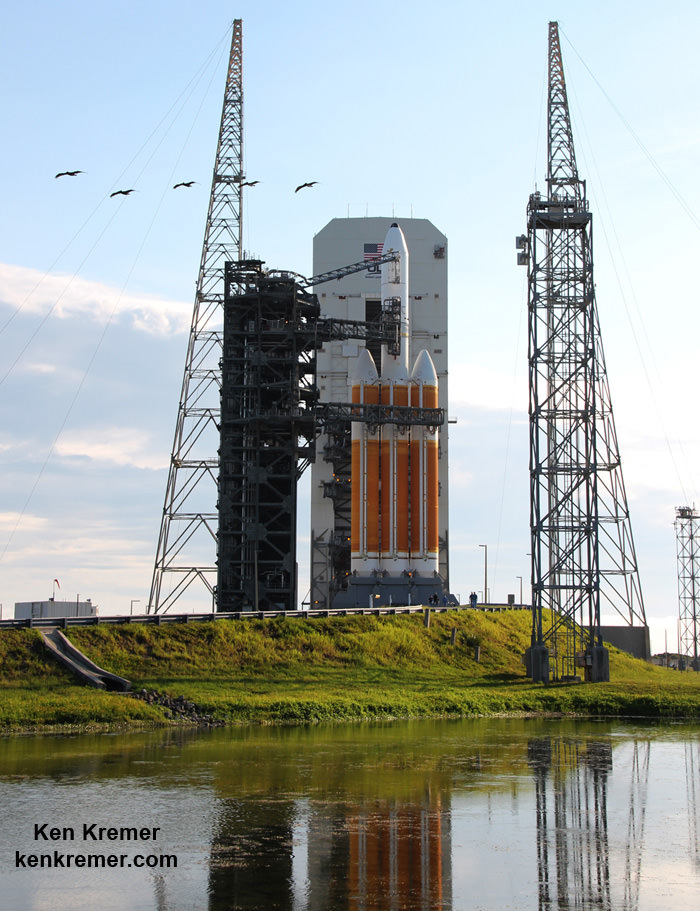
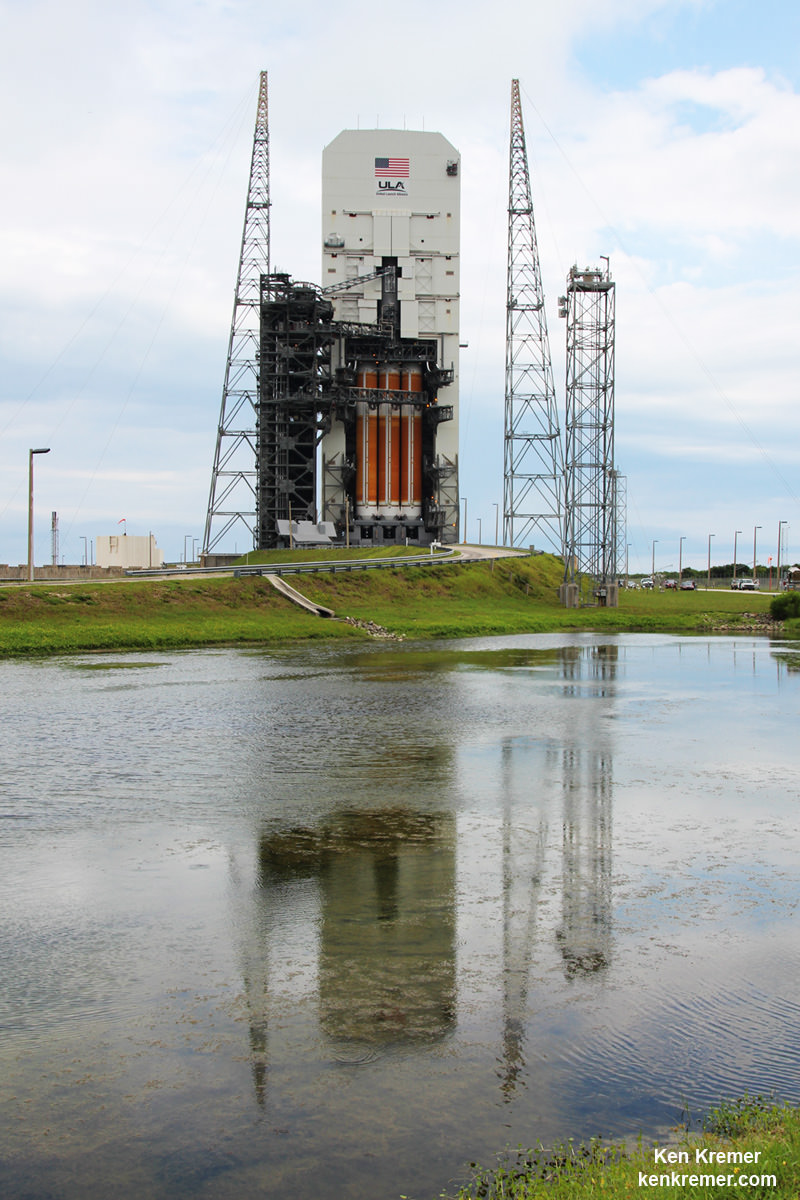
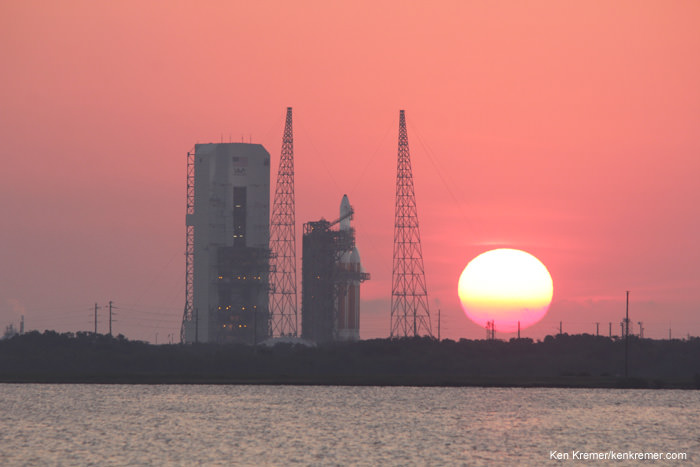
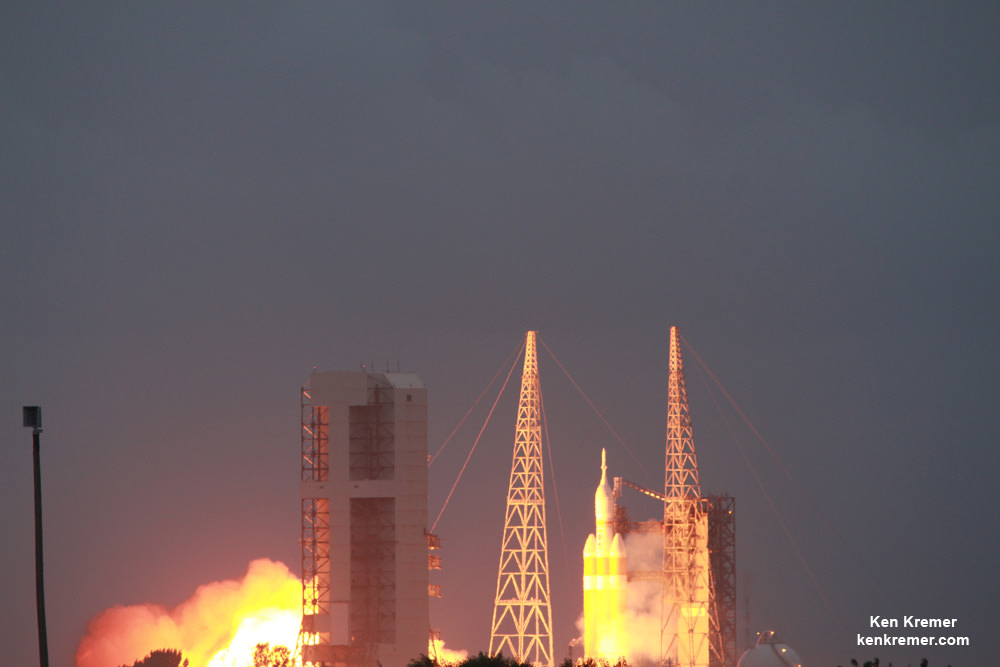
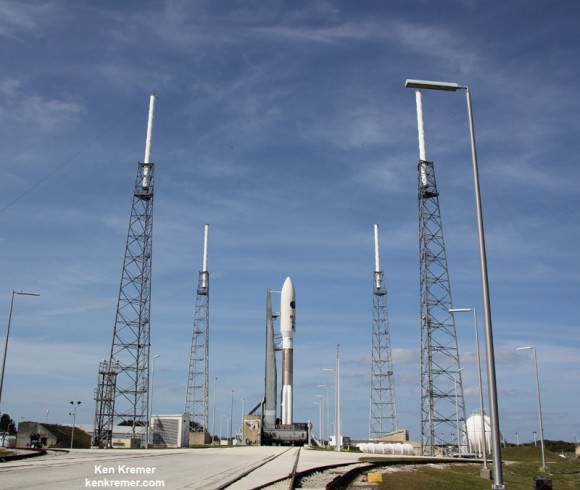
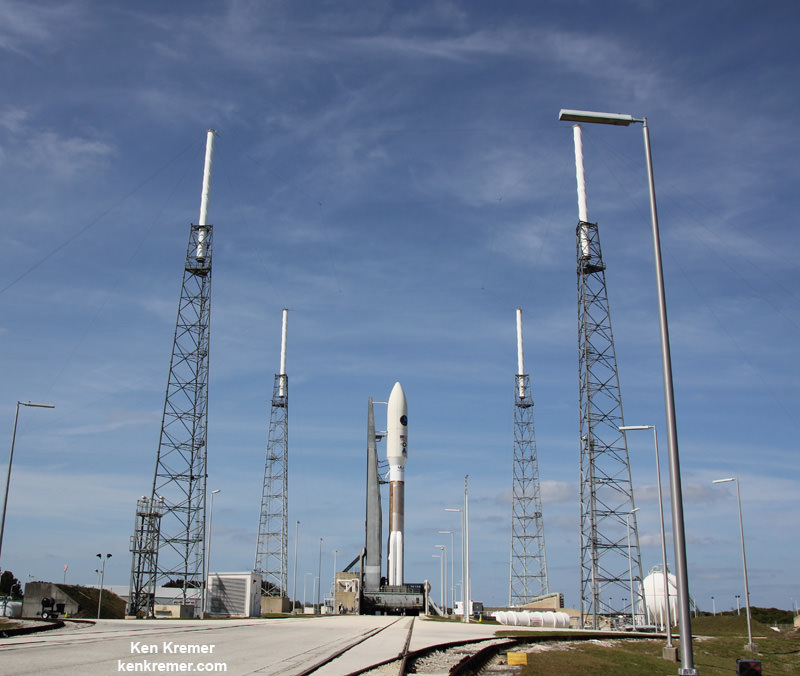
