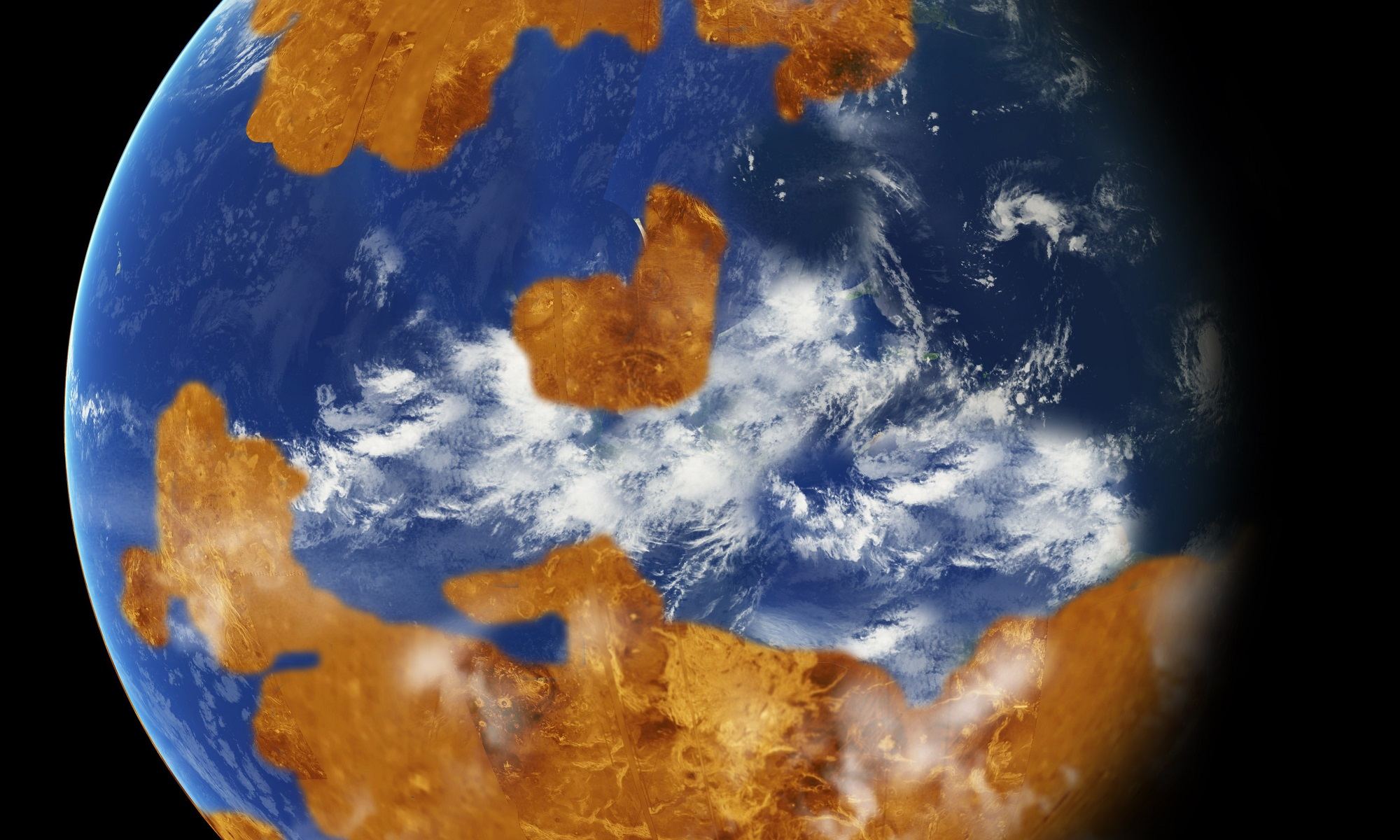
There’s no sense in sugar-coating it – Venus is a hellish place! It is the hottest planet in the Solar System, with atmospheric temperatures that are hot enough to melt lead. The air is also a toxic plume, composed predominantly of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid rain clouds. And yet, scientists theorize that Venus was once a much different place, with a cooler atmosphere and liquid oceans on its surface.
Unfortunately, this all changed billions of years ago as Venus experienced a runaway greenhouse effect, changing the landscape into the hellish world we know today. According to a NASA-supported study by an international team of scientists, it may have actually been the presence of this ocean that caused Venus to experience this transition in the first place.
Continue reading “Theory proposes that Venus could have been habitable, but a large ocean slowed down its rotation, killing it”