Dark energy is central to our modern theory of cosmology. We know the universe is expanding at an ever-increasing rate, and the clearest explanation is that some kind of energy is driving it. Since this energy doesn’t emit light, we call it dark energy. But simply giving dark energy a name doesn’t mean we fully understand it. We can see what dark energy does, but its fundamental nature is perhaps the biggest scientific mystery we have.
Continue reading “Neutron Stars Could be the Best way to Measure Dark Energy”Twin Stars Prove Einstein at Least 99.99% Right
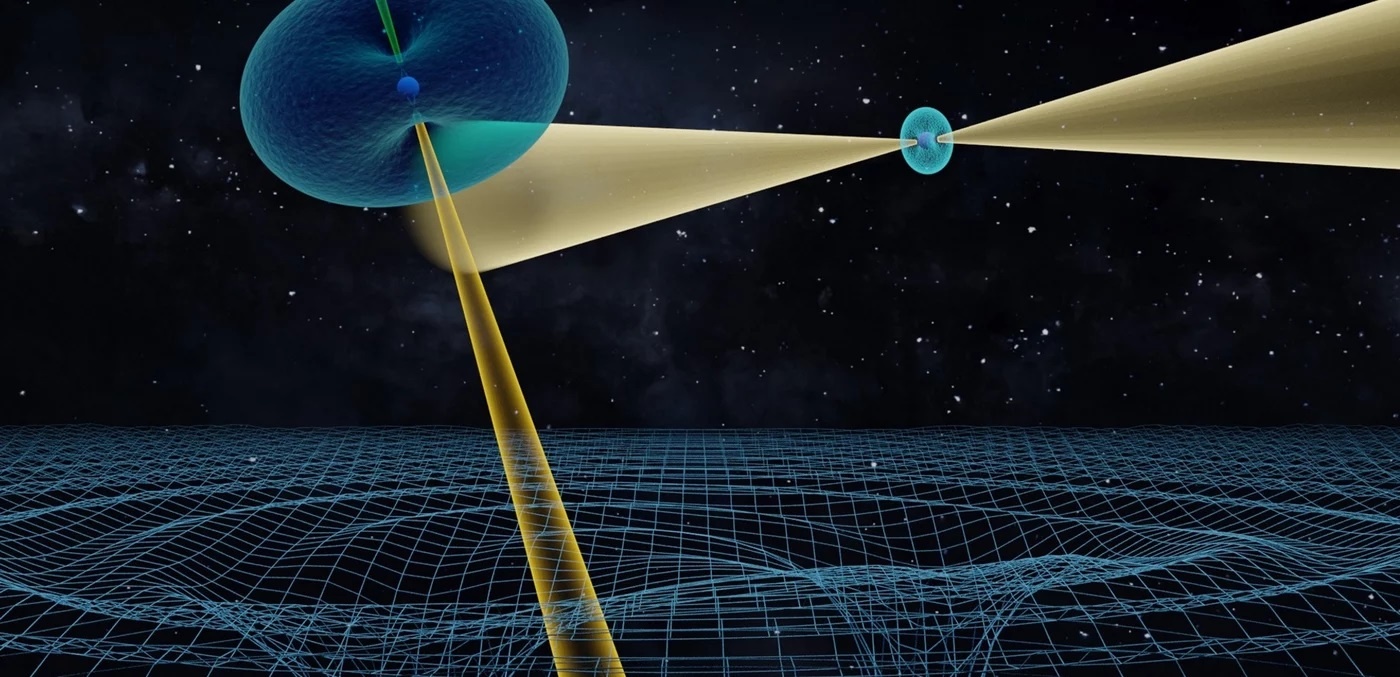

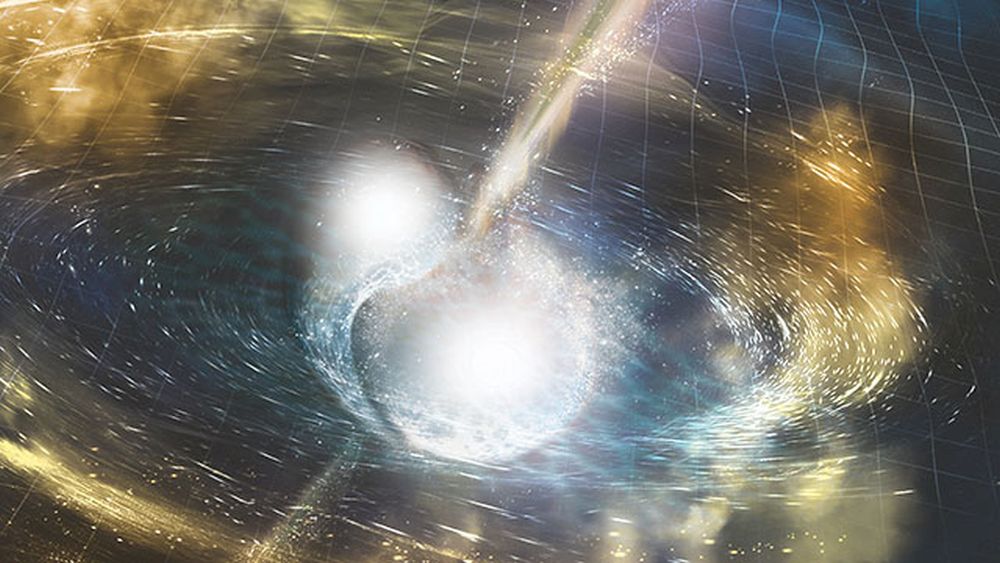
More than a hundred years have passed since Einstein formalized his theory of General Relativity (GR), the geometric theory of gravitation that revolutionized our understanding of the Universe. And yet, astronomers are still subjecting it to rigorous tests, hoping to find deviations from this established theory. The