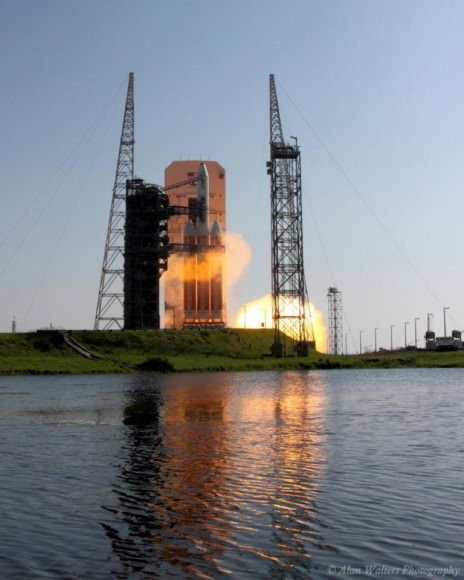
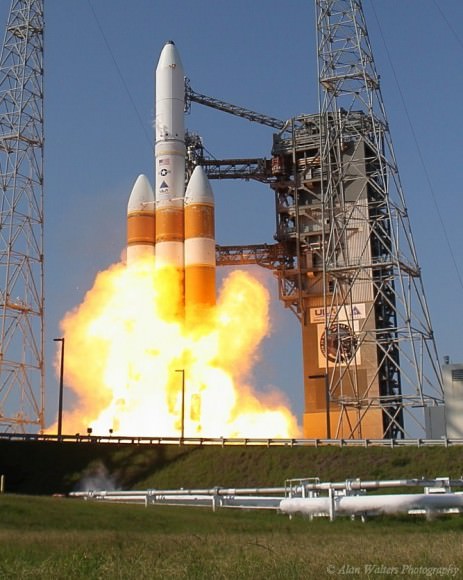
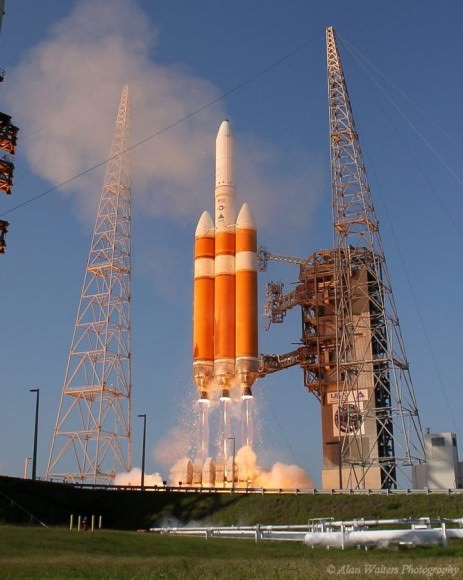
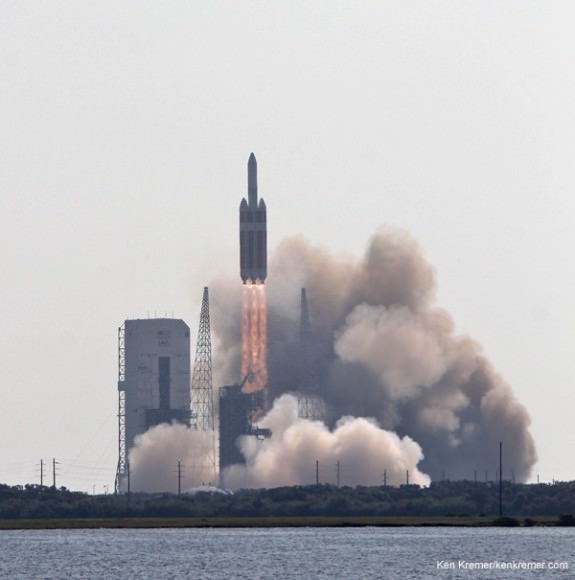
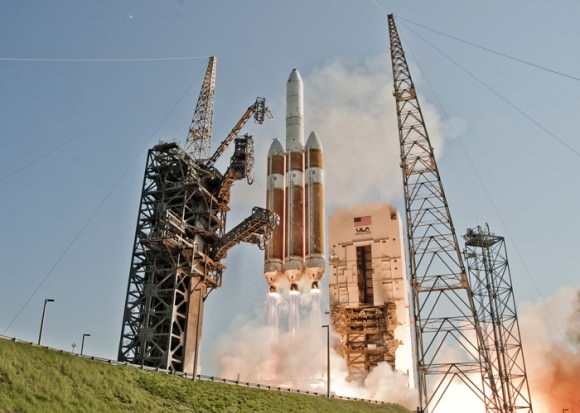
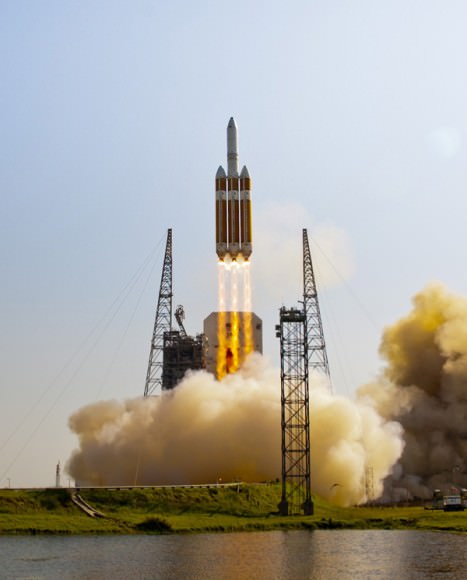
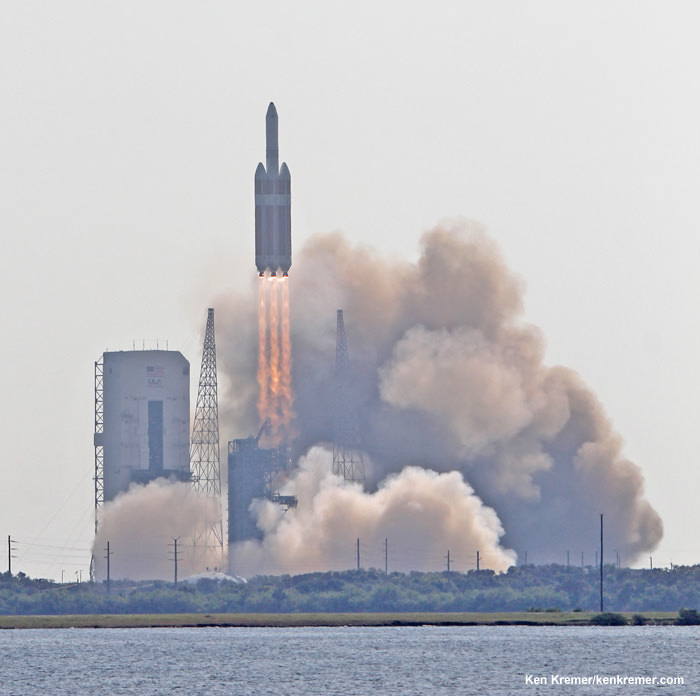
