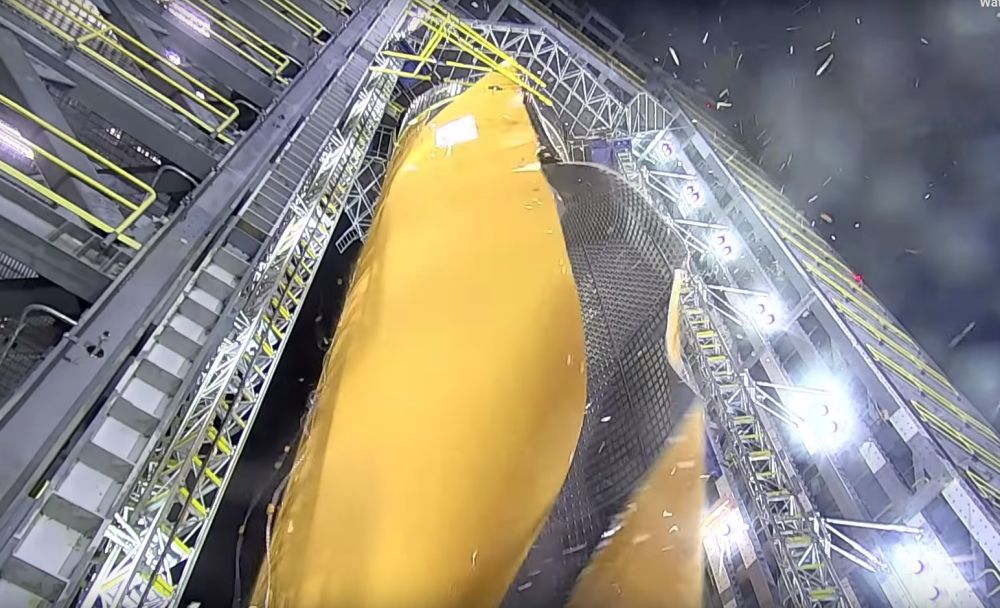
By the time a rocket actually launches, it’s components have been through a ton of rigorous testing. That’s certainly true of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) which is the most powerful rocket ever built. That’s right, something is finally going to surpass the Saturn V, the rocket that took Apollo astronauts to the Moon.
Continue reading “Watch NASA Test an SLS Tank to Destruction”It’s Time to Decide. Where Should OSIRIS-REx Take a Sample from Bennu?
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx arrived at asteroid Bennu in December 2018. During the past year, it’s been imaging the surface of the asteroid extensively, looking for a spot to take a sample from. Though the spacecraft has multiple science objectives, and a suite of instruments to meet them, the sample return is the key objective.
Now, NASA has narrowed the choice down to four potential sampling locations on the surface of the asteroid.
Continue reading “It’s Time to Decide. Where Should OSIRIS-REx Take a Sample from Bennu?”NASA Supercomputer Simulates the Weather on Mars
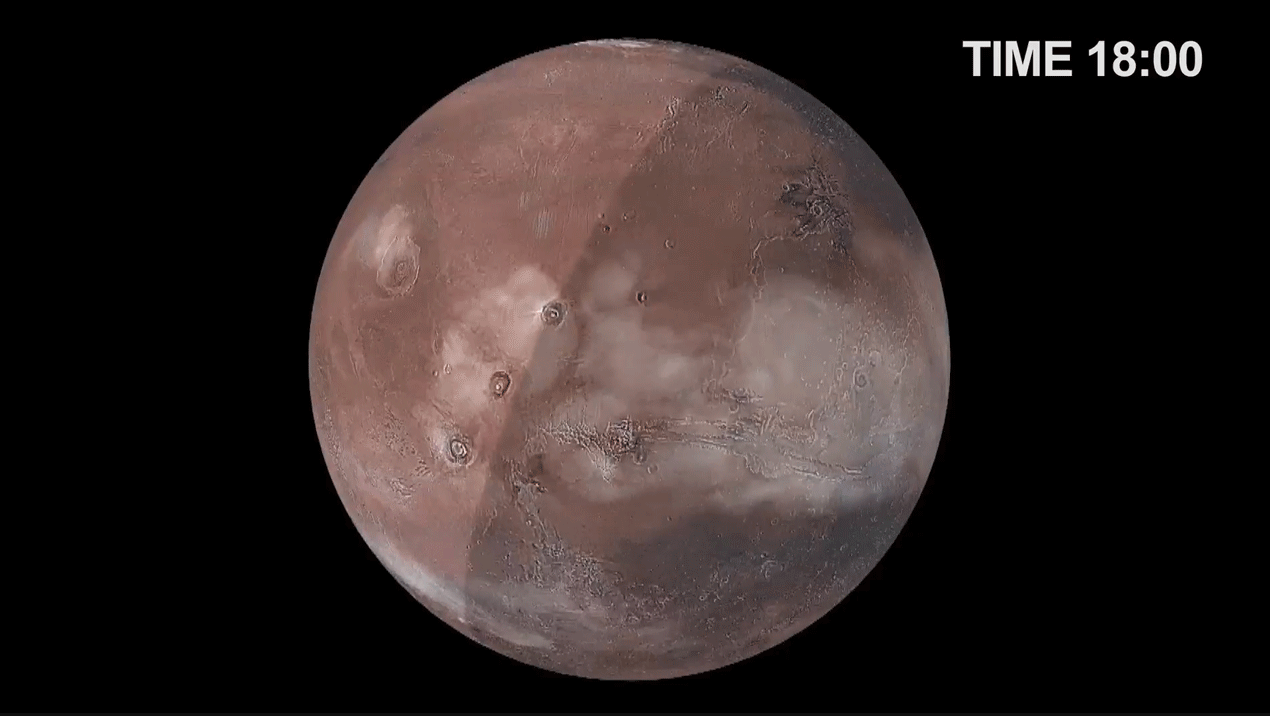
