Looking to the future of space exploration, NASA’s priorities are sometimes subject to change. In 2004, the Bush administration released it’s “Vision for Space Exploration“, which called for the development of rockets that would return astronauts to the Moon. This policy was later replaced by the NASA Authorization Act of 2010, which outlined plans to send humans to an asteroid by 2025 and to Mars in the 2030s.
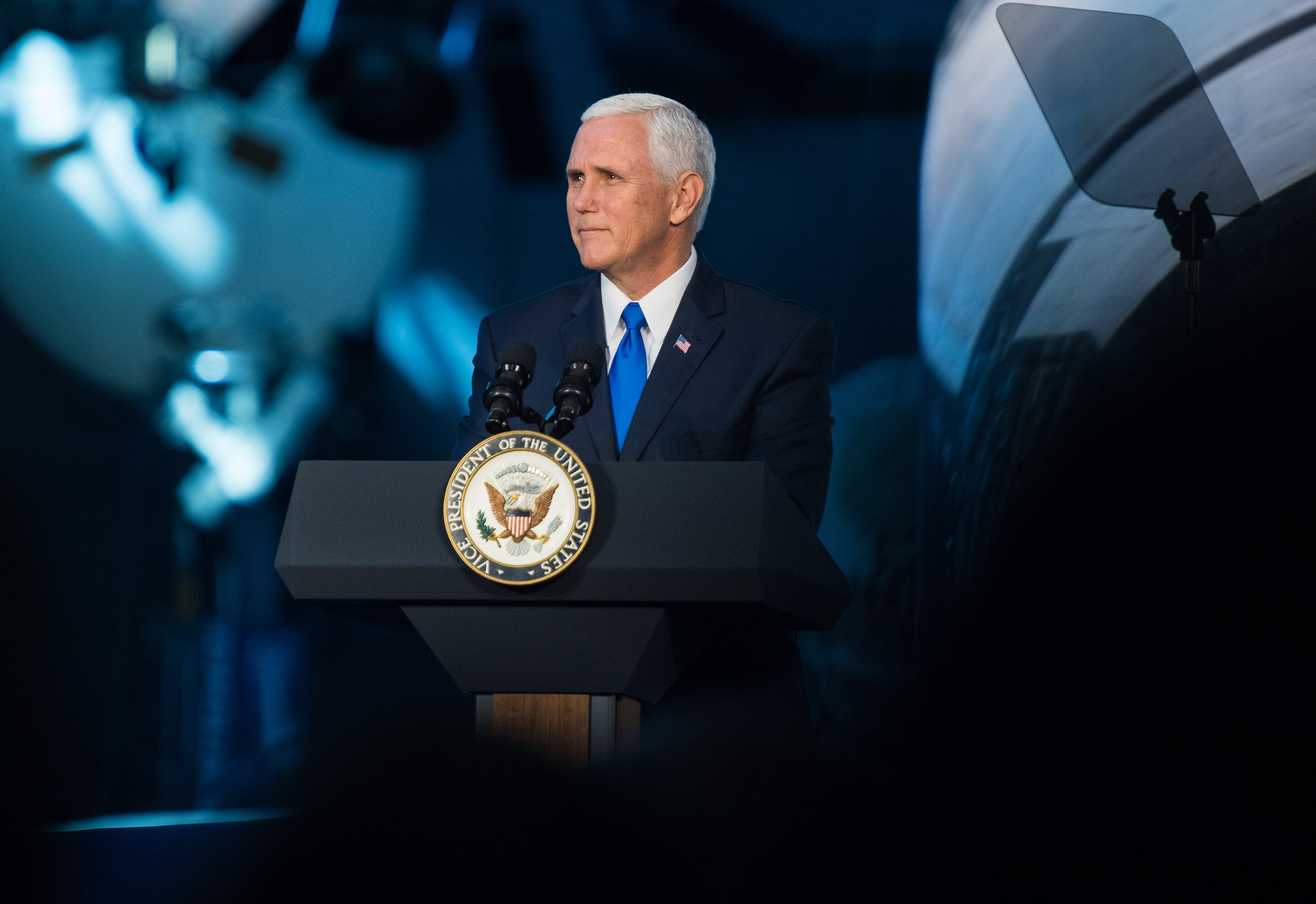
Earlier today, on Thursday, October 5th, Vice President Mike Pence and several members of the Trump administration announced that their priorities have shifted once again. Instead of proceeding with NASA’s proposed “Journey to Mars“, the administration has set its sights on once again mounting crewed missions to the Moon and establishing a permanent presence on the lunar surface.
The announcement came during the inaugural meeting of the National Space Council, the newly-reestablished executive group that will be guiding US space policy in the coming years. Originally established in 1989 by then-president George H.W. Bush (and disbanded in 1993 by the Clinton administration), this council served the same purpose as the National Aeronautics and Space Council – which oversaw space policy between 1958 and 1973.