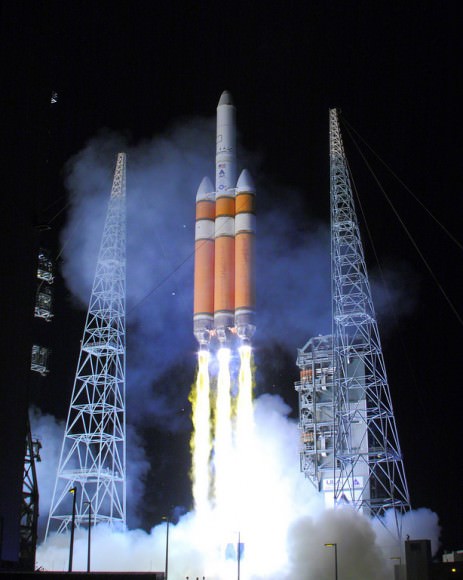
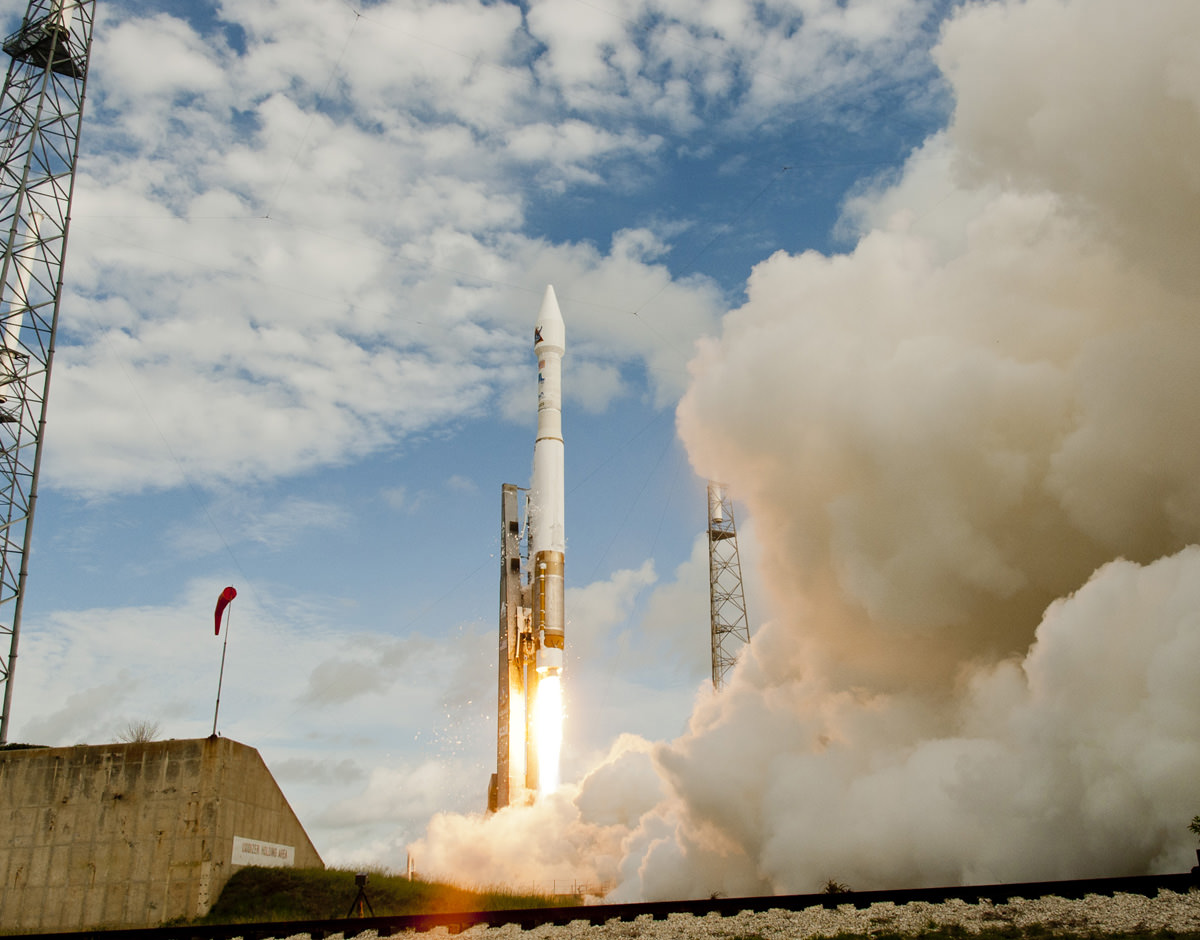
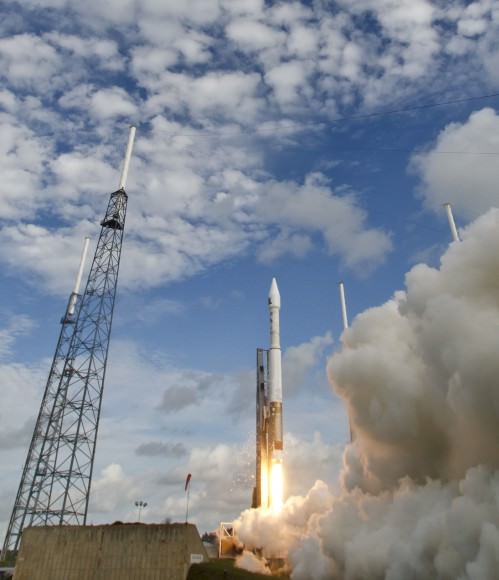
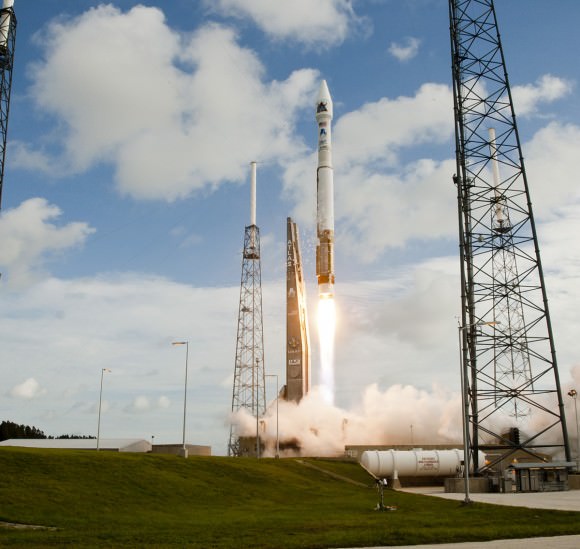
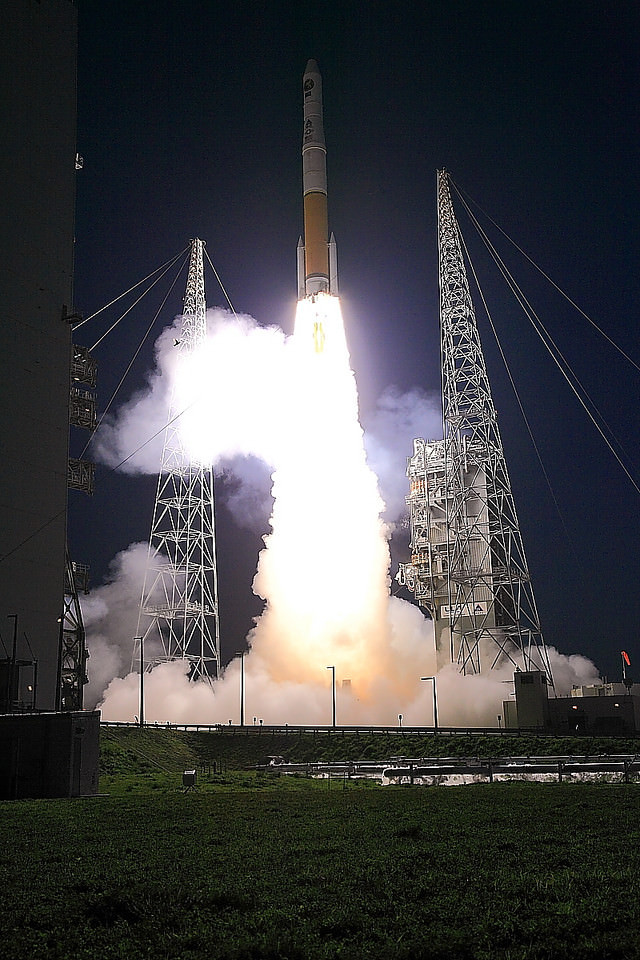
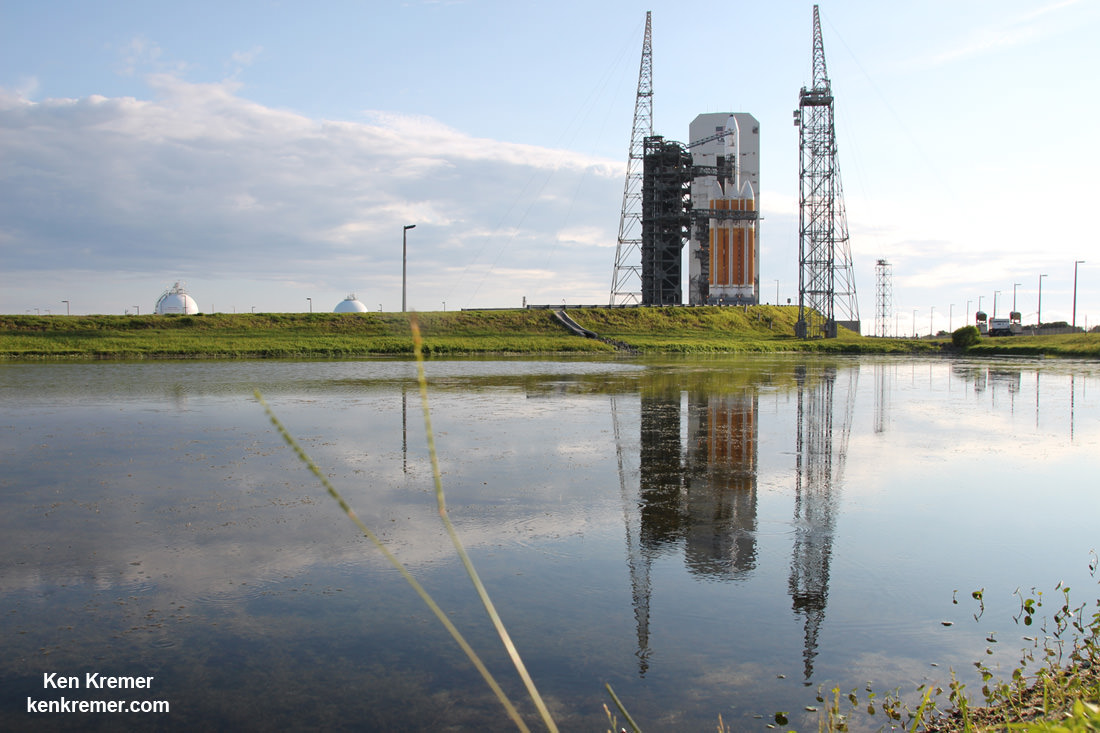
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL — The world’s largest rocket was ready to rumble with a secret spy satellite for the NRO until Thursday’s stormy weather across the so-called ‘sunshine state’ postponed the engines roar by 48 hours to Saturday, June 11.