The Martian atmosphere is a lot different than Earth’s. It’s over 95% carbon dioxide, and contains only trace amounts of oxygen and water vapor. But that trace amount of water vapor still plays a pronounced role in the climate.
Continue reading “NASA Supercomputer Simulates the Weather on Mars”Here’s a Deepfake of Nixon Giving a Eulogy for the Apollo 11 Astronauts if Their Mission Failed

It’s July 16th, 1969. The Apollo 11 crew have completed their training, and they’re in the Columbia Command Module atop a Saturn V rocket, to this day the most powerful rocket ever built. At 9:32 EDT the rocket lifts off, delivering the crew into Earth orbit 12 minutes after launch.
Continue reading “Here’s a Deepfake of Nixon Giving a Eulogy for the Apollo 11 Astronauts if Their Mission Failed”Aquatic Rover Drives on the Underside of the Ice in Antarctica
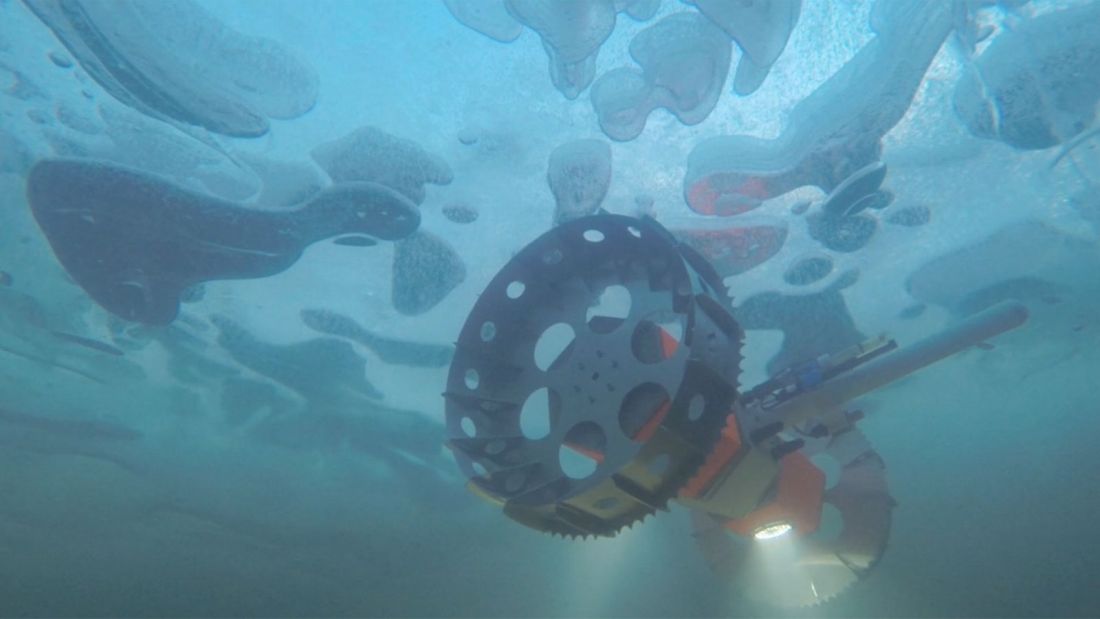

Not all rovers are designed to roam around on the surface of other worlds like Mars. One rover, at least, is aquatic; a necessary development if we’re going to explore Enceladus, Europa, and the Solar System’s other watery worlds. This rover is called the Buoyant Rover for Under-Ice Exploration, or BRUIE.
Continue reading “Aquatic Rover Drives on the Underside of the Ice in Antarctica”Stingray Glider to Explore the Cloudtops of Venus
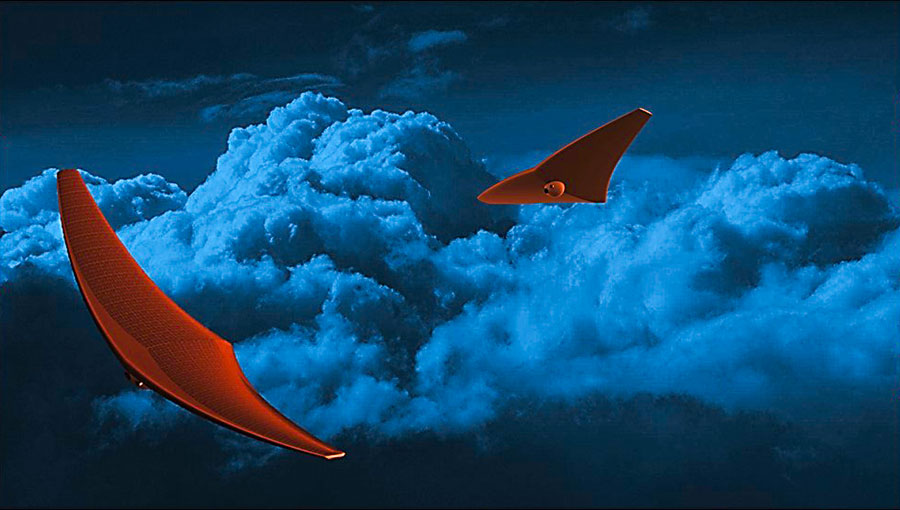

Venus is colloquially referred to as “Earth’s Twin”, owing to the similarities it has with our planet. Not surprisingly though, there is a great deal that scientists don’t know about Venus. Between the hot and hellish landscape, extremely thick atmosphere, and clouds of sulfuric rain, it is virtually impossible to explore the planet’s atmosphere and surface. What’s more, Venus’ slow rotation makes the study of its “dark side” all the more difficult.
However, these challenges have spawned a number of innovative concepts for exploration. One of these comes from the University of Buffalo’s Crashworthiness for Aerospace Structures and Hybrids (CRASH) Laboratory, where researchers are designing a unique concept known as the Bio-inspired Ray for Extreme Environments and Zonal Explorations (BREEZE).
Continue reading “Stingray Glider to Explore the Cloudtops of Venus”Mars 2020 Rover is Going to a Place on Mars That’s Perfect for Preserving Fossils
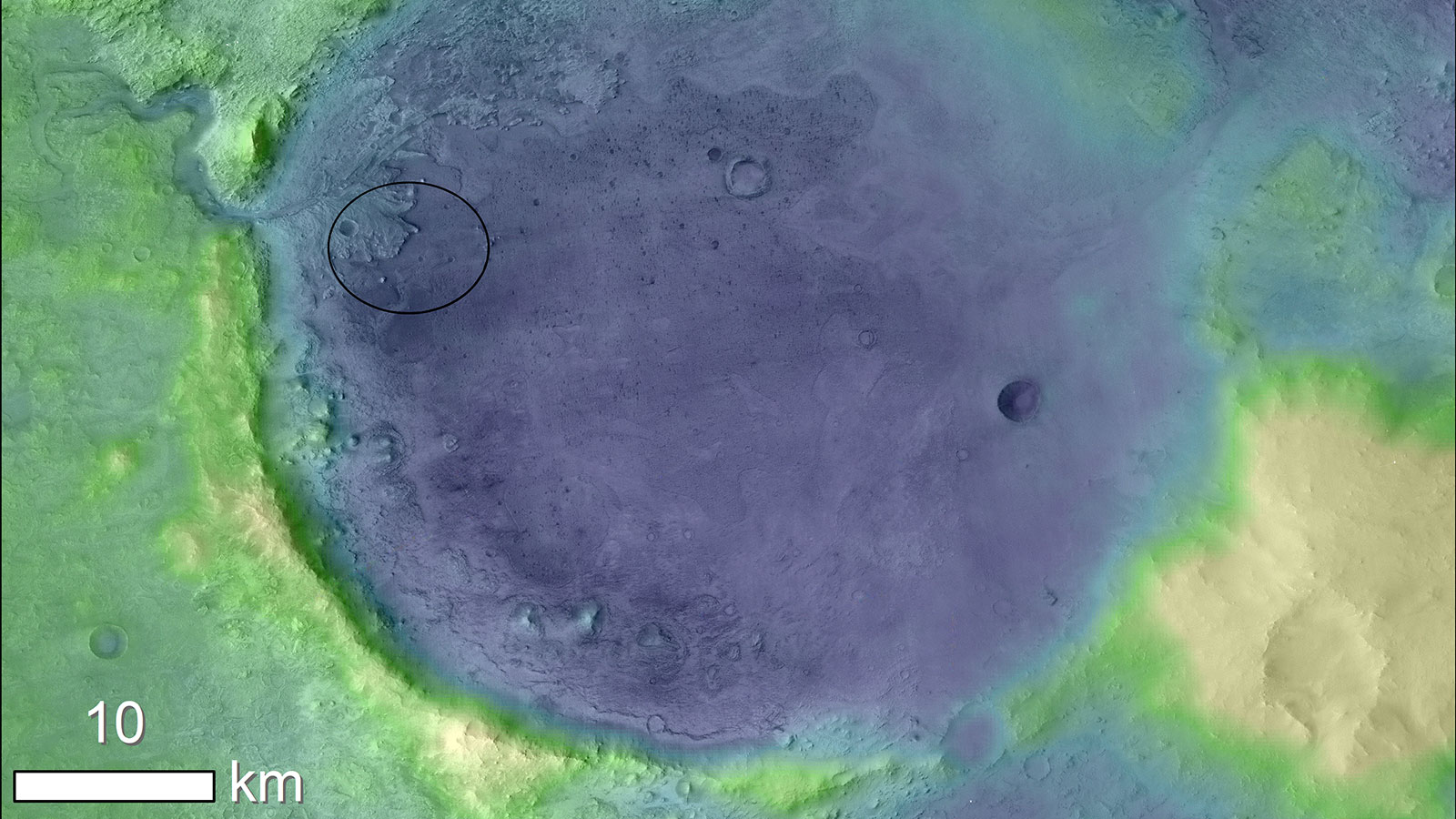

Back in November 2018, NASA announced that the Mars 2020 rover would land in the Jezero Crater. Jezero Crater is a geologically diverse area, with an alluvial fan of sediment deposited by an incoming river. That sediment may contain preserved ancient organic molecules, and the deposit is clearly visible in satellite images of the Crater.
But the crater holds something else that has scientists intrigued, something that doesn’t show up so clearly in visible light images: a “bathtub ring” of carbonates, which scientists think could hold fossils.
Continue reading “Mars 2020 Rover is Going to a Place on Mars That’s Perfect for Preserving Fossils”TESS Has Now Captured Almost the Entire Southern Sky. Here’s a Mosaic Made of 15,347 Photographs
