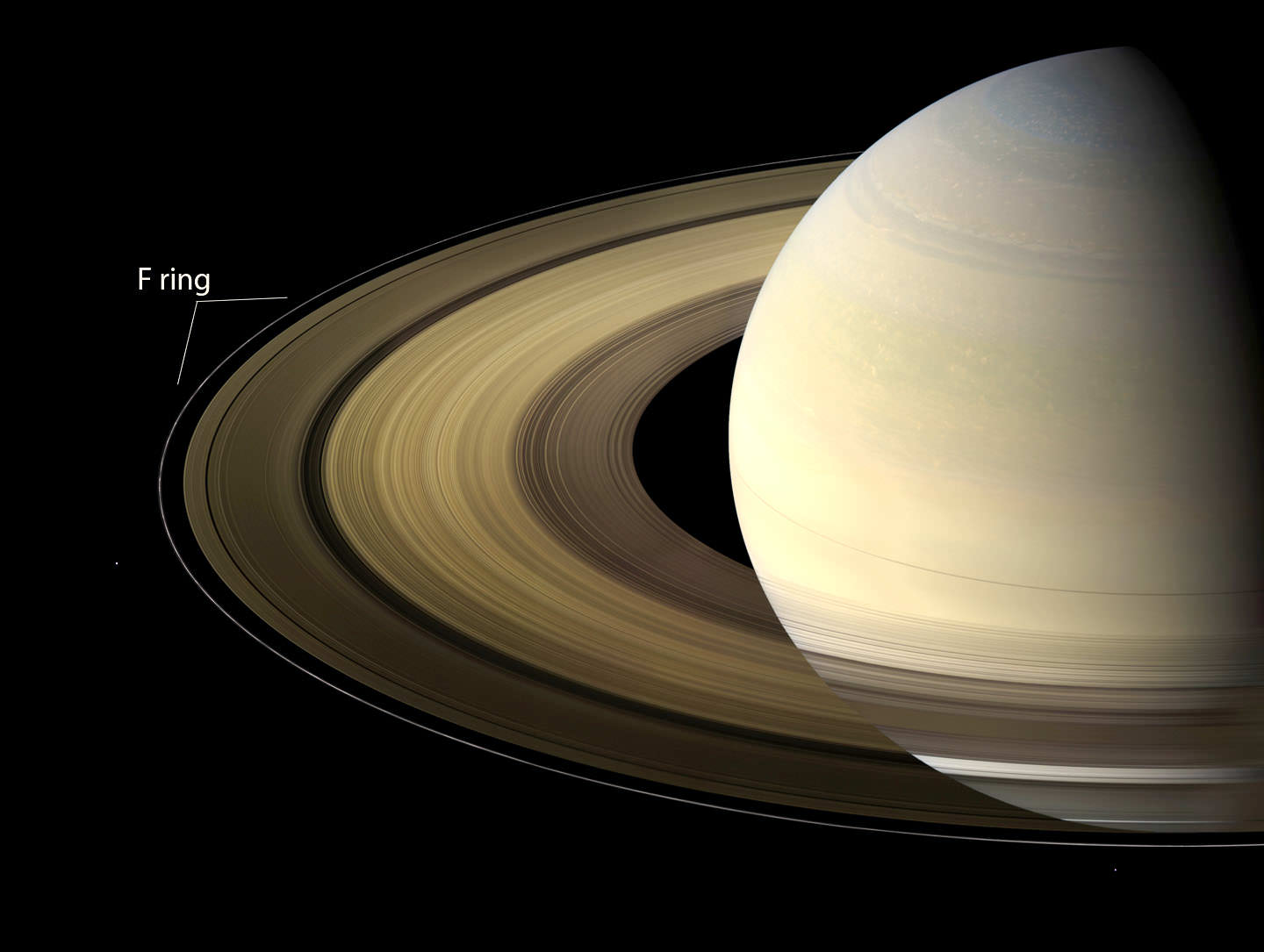
Saturn’s rings are one of the most recognized and revered celestial objects known to the human race. From a distance, they look like a disk of layered crystal or multicolored disks within disks that wrap around Saturn’s hazy umber face. When viewed up close, we see that these rings are actually particles of water ice (from microns to icebergs), as well as silicates, carbon dioxide, and ammonia.
We would also noticed that the rings have some interesting orbital mechanics. In fact, each ring has a different orbit that is the result of its proximity to Saturn (i.e., the closer they are, the faster they orbit). To illustrate what this complex system look like, NASA Fellow Dr. James O’Donoghue created a stunning animation that shows how each of Saturn’s major ring segments (A-Ring to F-Ring) orbit together around the planet.
Continue reading “Animation Shows how Saturn’s Rings Move at Different Speeds”