After a forlorn four hour wait in hopes of a parting of the gloomy gray rainy skies around the Florida Space Coast, launch officials with rocker maker United Launch Alliance (ULA) threw in the towel at 6 p.m. EDT and kept the triple barreled Delta 4 Heavy rocket and its over $1.5 Billion clandestine cargo critical to national defense prudently grounded for a better day.
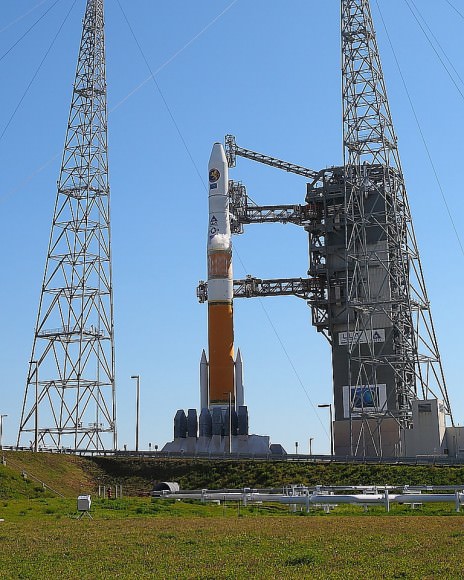
An early afternoon blastoff of the classified NROL-37 spy satellite for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) atop the powerful ULA Delta IV Heavy rocket is now slated for 1:51 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 37 (SLC-37) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Saturday, June 11.

In an unusual move, the launch time of America’s newest spy satellite on America’s most powerful rocket had been announced in advance of Thursday’s plans by ULA. Liftoff of the NROL-37 surveillance satellite had been slated for 1:59 p.m. June 9. Saturdays launch time has moved up 8 minutes.
The good news is you can watch the now weekend launch live via a ULA broadcast which starts 20 minutes prior to the given launch time at 1:31 p.m. EDT June 11.
Webcast link: http://bit.ly/div_nrol37
Or – if you are free and mobile – you can watch this truly impressive feat with your own eyes as a rarely afforded treat – by making your way to the many excellent viewing locations surrounding Cape Canaveral.
Since this is a national security launch, the exact launch time and launch window are both actually classified. So the liftoff could easily occur later than 1:51 p.m. EDT Saturday.
Although the announced ‘launch period’ on Thursday extended until 6:30 p.m. EDT (2230 GMT), the actual launch window was also classified and fell somewhere within that lengthy launch period.