reason is simple: any indication of physics beyond GR would open new windows onto the Universe and help resolve some of the deepest mysteries about the cosmos.
One of the most rigorous tests ever was recently conducted by an international team of astronomers led by Michael Kramer of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfR) in Bonn, Germany. Using seven radio telescopes from across the world, Kramer and his colleagues observed a unique pair of pulsars for 16 years. In the process, they observed effects predicted by GR for the first time, and with an accuracy of at least 99.99%!
Continue reading “Twin Stars Prove Einstein at Least 99.99% Right”NASA Launches a New X-ray Observatory
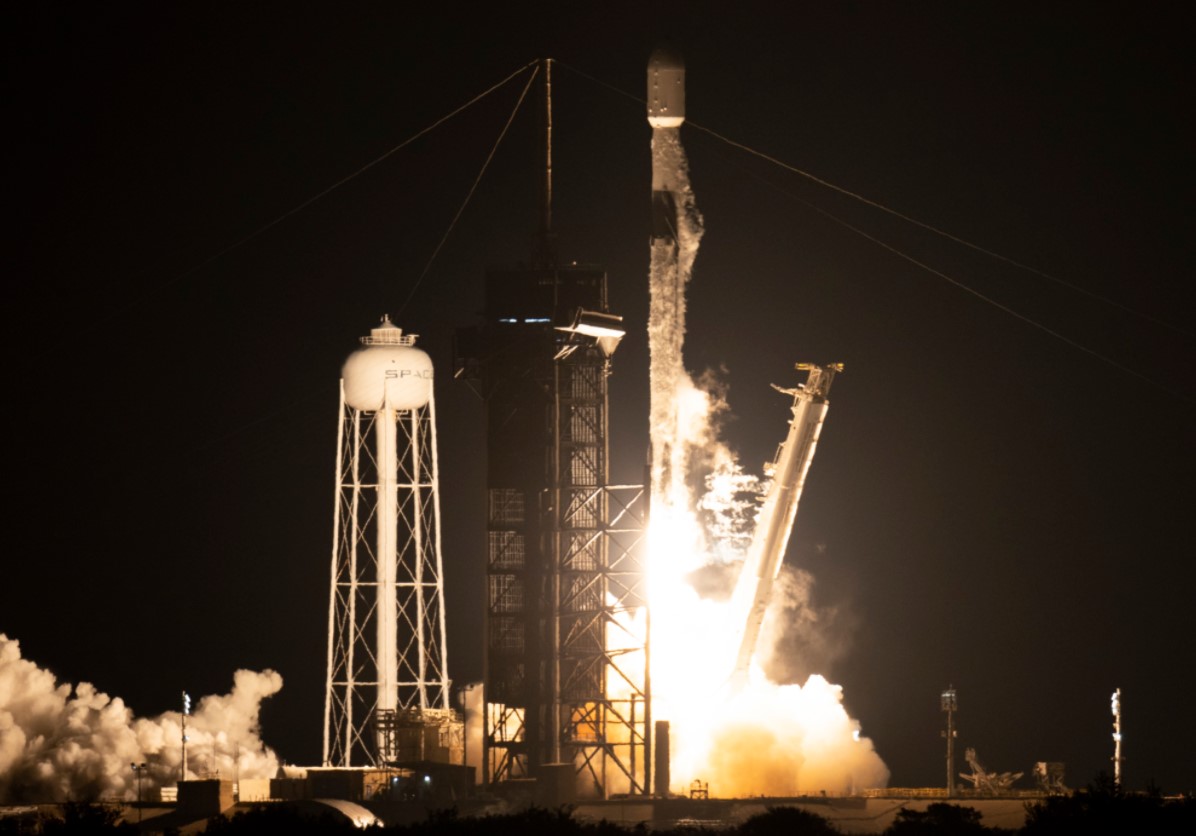

A new mission has launched to study some the most intriguing secrets of the universe. No, not THAT spacecraft (JWST is scheduled for launch on December 22). Another new and exciting mission is called Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) and it will allow scientists to explore the hidden details of some of the most extreme and high-energy objects in the cosmos, such as black holes, neutron stars, pulsars and dozens of other objects.
Continue reading “NASA Launches a New X-ray Observatory”Neutron Stars Have Mountains, They’re Just a Fraction of a Millimeter High
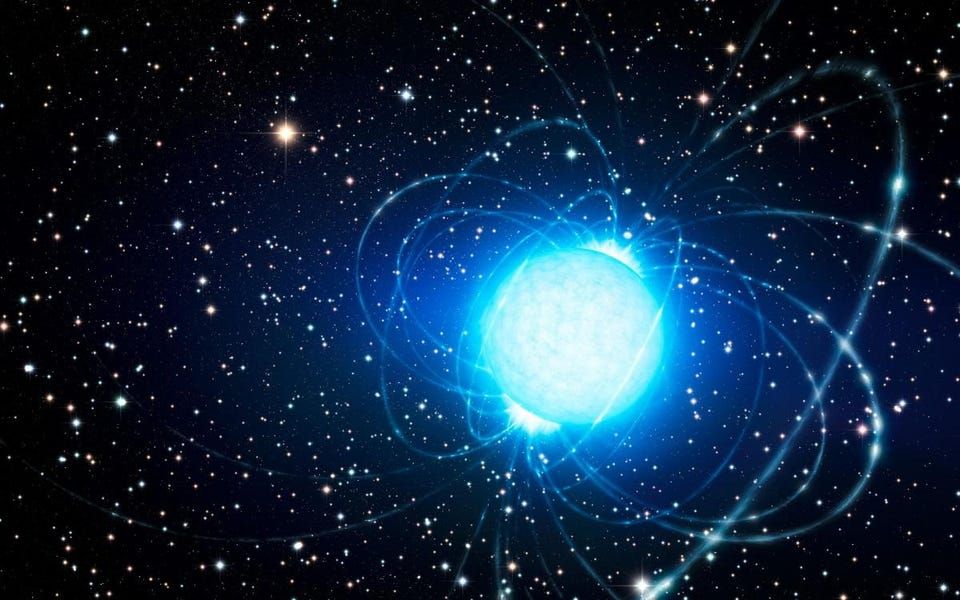
The universe has some very extreme places in it – and there are few places more extreme than the surface of a neutron star. These ultradense objects form after a supergiant star collapses into a sphere about 10 kilometers (6 miles) in diameter. Their surface is extreme because of the gravity, which is about a billion times stronger than Earth. However, that gravity also forces the stellar remnant to be extraordinarily flat. Just how flat is the outcome of a new set of theoretical research by PhD student Fabian Gittins from the University of Southampton.
