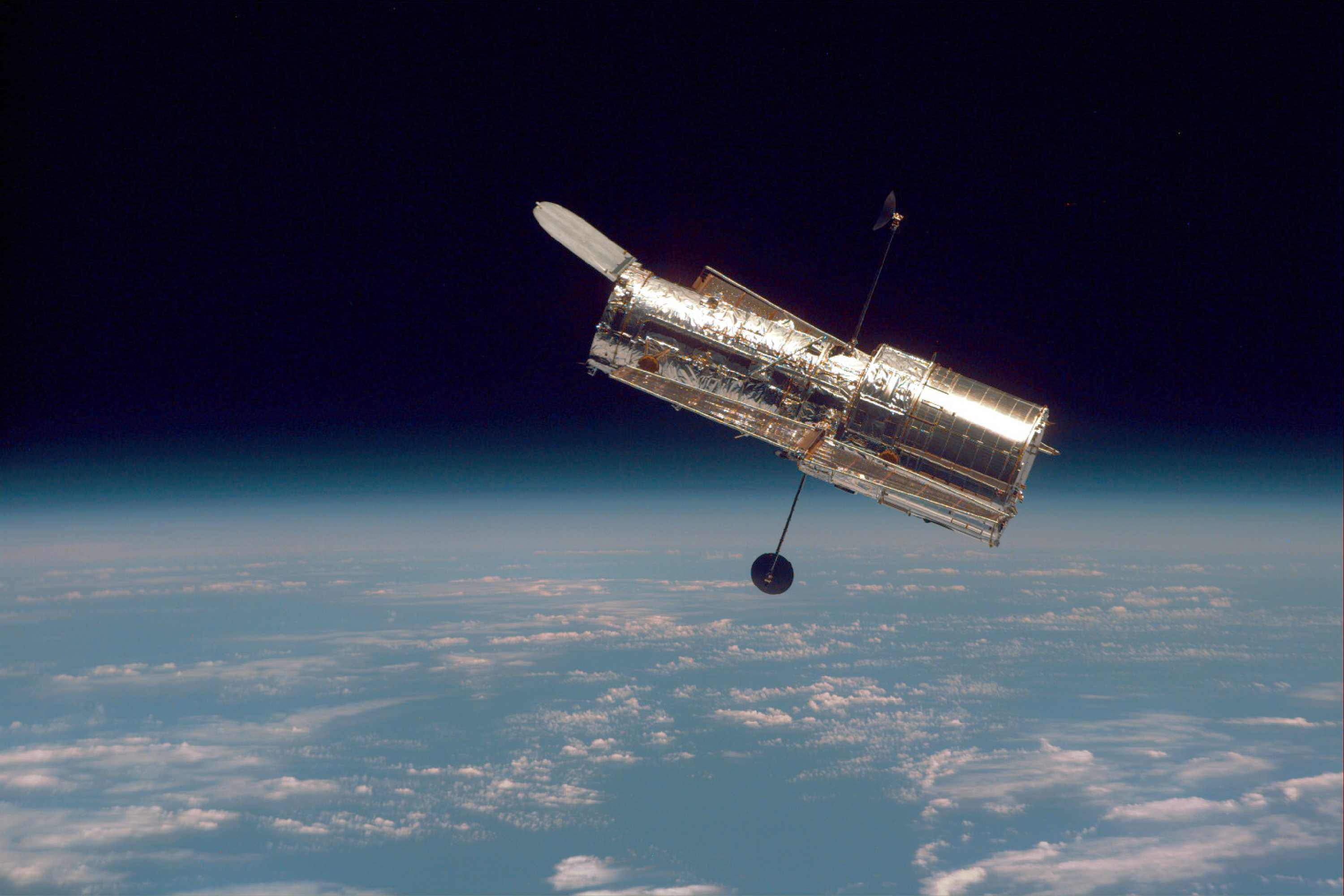
Things are not looking very good for the Hubble Space Telescope right now. On Sunday, June 13th, the telescope’s payload computer suddenly stopped working, prompting the main computer to put the telescope into safe mode. While the telescope itself and its science instruments remain in working order, science operations have been suspended until the operations team can figure out how to get the payload computer back online.
While attempting to restart the computer, the operations team has also tried to trace the issue to specific components in the payload computer and switch to their backup modules. As of June 30th, the team began looking into the Command Unit/Science Data Formatter (CU/SDF) and the Power Control Unit (PCU). Meanwhile, NASA is busy preparing and testing procedures to switch to backup hardware if either of these components are the culprit.
Continue reading “NASA Continues to Try and Rescue Failing Hubble”