Due to Thursday’s weather scrub at 6 p.m. , we can now probably conclude that the actual launch window for NROL-37 lasts about 4 hours. So Saturday’s full launch window should run until shortly before 6 p.m. EDT.
Unfortunately the weather outlook has deteriorated from earlier indications and may be as trying as Thursday’s launch attempt.
The official Air Forces prognosis calls for only a 40% chance of favorable weather conditions on June 11.
The primary concerns are for Anvil Clouds, Cumulus Clouds and Lightning – quite similar to those on June 9.
“The trough that lingered in the area all week and caused multiple weather Launch Commit Criteria violations yesterday will continue to plague the area today.
Meteorological models are now showing the boundary still lingering in the area Saturday, and an upper-level short wave will also move through during the launch window,” according to the official Air Force forecast for June 11.
“Showers and thunderstorms are still likely along the trough. Also, anvils from inland thunderstorms will migrate toward the Space Coast.”
In case of a scrub for any reason related to technical or weather issues, ULA has NOT announced the next launch opportunity, a ULA spokesperson told Universe Today.
The Air Force did say that the weather odds rise significantly to an 80% chance of favorable weather conditions in case of a potential 48 hour scrub turnaround for potential on Monday, June 13.
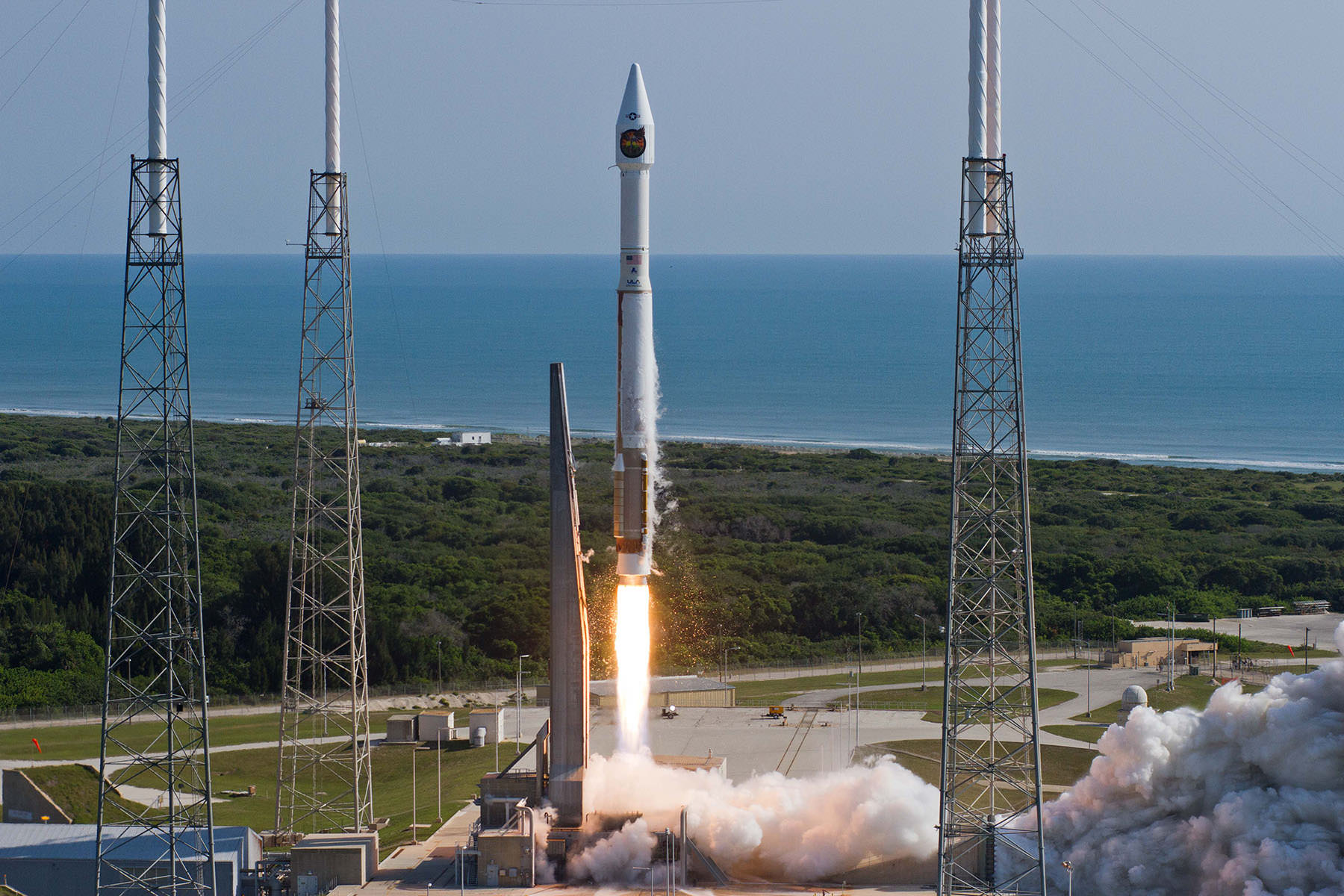
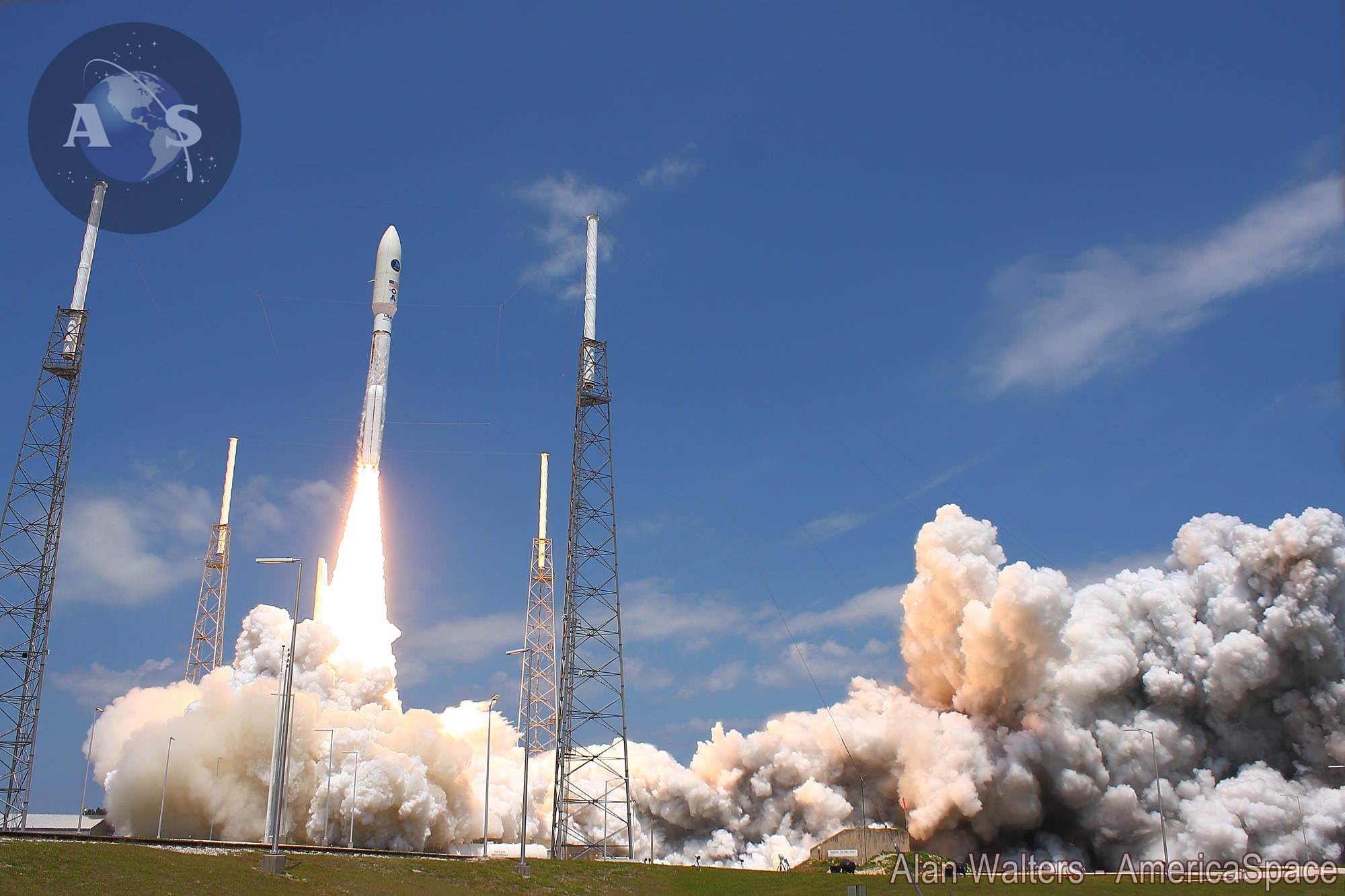
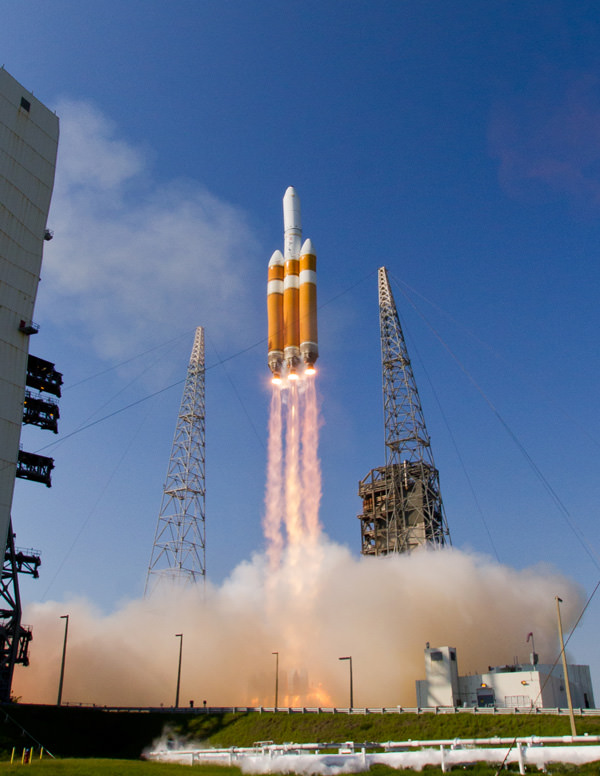
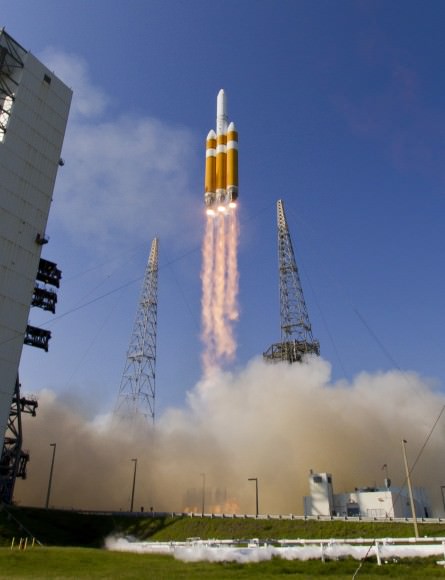
Whenever the 24 story tall rocket soars skyward it will put on a spectacular sky show.