Continue reading “Neutron Stars Have Mountains, They’re Just a Fraction of a Millimeter High”A Nearby White Dwarf Might be About to Collapse Into a Neutron Star
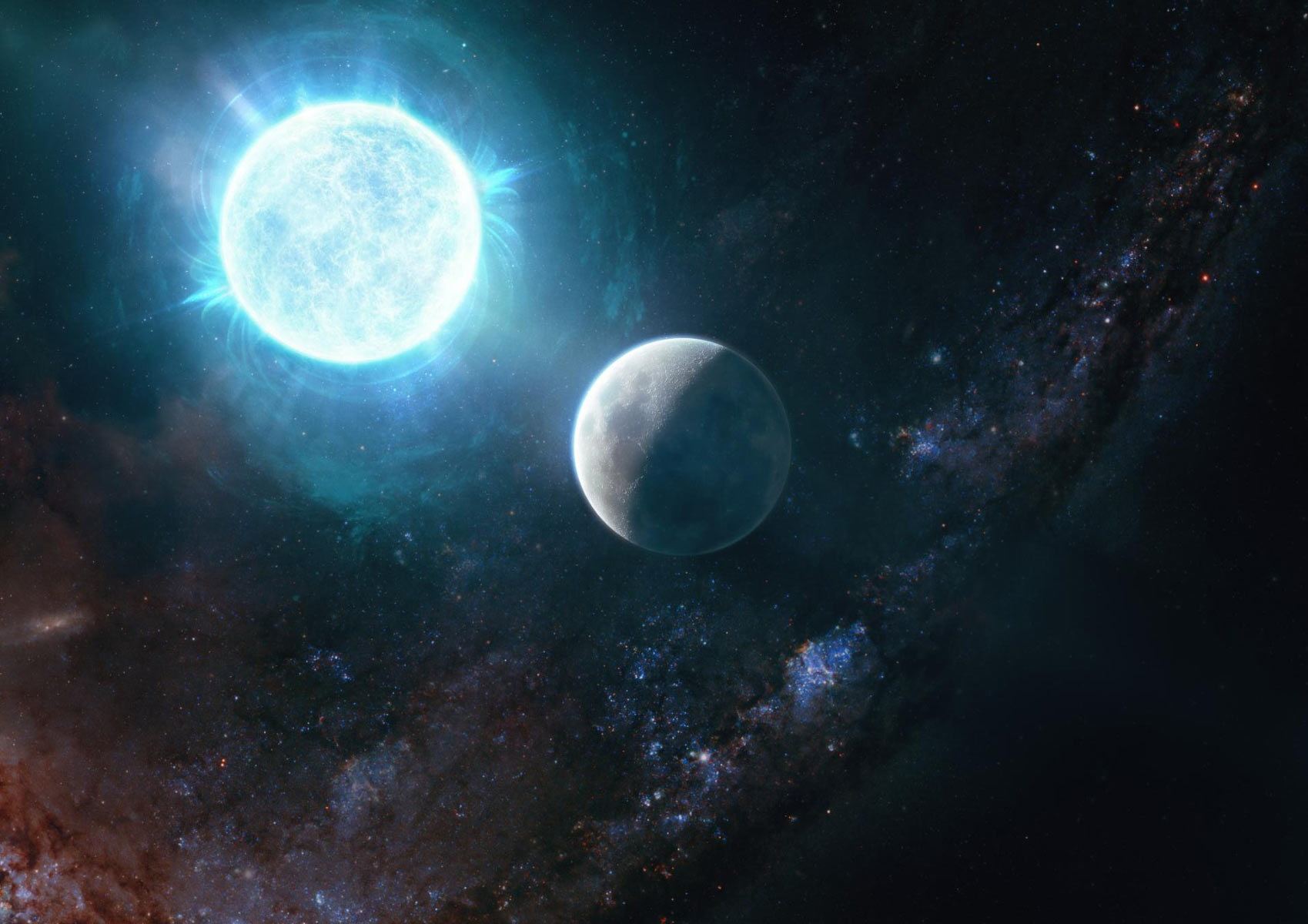
About 97% of all stars in our Universe are destined to end their lives as white dwarf stars, which represents the final stage in their evolution. Like neutron stars, white dwarfs form after stars have exhausted their nuclear fuel and undergo gravitational collapse, shedding their outer layers to become super-compact stellar remnants. This will be the fate of our Sun billions of years from now, which will swell up to become a red giant before losing its outer layers.
Unlike neutron stars, which result from more massive stars, white dwarfs were once about eight times the mass of our Sun or lighter. For scientists, the density and gravitational force of these objects is an opportunity to study the laws of physics under some of the most extreme conditions imaginable. According to new research led by researchers from Caltech, one such object has been found that is both the smallest and most massive white dwarf ever seen.
Continue reading “A Nearby White Dwarf Might be About to Collapse Into a Neutron Star”Astronomers Detected a Black Hole-Neutron Star Merger, and Then Another Just 10 Days Later
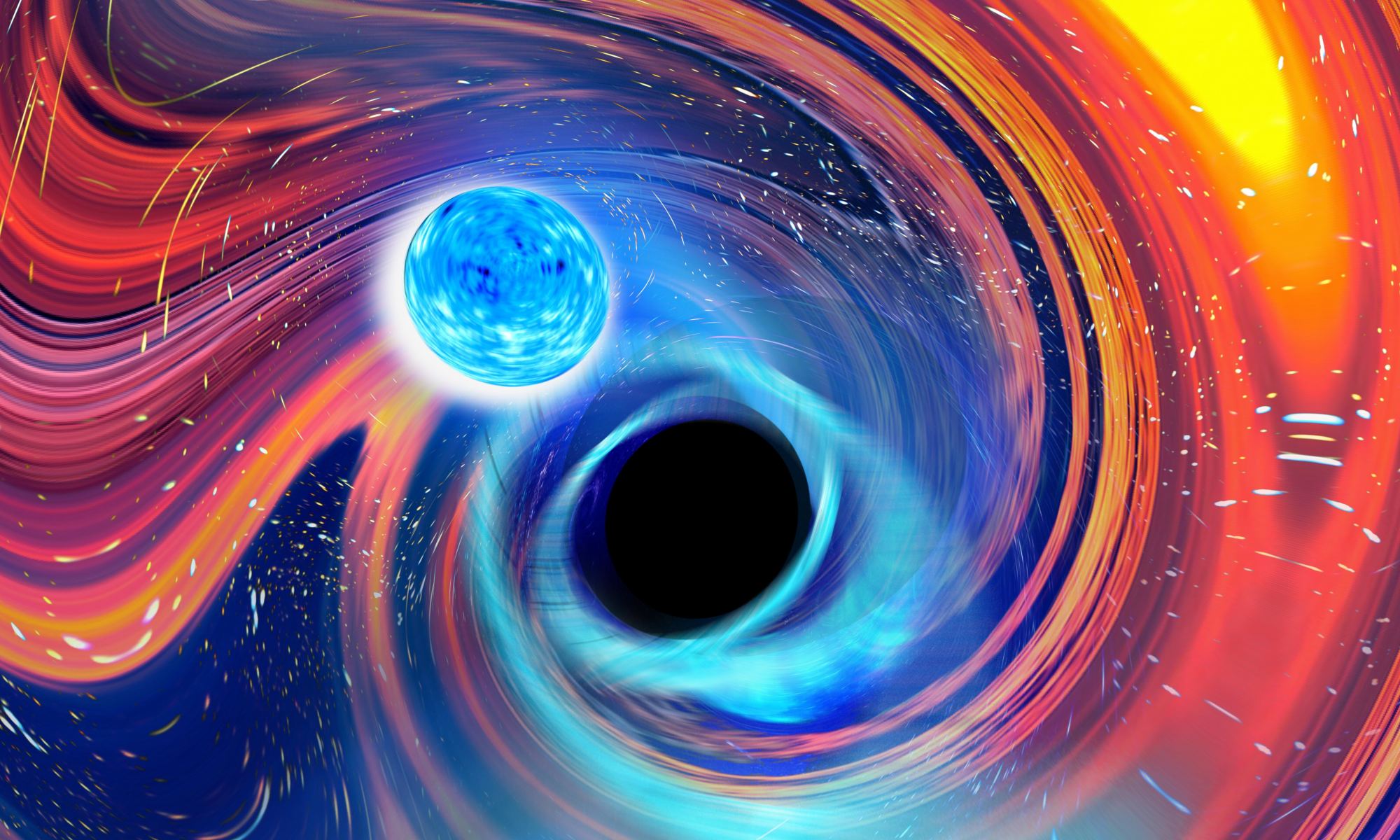

The interior of a neutron star is perhaps the strangest state of matter in the universe. The material is squeezed so tightly that atoms collapse into a sea of nuclear material. We still aren’t sure whether nucleons maintain their integrity in this state, or whether they dissolve into quark matter. To really understand neutron star matter we need to pull it apart to see how it works and to do that takes a black hole. This is why astronomers are excited about the recent discovery of not one, but two mergers between a neutron star and a black hole.
Continue reading “Astronomers Detected a Black Hole-Neutron Star Merger, and Then Another Just 10 Days Later”How Squeezable are Neutron Stars?
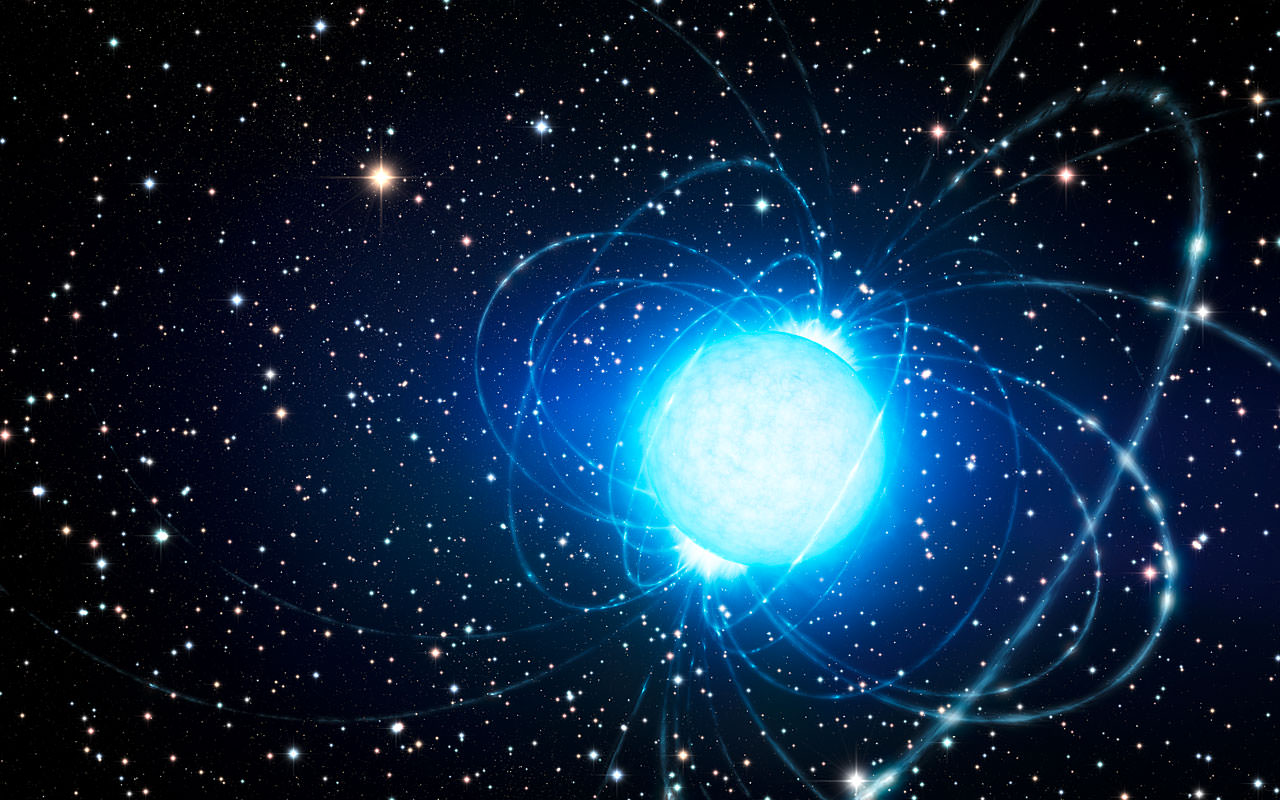

Two neutron stars. One is 50% more massive than the other, yet they are almost exactly the same size. The results have big implications for understanding what neutron stars are really made of.
Continue reading “How Squeezable are Neutron Stars?”Black Hole-Neutron Star Collisions Could Finally Settle the Different Measurements Over the Expansion Rate of the Universe
If you’ve been following developments in astronomy over the last few years, you may have heard about the so-called “crisis in cosmology,” which has astronomers wondering whether there might be something wrong with our current understanding of the Universe. This crisis revolves around the rate at which the Universe expands: measurements of the expansion rate in the present Universe don’t line up with measurements of the expansion rate during the early Universe. With no indication for why these measurements might disagree, astronomers are at a loss to explain the disparity.
The first step in solving this mystery is to try out new methods of measuring the expansion rate. In a paper published last week, researchers at University College London (UCL) suggested that we might be able to create a new, independent measure of the expansion rate of the Universe by observing black hole-neutron star collisions.
Continue reading “Black Hole-Neutron Star Collisions Could Finally Settle the Different Measurements Over the Expansion Rate of the Universe”Smallest, Closest Black Hole Ever Discovered is Only 1,500 Light-Years Away
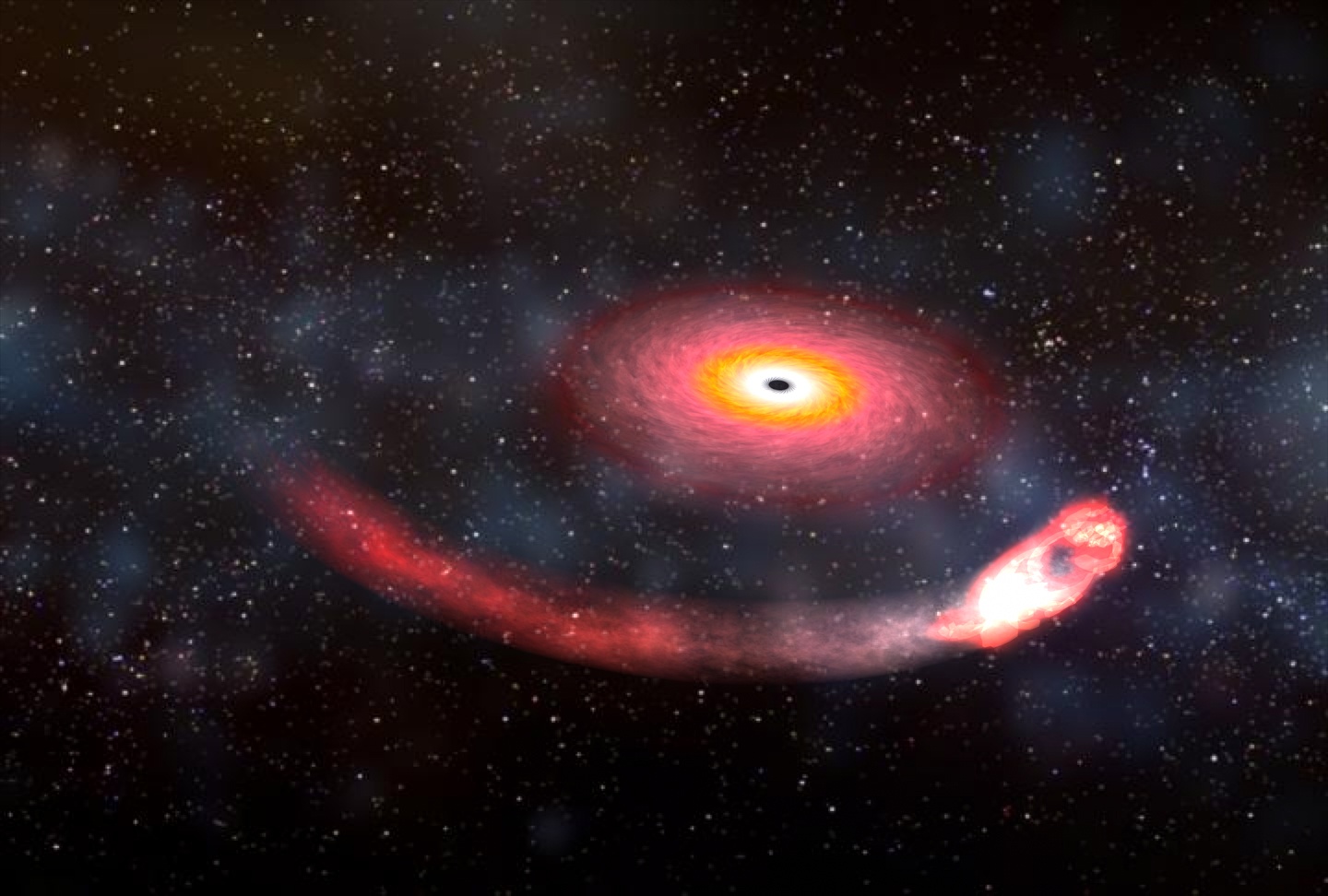
In theory, a black hole is easy to make. Simply take a lump of matter, squeeze it into a sphere with a radius smaller than the Schwarzschild radius, and poof! You have a black hole. In practice, things aren’t so easy. When you squeeze matter, it pushes back, so it takes a star’s worth of weight to squeeze hard enough. Because of this, it’s generally thought that even the smallest black holes must be at least 5 solar masses in size. But a recent study shows the lower bound might be even smaller.
Continue reading “Smallest, Closest Black Hole Ever Discovered is Only 1,500 Light-Years Away”What's the Connection Between Stellar-Mass Black Holes and Dark Matter?
Imagine you are a neutron star. You’re happily floating in space, too old to fuse nuclei in your core anymore, but the quantum pressure of your neutrons and quarks easily keeps you from collapsing under your own weight. You look forward to a long stellar retirement of gradually cooling down. Then one day you are struck by a tiny black hole. This black hole only has the mass of an asteroid, but it causes you to become unstable. Gravity crushes you as the black hole consumes you from the inside out. Before you know it, you’ve become a black hole.
Continue reading “What's the Connection Between Stellar-Mass Black Holes and Dark Matter?”




