After many delays and two scrubbed launch attempts, Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner successfully launched earlier today! The Crewed Flight Test (CFT) took off from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida, at 10:52 a.m. EDT (07:52 PDT) atop a ULA Atlas V rocket. For this mission, the capsule is carrying two NASA astronauts: Barry “Butch” Wilmore (commander) and Sunita “Suni” Williams (pilot). They are expected to reach the International Space Station (ISS) at 12:15 p.m. EDT (09:15 a.m. PDT) on Thursday, June 6th.
Continue reading “Starliner Finally Launches, Carrying Two Astronauts Into Orbit”Metal is 3D Printed on the Space Station
I have always wanted a 3D printer but never quite found a good enough reason to get one. Seeing that NASA are now 3D printing metal is even more tantalising than a plastic 3D printer. However, thinking about it, surely it is just a computer controlled soldering iron! I’m sure it’s far more advanced than that! Turns out that the first print really wasn’t much to right home about, just an s-curve deposited onto a metal plate! It does however prove and demonstrate the principle that a laser can liquify stainless steel and then deposit it precisely in a weightless environment.
Continue reading “Metal is 3D Printed on the Space Station”NASA has a New Database to Predict Meteoroid Hazards for Spaceflight
There are plenty of problems that spacecraft designers have to consider. Getting smacked in the sensitive parts by a rock is just one of them, but it is a very important one. A micrometeoroid hitting the wrong part of the spacecraft could jeopardize an entire mission, and the years of work it took to get to the point where the mission was actually in space in the first place. But even if the engineers who design spacecraft know about this risk, how is it best to avoid them? A new programming library from research at NASA could help.
Continue reading “NASA has a New Database to Predict Meteoroid Hazards for Spaceflight”Highlights from the 10th Achieving Mars Workshop

Back in December, NASA officials, space industry experts, members of the academic community, and science communicators descended on Washington, D.C., for the Achieving Mars Workshop X (AM X). This workshop is hosted by Explore Mars Inc., a non-profit organization dedicated to bringing leading experts from disparate fields together to contribute to creating the first crewed missions to Mars. On May 17th, the results of this year’s workshop were summarized in a report titled “The Tenth Community Workshop for Achievability and Sustainability of Human Exploration of Mars.”
Continue reading “Highlights from the 10th Achieving Mars Workshop”Pluto Has an Ocean of Liquid Water Surrounded by a 40-80 km Ice Shell
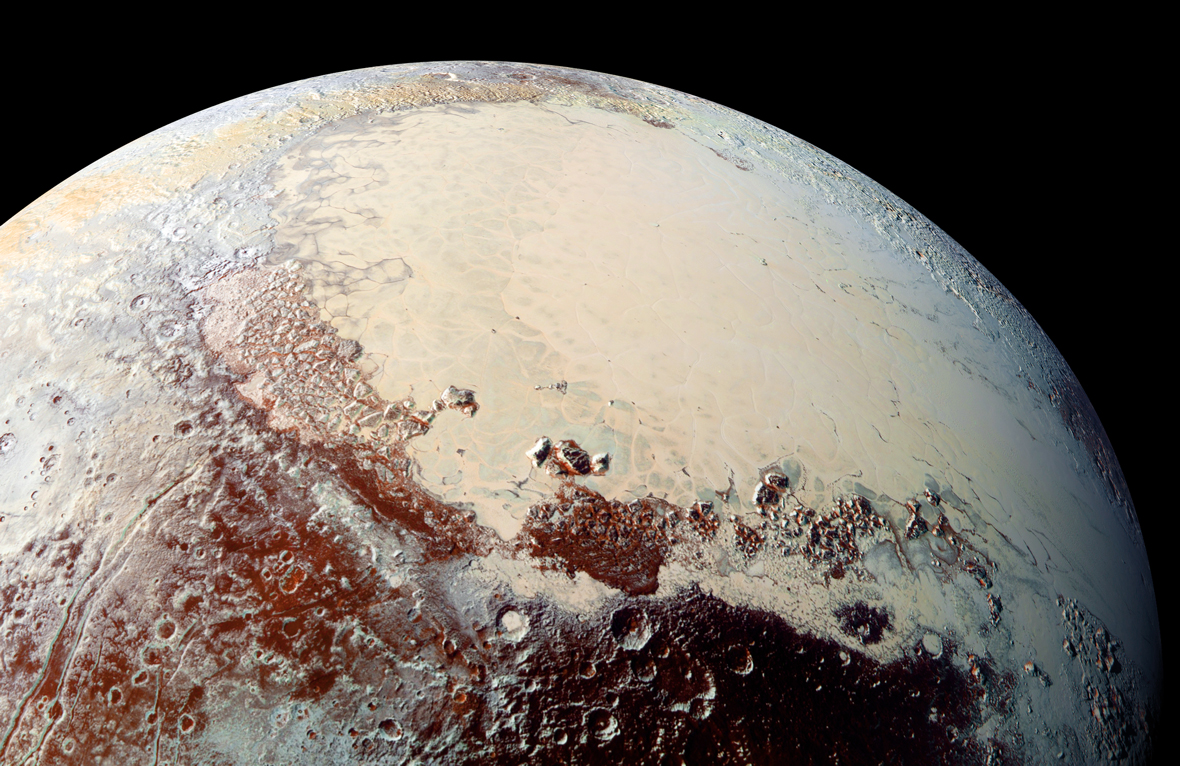

On July 14th, 2015, the New Horizons spacecraft conducted the first-ever flyby of Pluto, which once was (and to many, still is) the ninth planet of the Solar System. While the encounter was brief, the stunning images and volumes of data it obtained revealed a stunningly vibrant and dynamic world. In addition to Pluto’s heart, floating ice hills, nitrogen icebergs, and nitrogen winds, the New Horizons data also hinted at the existence of an ocean beneath Pluto’s icy crust. This effectively made Pluto (and its largest moon, Charon) members of the “Ocean Worlds” club.
Almost a decade after that historic encounter, scientists are still making discoveries from New Horizons data. In a new paper, planetary scientists Alex Nguyen and Dr. Patrick McGovern used mathematical models and images to learn more about the possible ocean between Pluto’s icy surface and its silicate and metallic core. According to their analysis, they determined that Pluto’s ocean is located beneath a surface shell measuring 40 to 80 km (25 to 50 mi), an insulating layer thick enough to ensure that an interior ocean remains liquid.
Continue reading “Pluto Has an Ocean of Liquid Water Surrounded by a 40-80 km Ice Shell”Galaxies in the Early Universe Preferred their Food Cold
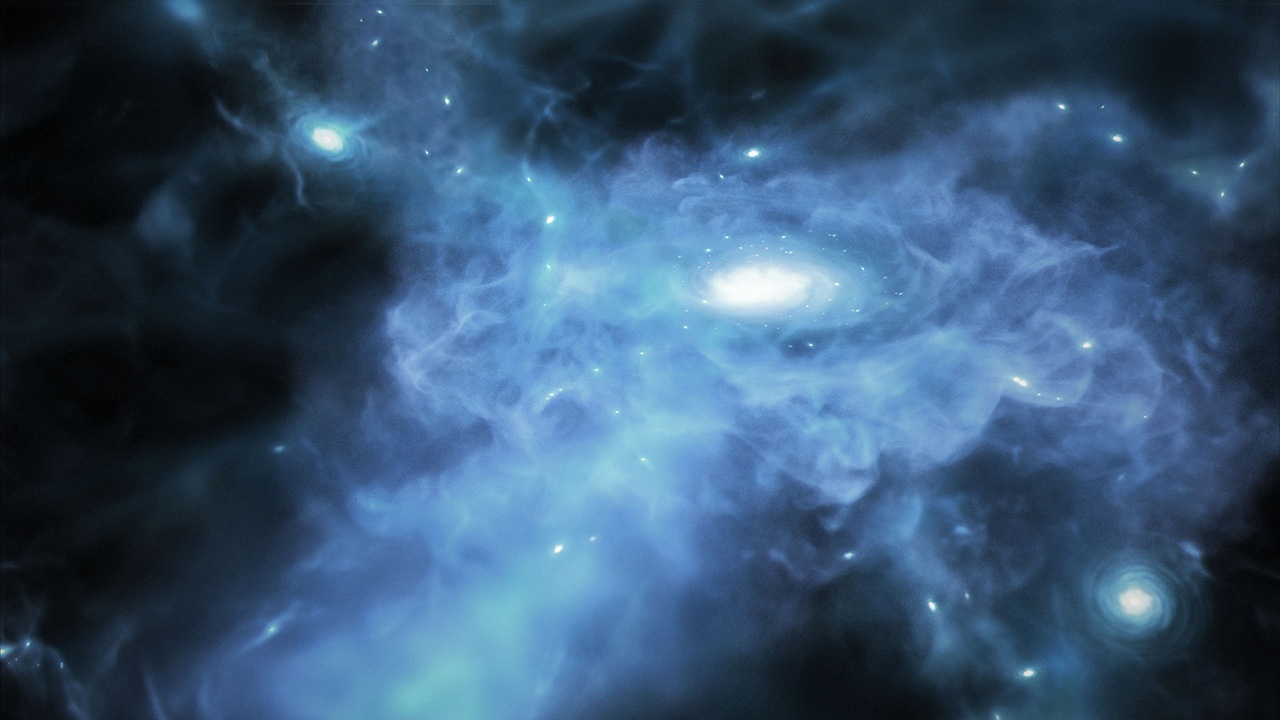

One of the main objectives of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is to study the early Universe by using its powerful infrared optics to spot the first galaxies while they were still forming. Using Webb data, a team led by the Cosmic Dawn Center in Denmark pinpointed three galaxies that appear to have been actively forming just 400 to 600 million years after the Big Bang. This places them within the Era of Reionization, when the Universe was permeated by opaque clouds of neutral hydrogen that were slowly heated and ionized by the first stars and galaxies.
This process caused the Universe to become transparent roughly 1 billion years after the Big Bang and (therefore) visible to astronomers today. When the team consulted the data obtained by Webb, they observed that these galaxies were surrounded by an unusual amount of dense gas composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium, which likely became fuel for further galactic growth. These findings already reveal valuable information about the formation of early galaxies and show how Webb is exceeding its mission objectives.
Continue reading “Galaxies in the Early Universe Preferred their Food Cold”Astronomers Propose a 14-Meter Infrared Space Telescope
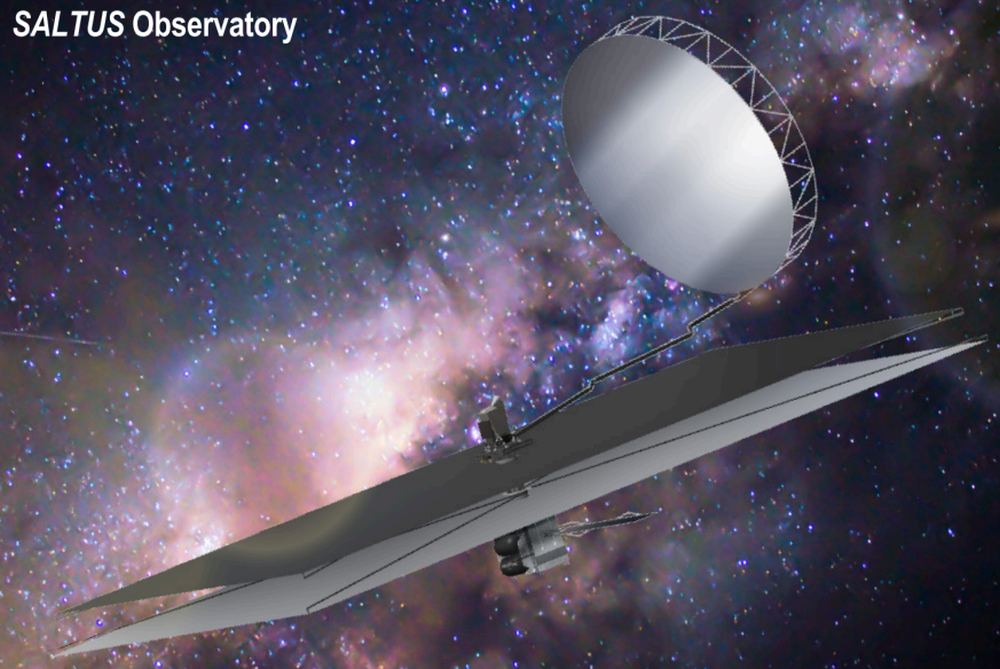

The Universe wants us to understand its origins. Every second of every day, it sends us a multitude of signals, each one a clue to a different aspect of the cosmos. But the Universe is the original Trickster, and its multitude of signals is an almost unrecognizable cacophony of light, warped, shifted, and stretched during its long journey through the expanding Universe.