The meeting, titled “Leading the Next Frontier: An Event with the National Space Council“, took place at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum’s (NASM) Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia. The meeting was chaired by Vice President Mike Pence with the participation of NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot, and was attended by Trump Administration cabinet members, senior officials, and aerospace industry leaders.
During the course of the meeting, which was live-streamed, Vice President Mike Pence laid out the administration’s plans for returning astronauts to the Moon. Emphasizing the need to restore NASA and America’s leadership in space, Pence compared the current situation to the early years of the Space Race and the crowing achievement that was the Apollo 11 mission. As he said:
“It is altogether fitting that we chose this week for the first meeting of the National Space Council. Yesterday marked the 60th anniversary of Sputnik, that 184-pound satellite that changed the course of history. On that day, six decades ago yesterday, the race for space began and the then-Soviet Union took an early lead. But the sight of that light blinking across that October sky spurred America to action. We refused to accept a future in space written by the enemies of freedom, and so the United States of America vowed to claim our rightful place as the undisputed leader in the exploration of the heavens. And twelve years later, with “one giant leap for mankind”, America led in space.
Moving to the present, Pence indicated that the reestablishment of he National Space Council would put an end to the ways in which space exploration has stalled in recent decades. He also indicated how a return to the Moon – a goal which diminished in important in the post-Apollo era – would recapture the spirit of the past and reinvigorate modern space exploration.

As he expressed during the course of the meeting, the way space exploration has stalled is in part due to the way in which the Moon (as a destination) has diminished in importance:
“Our struggle to define the direction and purpose of America’s space program dates back decades to the post-Apollo period. We had just won the race to the Moon and suddenly the question became, ‘What should we do? Where should we go next?’ In the debate that followed, sending Americans to the Moon was treated as a triumph to be remembered, but not repeated. Every passing year that the Moon remained squarely in the rear-view mirror further eroded our ability to return to the lunar domain and made it more likely that we would forget why we ever wanted to go in the first place.”
A renewed mission to the Moon, claimed Pence, will put an end to decades in which not a single NASA astronaut has ventured beyond Low Earth Orbit. He further indicated how after the retirement of the Space Shuttle Program, the US has been dependent on Russia to ferry astronauts to the International Space Station. He also voiced criticism for the Obama administration, claiming that it chose “capitulation” when it came to the space race.
While this new policy technically represents a break from the policy of the Obama administration, and a return to the policy of the Bush administration, Pence emphasized that returning to the Moon would be a stepping stone towards an eventual crewed mission to the Red Planet. This announcement also put an end to months of ambiguity regarding the Trump administration’s space policy.

In the past, VP Pence has spoken about the need to return to the Moon and puts boots on Mars, but nothing definitive was said. This ambiguity, it is worth noting, has also been a source of anxiety for those at NASA, who were unsure about the future budget environment. And while this meeting did indicate that the Trump administration has a policy, many aspects of it were already in place before the administration took office.
After the meeting concluded, acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot spoke of the results in a NASA press statement. In reference to the direction VP Pence had indicated for the agency, he said the following:
“Specifically, NASA has been directed to develop a plan for an innovative and sustainable program of exploration with commercial and international partners to enable human expansion across the solar system, returning humans to the Moon for long-term exploration and utilization, followed by human missions to Mars and other destinations.”
Much of the details discussed at the meeting were already established as early as last September. It was at this time that the NASA Transition Authorization Act of 2016, a provisional measure that guaranteed short-term stability for the agency by allocating $19.5 billion in funding for NASA for fiscal year 2017. Intrinsic to the Act was the cancellation for the NASA’s Asteroid Robotic Redirect Missions (ARRM) in favor of a more cost-effective alternative.

As Lightfoot indicated, this would still be the case under the current administration’s plan:
“The recommendation to the president would modify the existing National Space Policy to provide focus and direction to some of NASA’s current activities and plans, and remove a previous guideline that NASA should undertake a human mission to an asteroid as the next human spaceflight milestone beyond low-Earth orbit.”
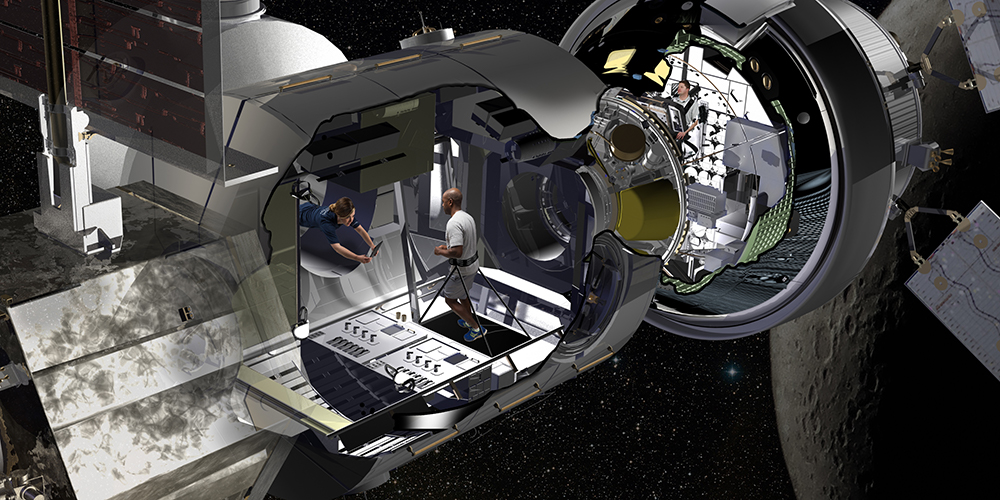
Lighfoot also reiterated what Pence said during the meeting, how renewed missions to the Moon would ultimately assist NASA’s efforts to mount crewed missions to Mars. These included the importance of cis-lunar space to the exploration of both the Moon and the Mars, as well as its use as a proving ground for future mission to Mars and beyond in the Solar System.
“Based on a number of conversations I’ve had with the council,” he said, “we have highlighted a number of initiatives underway in this important area, including a study of an orbital gateway or outpost that could support a sustained cadence of robotic and human missions, as well as ensuing human missions to the lunar and Mars surfaces, and other destinations.”

While this latest announcement does confirm what many have suspected for some time – that the Trump administration would prioritize lunar exploration – much ambiguity remains. While Pence emphasized that the re-establishment of the NSC was intrinsic to restoring American leadership in space, very little appears to have changed since the NASA Transition Authorization Act of 2016.
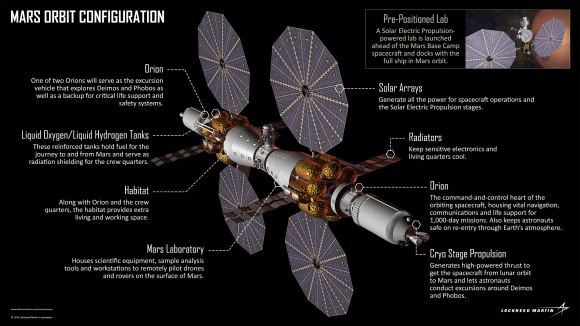
What’s more, despite Pence’s claims of “capitulation” on behalf of the Obama administration, much of the current administration’s policy represents a continuation of the NASA Authorization Act of 2010. These include the use of the Space Launch System (SLS), the Orion spacecraft, and the restoration of domestic launch capability. In short, much of the Trump administration’s plans to restore American leadership in space are piggybacking on the accomplishments of the Obama administration.
Beyond that, the creation of the Deep Space Gateway appears unaffected, since its existence is central to both renewed mission to the Moon and for crewed missions to Mars. And the long-term plan for the exploration of Mars appear to still be intact. So in many ways, this latest announcement is not much in the way of news, but also good news.
When it comes to organizations like NASA and space exploration in general, continuity is not only preferable, but necessary. And in the meantime, be sure to check out the live coverage of the event: