Imagine, if you will, that the Universe was once a much dirtier place than it is today. Imagine also that what we see around us, a relatively clean and unobscured Universe, is the result of billions of years of stars behaving like giant celestial Roombas, cleaning up the space around them in preparation for our arrival. According to a set of recently published catalogues, which detail the latest findings from the ESA’s Herschel Space Observatory, this description is actually quite fitting.
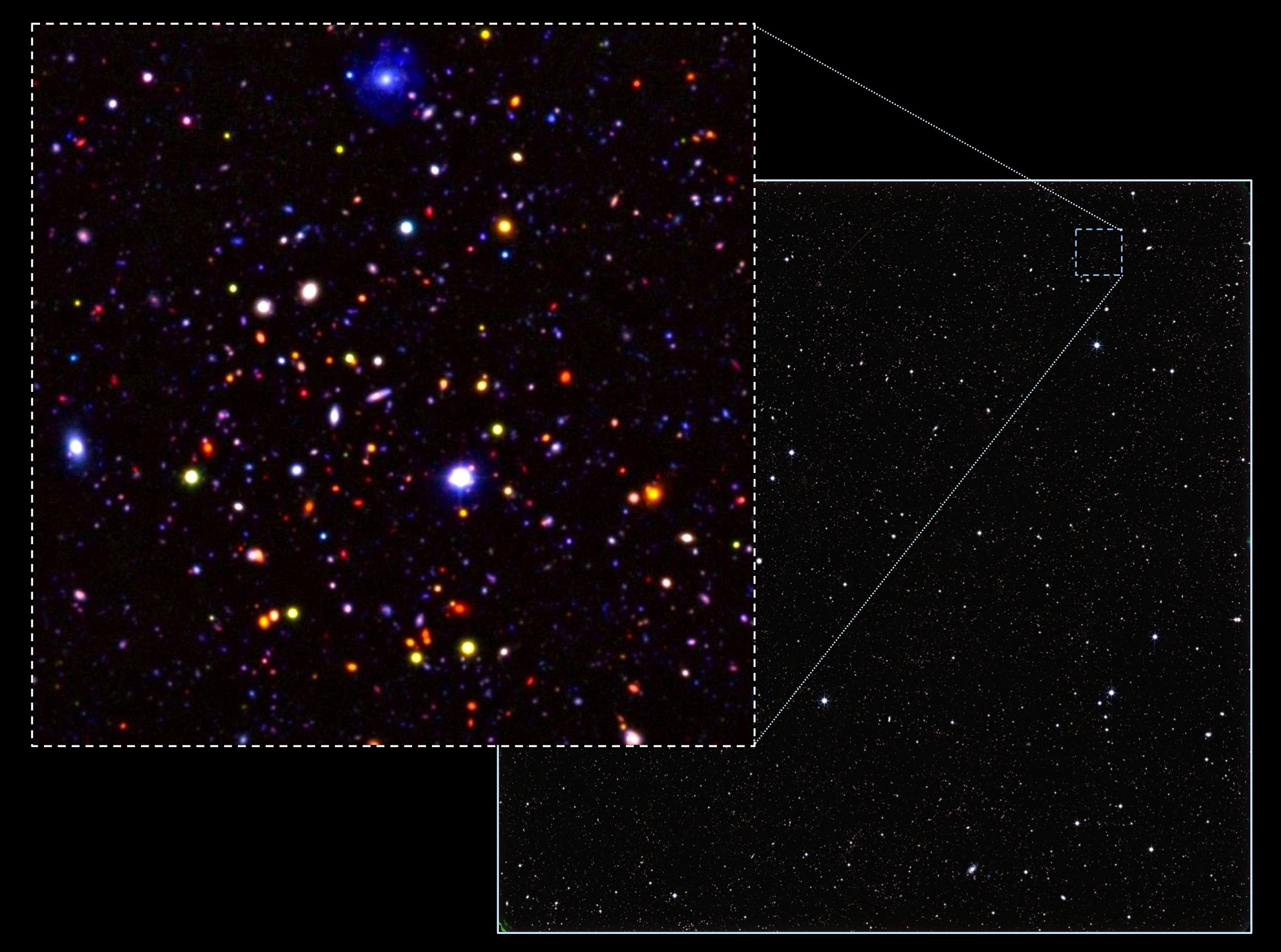
These catalogues represents the work of an international team of over 100 astronomers who have spent the past seven years analyzing the infrared images taken by the Herschel Astrophysical Terahertz Large Area Survey (Herschel-ATLAS). Presented earlier this week at the National Astronomy Meeting in Nottingham, this catalogue revealed that 1 billion years after the Big Bang, the Universe looked much different than it does today.
