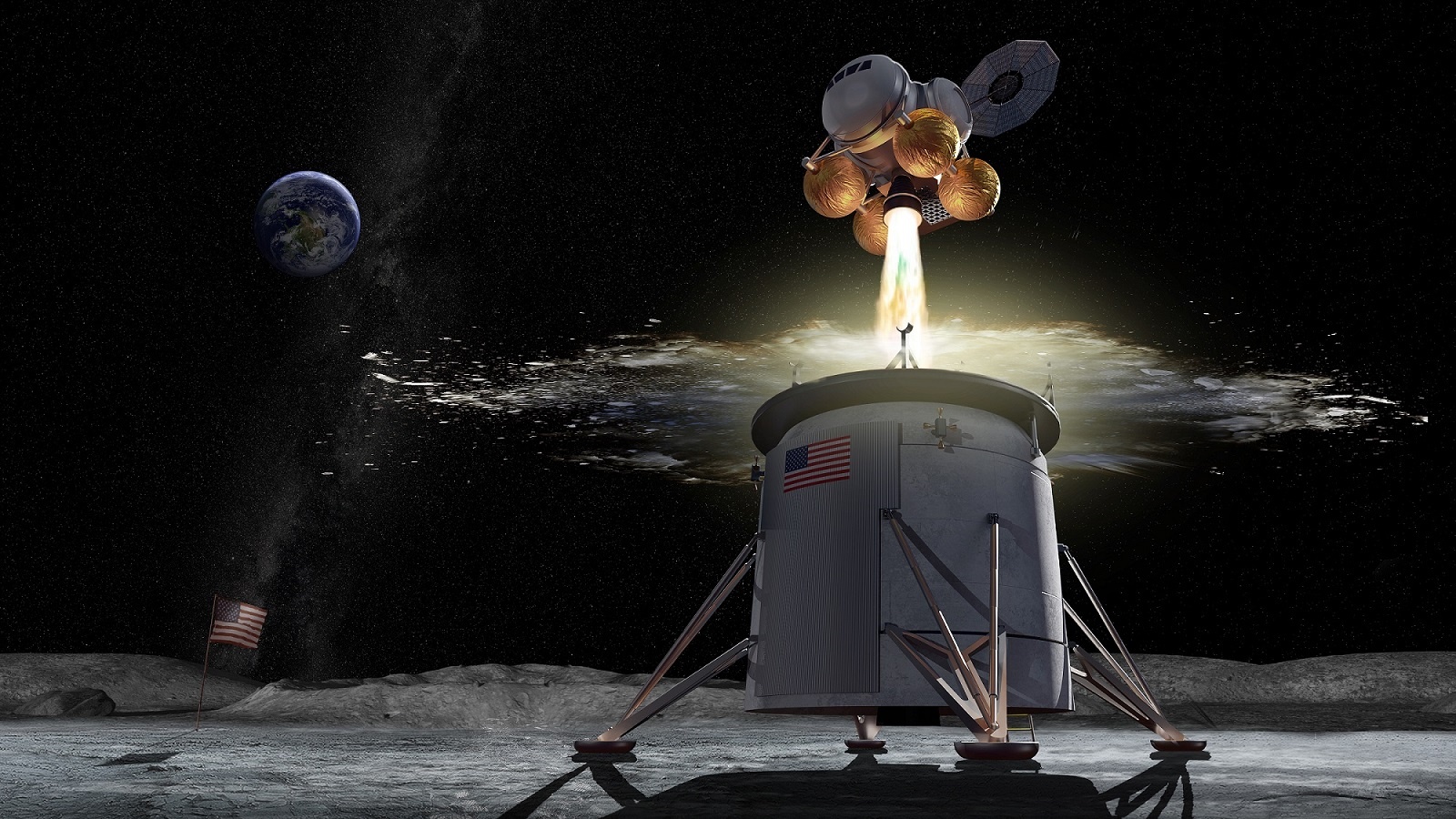
In 2010, President Barack Obama signed the NASA Authorization Act, which charged NASA with developing all the necessary technologies and components to allow for a crewed mission to Mars. Key to this was the development of the Space Launch System (SLS), the Orion spacecraft, and an orbiting lunar habitat (aka. the Lunar Gateway).
However, in recent years, these plans have been altered considerably to prioritize “returning to the Moon.” Formally named Project Artemis, VP Pence emphasized in March of 2019 that NASA must return to the Moon by 2024, even if it meant some shakeups were needed. In the latest news, NASA has indicated that the Lunar Gateway is no longer a priority, as part of a plan to “de-risk” the mandatory tasks associated with Artemis.
Continue reading “The Lunar Gateway is No Longer a Required Part of the Artemis Mission to Return to the Moon by 2024”