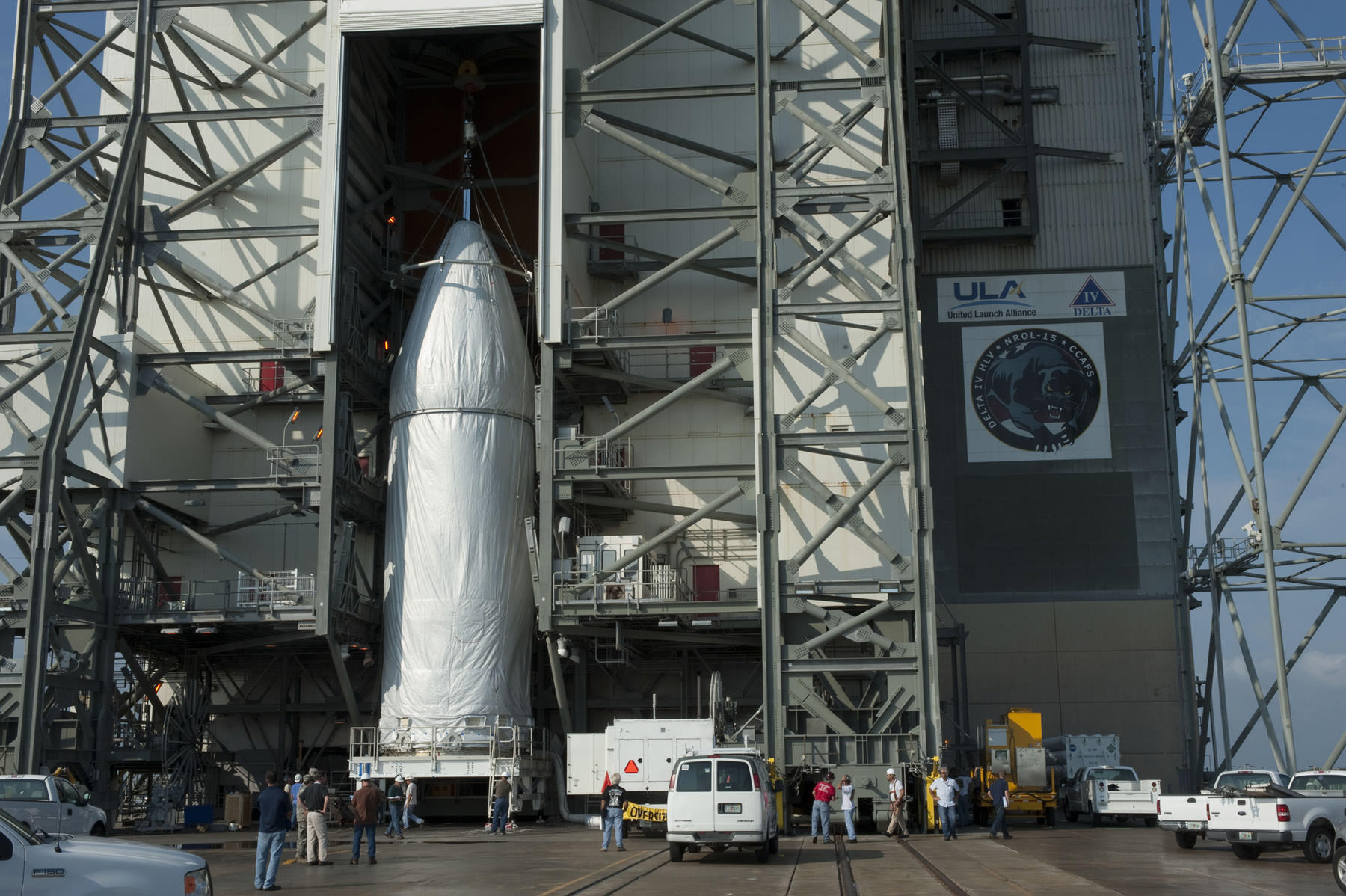
Virtually nothing is known about the clandestine payload, since its mission, purpose and goals are classified top secret – but it is absolutely vital to America’s national security.
The 235-foot-tall rocket will likely launch the classified NROL-37 surveillance satellite into a geosynchronous orbit and an altitude of 22,300 miles.
NROL-37 is being launched for the NRO on an intelligence gathering mission in support of US national defense.
The possible roles for the reconnaissance payload include signals intelligence, eavesdropping, imaging and spectroscopic observations, early missile warnings and much more.
Reports indicate it may be one of the largest satellites ever launched, weigh some 17,000 pounds and may deploy an antenna over 300 feet wide for eavesdropping purposes.
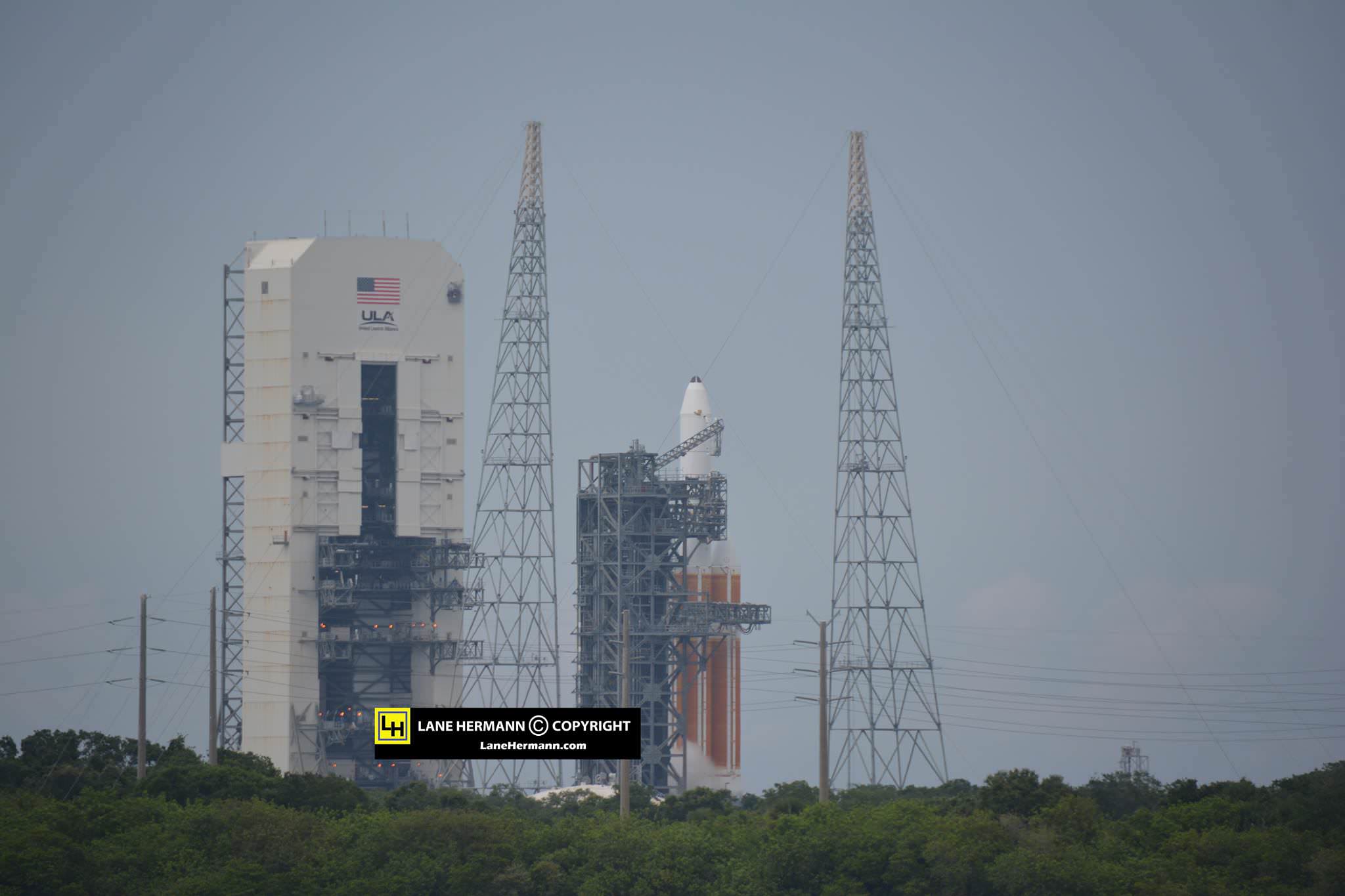

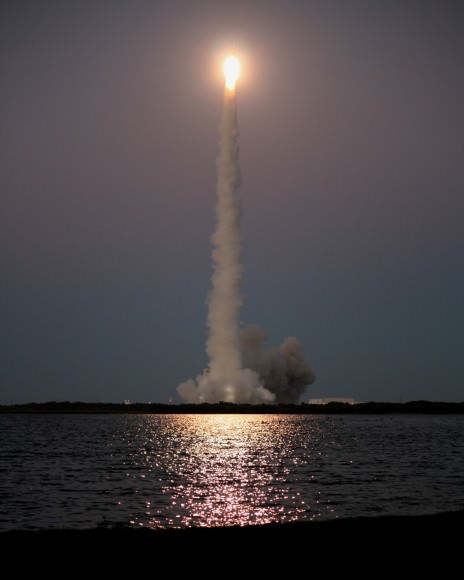
Seeing a Delta 4 Heavy soar to space is a rare treat since they launch infrequently.