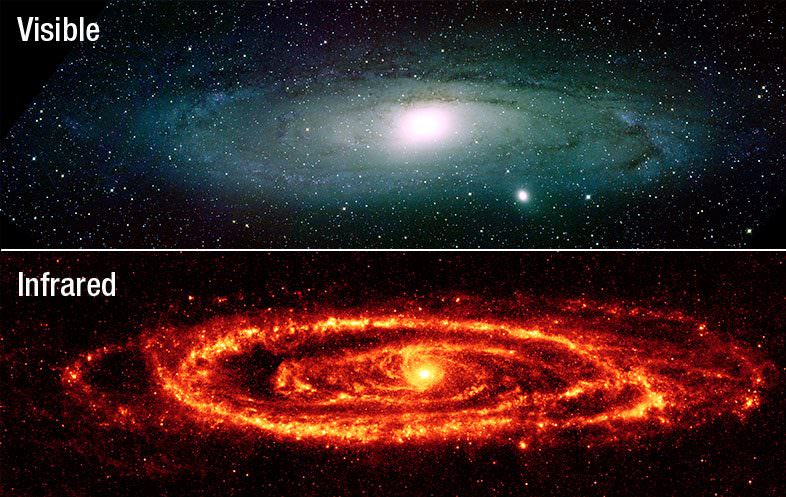
In order to put this research into context, it is important to understand the important of infrared astronomy. Prior to the deployment of missions like Herschel (which was launched in 2009), astronomers were unable to see a good portion of the light emitted by stars and galaxies. With roughly half of this light being absorbed by interstellar dust grains, research into the birth and lives of galaxies was difficult.
But thanks to surveys like Herschel ATLAS – as well NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope and the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) – astronomers have been able to account for this missing energy. And what they have seen (especially from this latest survey) has been quite remarkable, presenting a Universe that is far denser than previously expected.
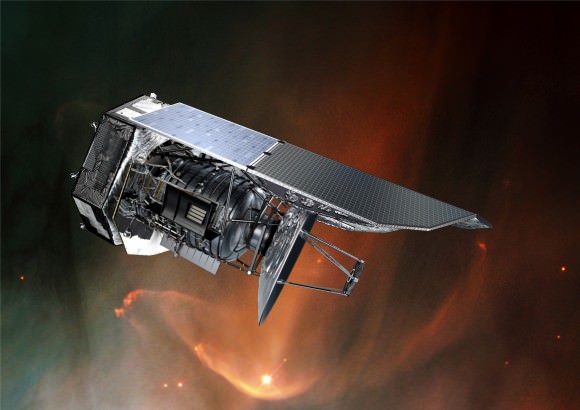

Professor Haley Gomez of Cardiff University presented this catalogue during the third day of the National Astronomy Meeting (which ran from June 27th to July 1st). As she told Universe Today via email:
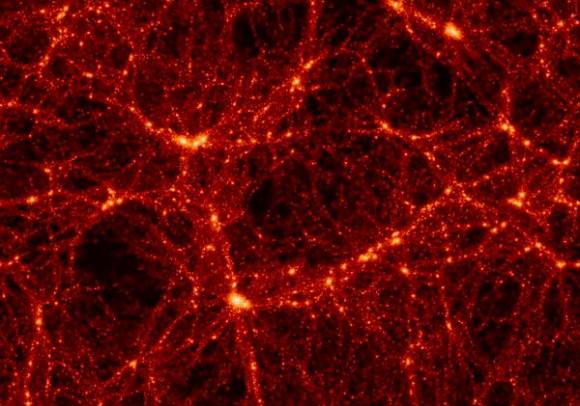
“The Herschel survey is the largest one of the sky in these special infrared light. Because of this we see rare objects that we might not see in a smaller patch of sky, but also we now see hundreds of thousands of dusty galaxies, compared to the few hundred we saw in previous telescopes. So this is a massive improvement in terms of knowing what kinds of galaxies there are. Some of these are so covered in dust we might never had seen them using visible light telescopes. Because of the unprecedented large area we have with this Herschel survey, we see a huge variety in the type of objects too, from nearby dusty star forming clouds, to nearby dusty galaxies like Andromeda, to galaxies that shone their infrared light more than 12 billion years ago. We can also use this survey to understand the structure of galaxies in the universe – the so-called cosmic web in a way we’ve never been able to do in the far infrared.”
