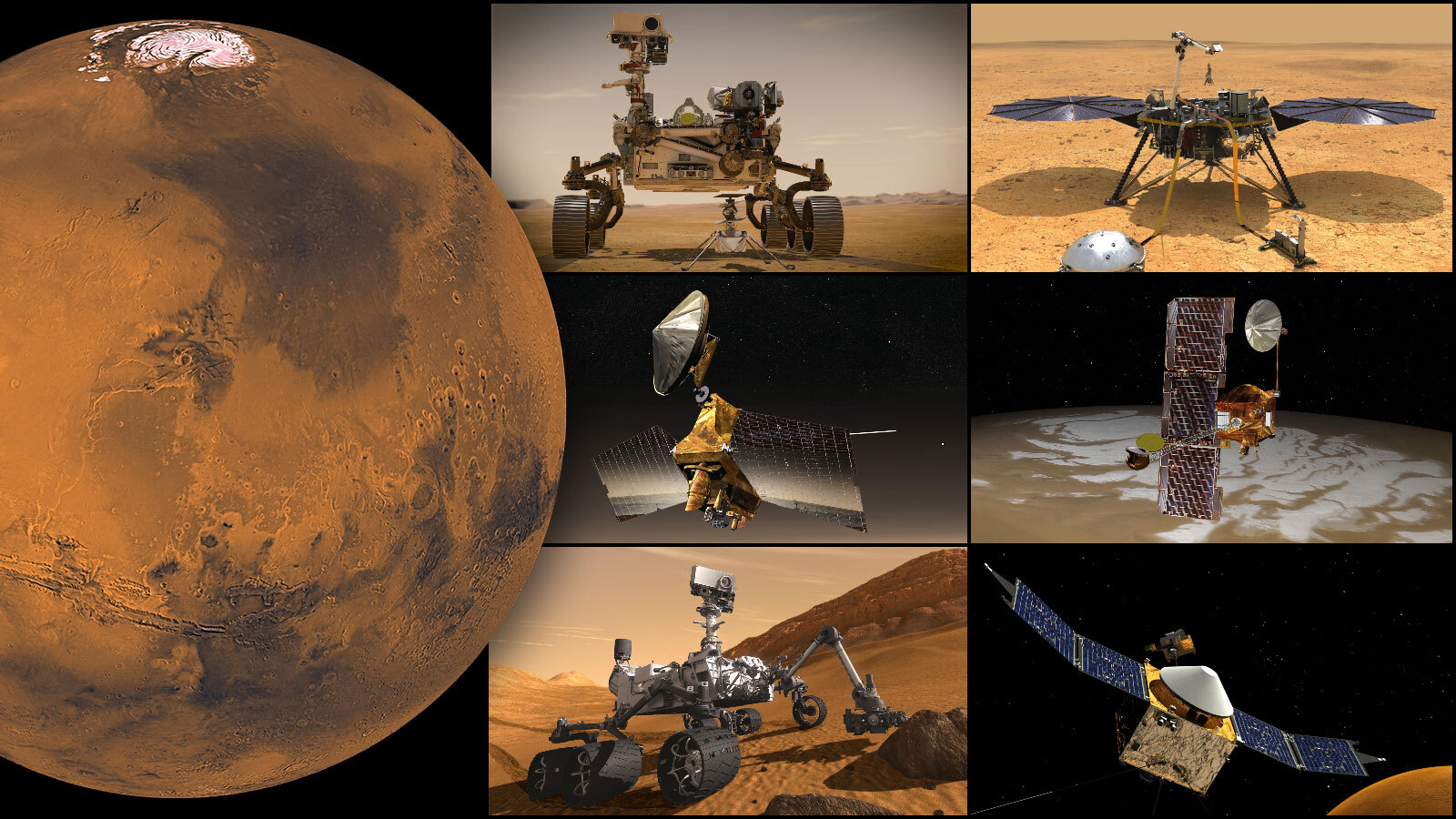
Mars has become something of an international playground over the past twenty years. There are currently eleven missions from five space agencies exploring the Red Planet, a combination of orbiters, landers, and rovers. Several additional robotic missions will be leaving for Mars in the next few years, and crewed missions are planned for the 2030s. Because of this increase in traffic, NASA and other space agencies are naturally worried about “planetary protection.”
With this in mind, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) recently released a new report that identified several criteria for future robotic missions to Mars. These would reduce these missions’ “bioburden” requirements, which are designed to prevent the unintentional contamination of the Red Planet with Earth-based organisms. Specifically, the report considers how Earth organisms would interfere with searches for indigenous life on the planet.
Continue reading “How to Prevent our Spacecraft From Contaminating Mars”