Continue reading “Astronomers Propose a 14-Meter Infrared Space Telescope”New Photos Show Jupiter’s Tiny Moon Amalthea
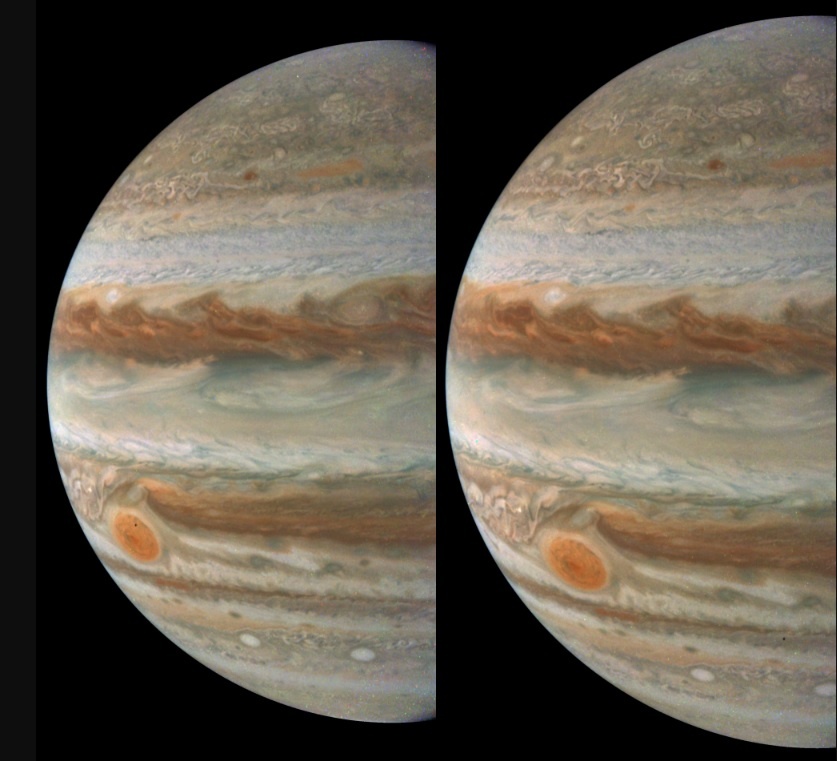
NASA’s Juno spacecraft spies a tiny inner moon of Jupiter, Amalthea.
It’s tiny, but it’s there. By now, we’re all used to seeing amazing photos of Jupiter courtesy of NASA’s Juno mission on a routine basis. Many of these are processed by volunteer ‘citizen scientists,’ and they show the swirling cloud-tops of Jove courtesy of the spacecraft’s JunoCam in stunning detail.
Continue reading “New Photos Show Jupiter’s Tiny Moon Amalthea”We Need to Consider Conservation Efforts on Mars

Astrobiology is the field of science that studies the origins, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the Universe. In practice, this means sending robotic missions beyond Earth to analyze the atmospheres, surfaces, and chemistry of extraterrestrial worlds. At present, all of our astrobiology missions are focused on Mars, as it is considered the most Earth-like environment beyond our planet. While several missions will be destined for the outer Solar System to investigate “Ocean Worlds” for evidence of life (Europa, Ganymede, Titan, and Enceladus), our efforts to find life beyond Earth will remain predominantly on Mars.
If and when these efforts succeed, it will have drastic implications for future missions to Mars. Not only will great care need to be taken to protect Martian life from contamination by Earth organisms, but precautions must be taken to prevent the same from happening to Earth (aka. Planetary Protection). In a recent study, a team from the University of New South Wales (UNSW) in Sydney, Australia, recommends that legal or normative frameworks be adopted now to ensure that future missions do not threaten sites where evidence of life (past or present) might be found.
Continue reading “We Need to Consider Conservation Efforts on Mars”NASA Takes Six Advanced Tech Concepts to Phase II
It’s that time again. NIAC (NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts) has announced six concepts that will receive funding and proceed to the second phase of development. This is always an interesting look at the technologies and missions that could come to fruition in the future.
Continue reading “NASA Takes Six Advanced Tech Concepts to Phase II”