The images they showed gave all those present a glimpse of the unseen stars and galaxies that have existed over the last 12 billion years of cosmic history. In sum, over half-a-million far-infrared sources have been spotted by the Herschel-ATLAS survey. Many of these sources were galaxies that are nearby and similar to our own, and which are detectable using using conventional telescopes.
The others were much more distant, their light taking billions of years to reach us, and were obscured by concentrations of cosmic dust. The most distant of these galaxies were roughly 12 billion light-years away, which means that they appeared as they would have 12 billion years ago.
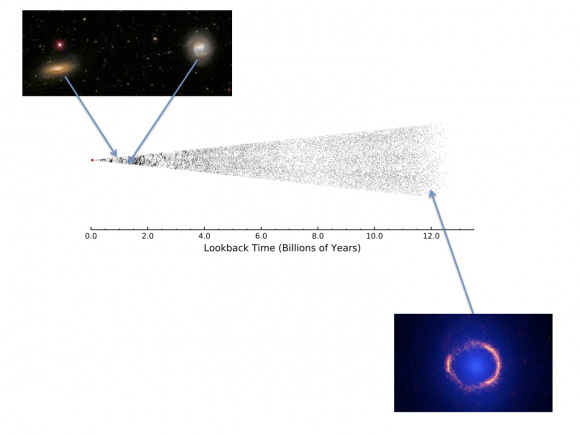
Ergo, astronomers now know that 12 billion years ago (i.e. shortly after the Big Bang)., stars and galaxies were much dustier than they are now. They further concluded that the evolution of our galaxies since shortly after the Big Bang has essentially been a major clean-up effort, as stars gradually absorbed the dust that obscured their light, thus making it the more “visible” place it is today.
The data released by the survey includes several maps and additional files which were described in an article produced by Dr. Elisabetta Valiante and a research team from Cardiff University – titled “The Herschel-ATLAS Data Release 1 Paper I: Maps, Catalogues and Number Counts“. As Dr. Valiante told Universe Today via email:
“Gas and dust are the main components of stars: they collapse to form stars and they are ejected at the end of stars’ life. The interesting thing that has been discovered thanks to the Herschel data is that the two phenomena are not in equilibrium. We knew this was true 10 billion years ago, but we expected, according to the current models, that some equilibrium was reached at more recent times. Instead, the amount of dust in galaxies 5 billion years ago was much larger than the amount we see in galaxies today: this was unexpected.”
Until recently, such a survey would have been impossible due to the fact that many of these infrared sources would have been invisible to astronomers. The reason for this, which was revealed by the survey, was that these galaxies were so dusty that they would have been virtually impossible to detect with conventional optics. What’s more, their light would have been gravitationally magnified by intervening galaxies.

The huge size of the survey has also meant that changes that have occurred in galaxies – relatively recent in cosmic history – can be studied for the first time. For instance, the survey showed that even only one billion years in the past, a small fraction of the age of the universe, galaxies were forming stars at a faster rate and contained more dust than they do today.
Dr. Nathan Bourne – from the University of Edinburgh – is the lead author of another other paper describing the catalogues. As he told Universe Today via email:
“We can think of galaxies as big recycling machines. When they form, they accrete gas (mostly hydrogen and helium, with traces of lithium and a couple of other elements) from the universe around them, and they turn it into stars. As time goes on, the stars pump this gas back out into the galaxy, into the interstellar medium. Due to the nuclear processes within the stars, the gas is now enriched by heavy elements (what we call metals, though they include both metals and non-metals), and some of these form microscopic solid particles of dust, as a sort of by-product.
“But there are still stars forming, and the next generations of stars recycle this interstellar material, and now that it contains heavy elements and dust, things are a bit different, and planets can also form around the new stars, from accumulations of this heavy material. So, if you look at the big picture, when the first galaxies started forming within the first billion years after the Big Bang, they began using up the gas around them, and then while they are active they fill their interstellar medium up with gas and dust, but by the end of a galaxy’s lifecycle, it has used up all this gas and dust, and you could say that it has cleaned itself.”
The catalogues and maps of the hidden universe are a triumph for the Herschel team. Despite the fact that the last information obtained by the Herschel observatory was back in 2013, the maps and catalogues produced from its years of service have become vital to astronomers. In addition to showing the Universe’s hidden energy, they are also laying the groundwork for future research.
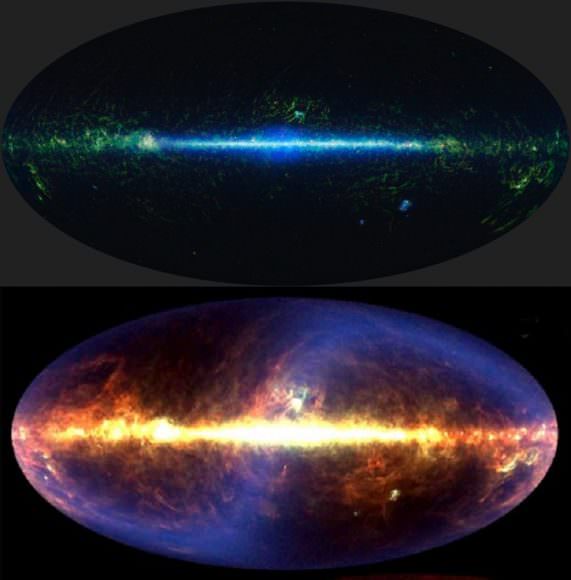

“Now we need to explain why there is dust where we did not expect to find it.” said Valiante. “And to explain this, we need to change our theories about how the Universe evolves. Our data poses a challenge we have accepted, but we haven’t overcome it yet!”
“[W]e understand a lot more about how galaxies evolve,” added Bourne, “about when most of the stars formed, what happens to the gas and dust as galaxies evolve, and how rapidly the star-forming activity in the Universe as a whole has faded in the latter half of the Universe’s history. It’s fair to say that this understanding comes from having a whole suite of different types of instruments studying different aspects of galaxies in complementary ways, but Herschel has certainly contributed a major part of that effort and will have a lasting legacy.”
Ensuring Herschel’s lasting legacy is one of the main aims of the Herschel Extragalactic Project (HELP) program, which is overseen by the EU Research Executive Agency. Other projects they oversee include the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES), which also released survey data late last month. All of this has left a lasting mark on the field of astronomy, despite the fact that Herschel is no longer in operation. As Professor Gomez said of the Herschel Observatory’s enduring contributions:
“The Herschel Space Observatory stopped taking data in 2013, yet our understanding of the dusty universe is really only just starting with the release of large surveys and galaxy catalogues in recent months. Ultimately, once astronomers have gone through all the valuable data, Herschel will have provided a view of the infrared universe covering 1000 square degrees of the sky.”
The implications of these findings are also likely to have a far-reaching effect, ranging from cosmology and astronomy, to perhaps shedding some light on that tricky Fermi paradox. Could it be intelligent life that emerged billions of years ago didn’t venture to other star systems because they couldn’t see them? Just a thought…
Further Reading: Royal Astronomical Society, ESA