The last of these to launch from the Cape was for NASA’s inaugural test flight of the Orion crew capsule on the EFT-1 launch in Dec. 5, 2014. No other rocket was powerful enough.
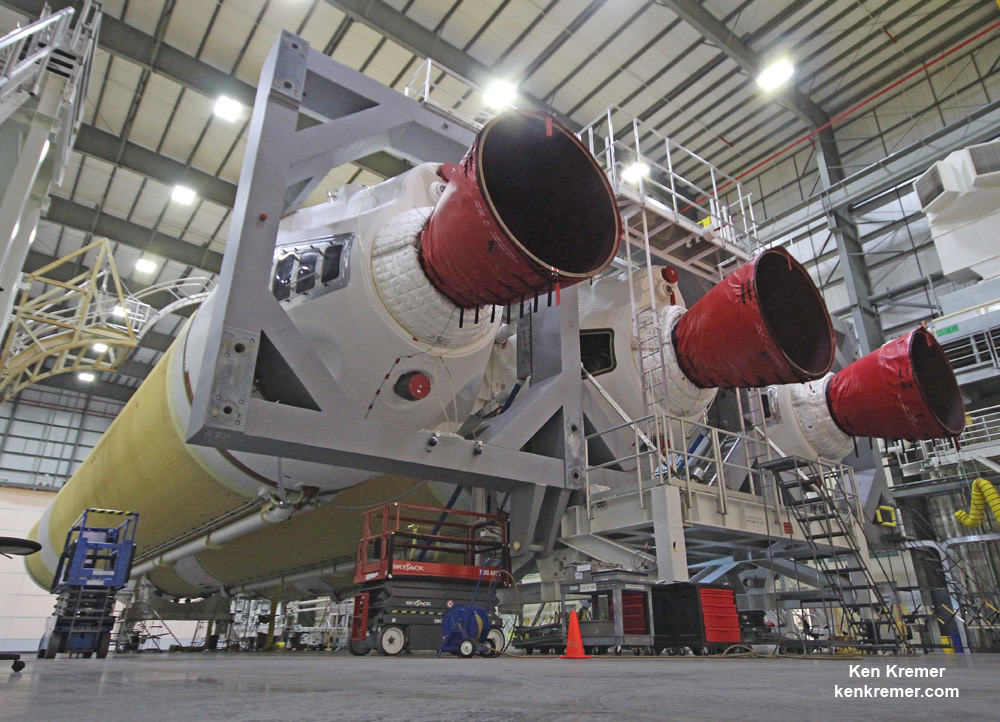
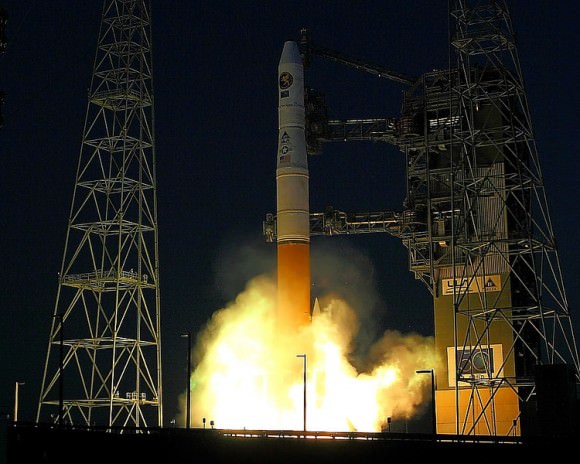
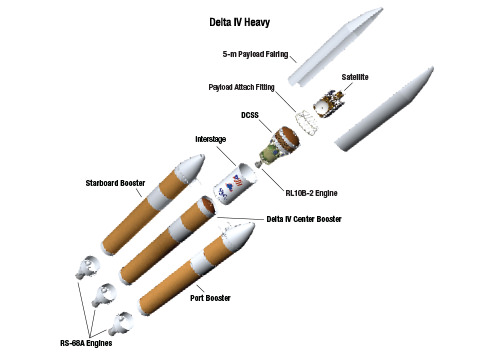
The Delta IV Heavy employs three Common Core Boosters (CBCs). Two serve as strap-on liquid rocket boosters (LRBs) to augment the first-stage CBC and 5-m-diameter payload fairing housing the payload.
Each first stage CBC is powered by an upgraded RS-68 engine, which generates a combined 2.1 million pounds of thrust fueled by cryogenic liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen.
Watch this up close video tour of the Delta 4 Heavy on pad 37 after retraction of the Mobile Service Structure from my space friends at USLaunchReport.
Video Caption: ULA is launching the 2.1 million lbs thrust “Heavy” on June 11, 2016 from Pad 37 on CCAFS. Credit: USLaunchReport
The NRO was formed in response to the Soviet launch of Sputnik and secretly created on September 6, 1961.
“The purpose is overseeing all satellite and overflight reconnaissance projects whether overt or covert. The existence of the organization is no longer classified today, but we’re still pressing to perform the functions necessary to keep American citizens safe,” according to the official NRO website.

Watch for Ken’s continuing on site reports direct from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and the SpaceX launch pad.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Orbital ATK Cygnus, ISS, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
June 10/11: “ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SpaceX, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings