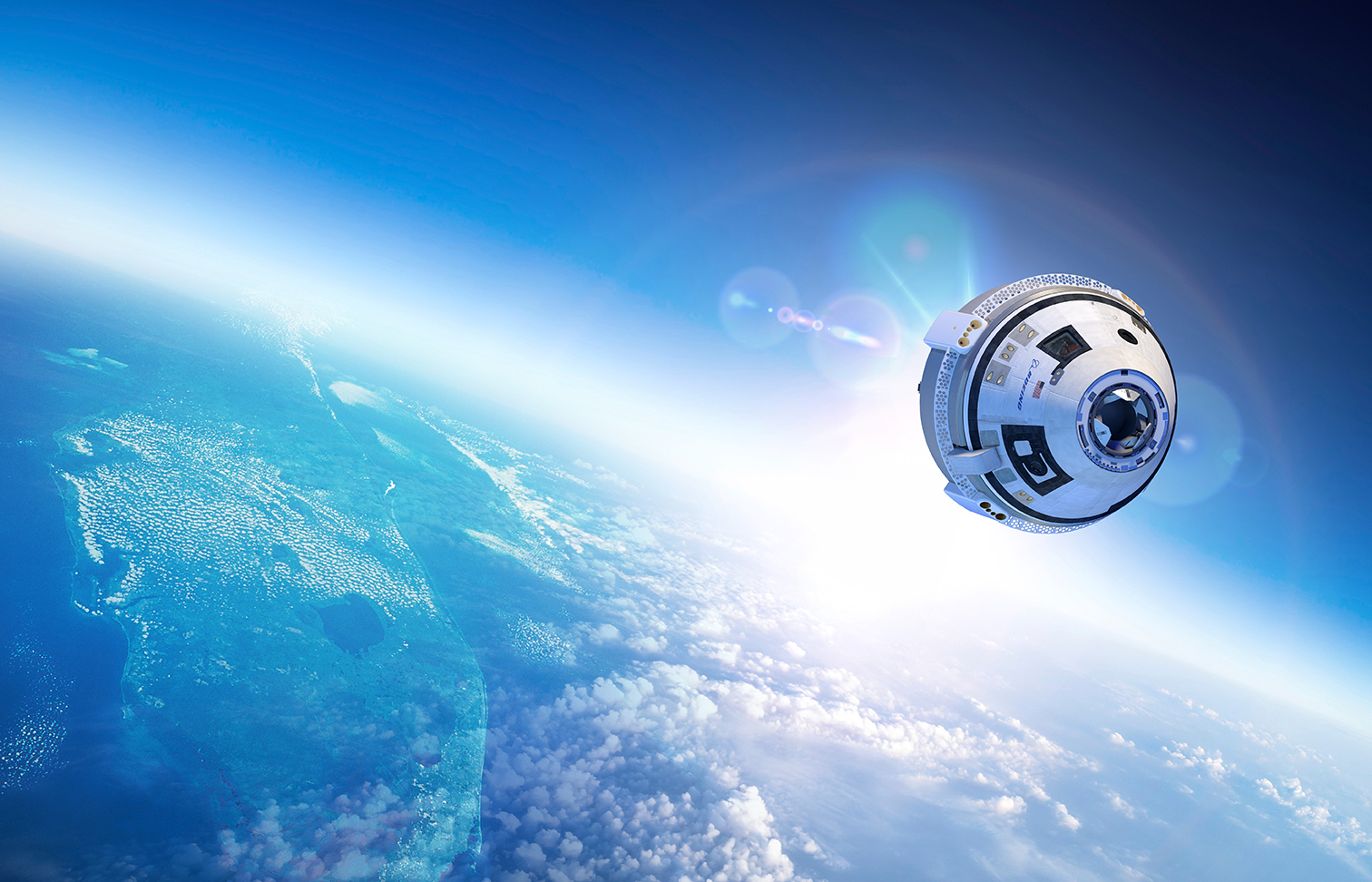
For years, NASA has been working to restore domestic launch capability to the US and send astronauts to the Moon and beyond. A crucial part of this is the development of next-generation crew capsules that can carry crews and payloads to space. These include Lockheed Martin’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) and the Crew Space Transportation (CST) -100 Starliner currently being developed by Boeing.
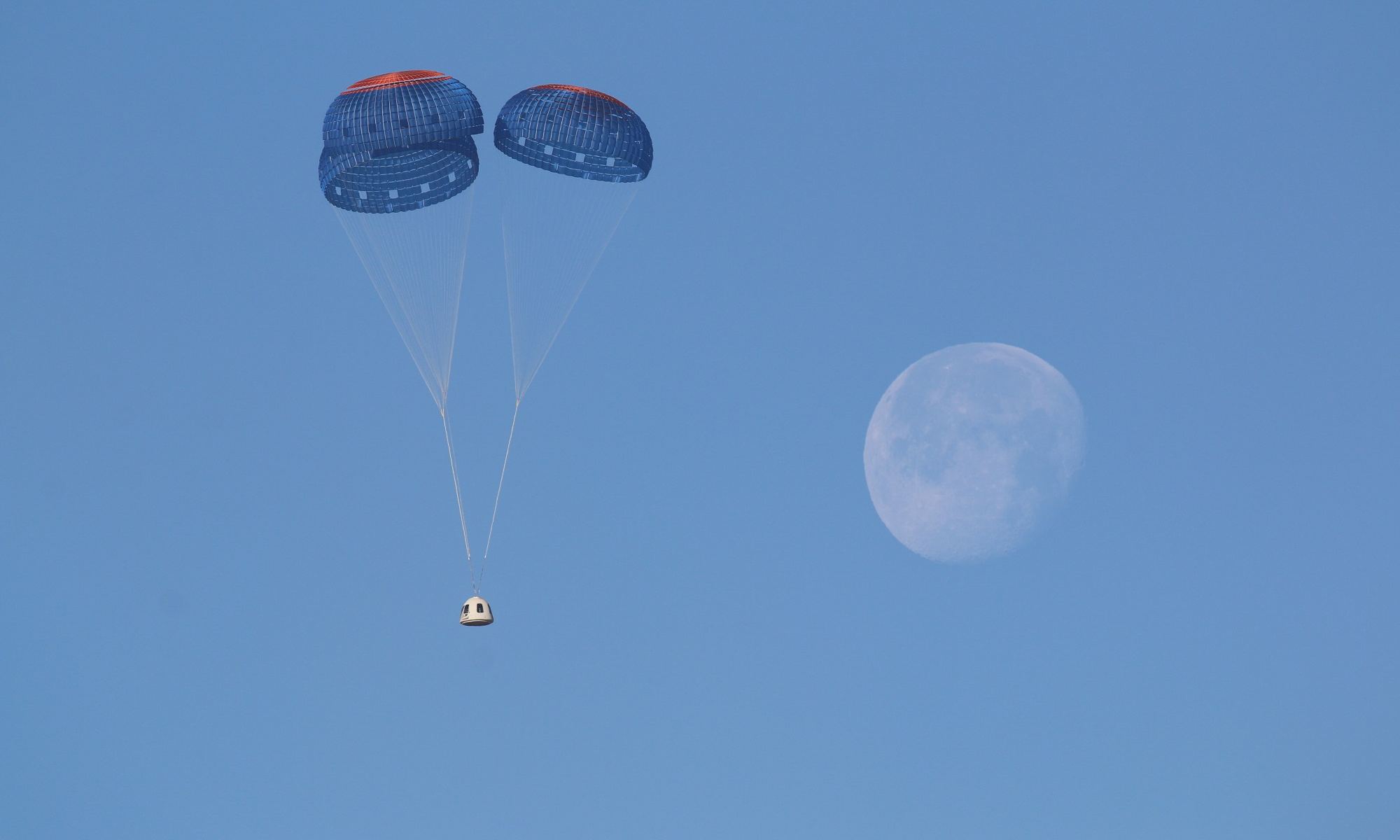
Earlier today (on Monday, Nov. 4th), the CST-100 passed a critical milestone with a successful end-to-end test of its abort system. The Pad Abort Test took place at Launch Complex 32 at the US Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. When crewed missions to space begin using the CST-100, this system will ensure that astronauts will be carried to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff.
Continue reading “Boeing’s Starliner Performed its Abort Test Today. One Parachute Failed to Deploy”