On April 18th, 2018, NASA’s Transitting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) took to space for the first time. By August, it began capturing the light curves of distant stars for signs of planetary transits, effectively picking up where the Kepler Space Telescope left off. Now, just a few months away from the end of its primary mission, NASA has put a year’s worth of images of the southern sky together to create the beautiful mosaic you see here.
Continue reading “TESS Has Now Captured Almost the Entire Southern Sky. Here’s a Mosaic Made of 15,347 Photographs”NASA is Testing a Coating to Help Astronauts and Their Equipment Shed Dangerous Lunar Dust

In the coming years, NASA is going back to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era. Rather than being a “footprints and flags” operation, Project Artemis is intended to be the first step in creating a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Naturally, this presents a number of challenges, not the least of which has to do with lunar regolith (aka. moondust). For this reason, NASA is investigating strategies for mitigating this threat.
Continue reading “NASA is Testing a Coating to Help Astronauts and Their Equipment Shed Dangerous Lunar Dust”Weekly Space Hangout: November 6, 2019 – Tiera & Myron Fletcher, Engineers on NASA’s Space Launch System
Hosts: Fraser Cain (universetoday.com / @fcain)
Nancy Atkinson ( @Nancy_A / @nancyatkinson_ut)
Beth Johnson (@planetarypan)
Veranika Klimovich ( @VeronikaSpace)
This week we welcome Tiera and Myron Fletcher, Aerospace Engineers with Boeing working on NASA’s Space Launch System.
Continue reading “Weekly Space Hangout: November 6, 2019 – Tiera & Myron Fletcher, Engineers on NASA’s Space Launch System”


