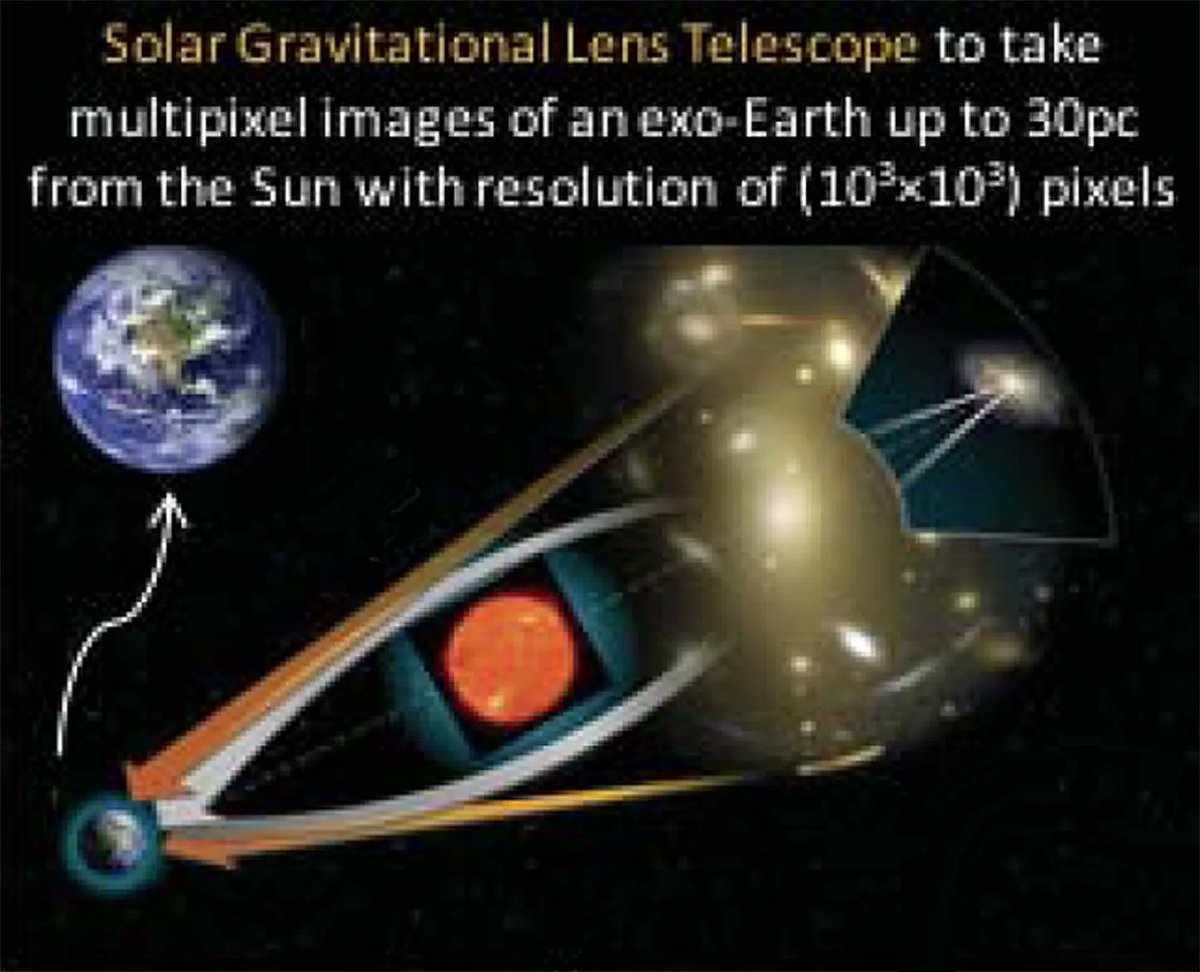
NASA’s Institute for Advanced Concepts is famous for supporting outlandish ideas in the astronomy and space exploration fields. Since being re-established in 2011, the institute has supported a wide variety of projects as part of its three-phase program. However, so far, only three projects have gone on to receive Phase III funding. And one of those just released a white paper describing a mission to get a telescope that could effectively see biosignatures on nearby exoplanets by utilizing the gravitational lens of our own Sun.
Continue reading “A Mission to Reach the Solar Gravitational Lens in 30 Years”A Huge Rotating Kilometer-Scale Space Station Could be Launched From a Single Rocket
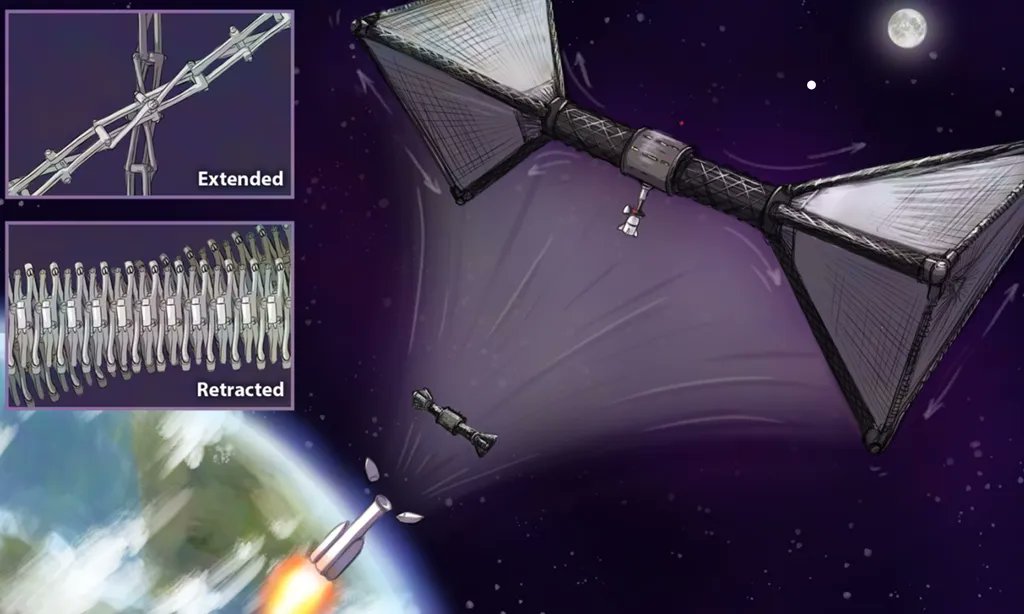
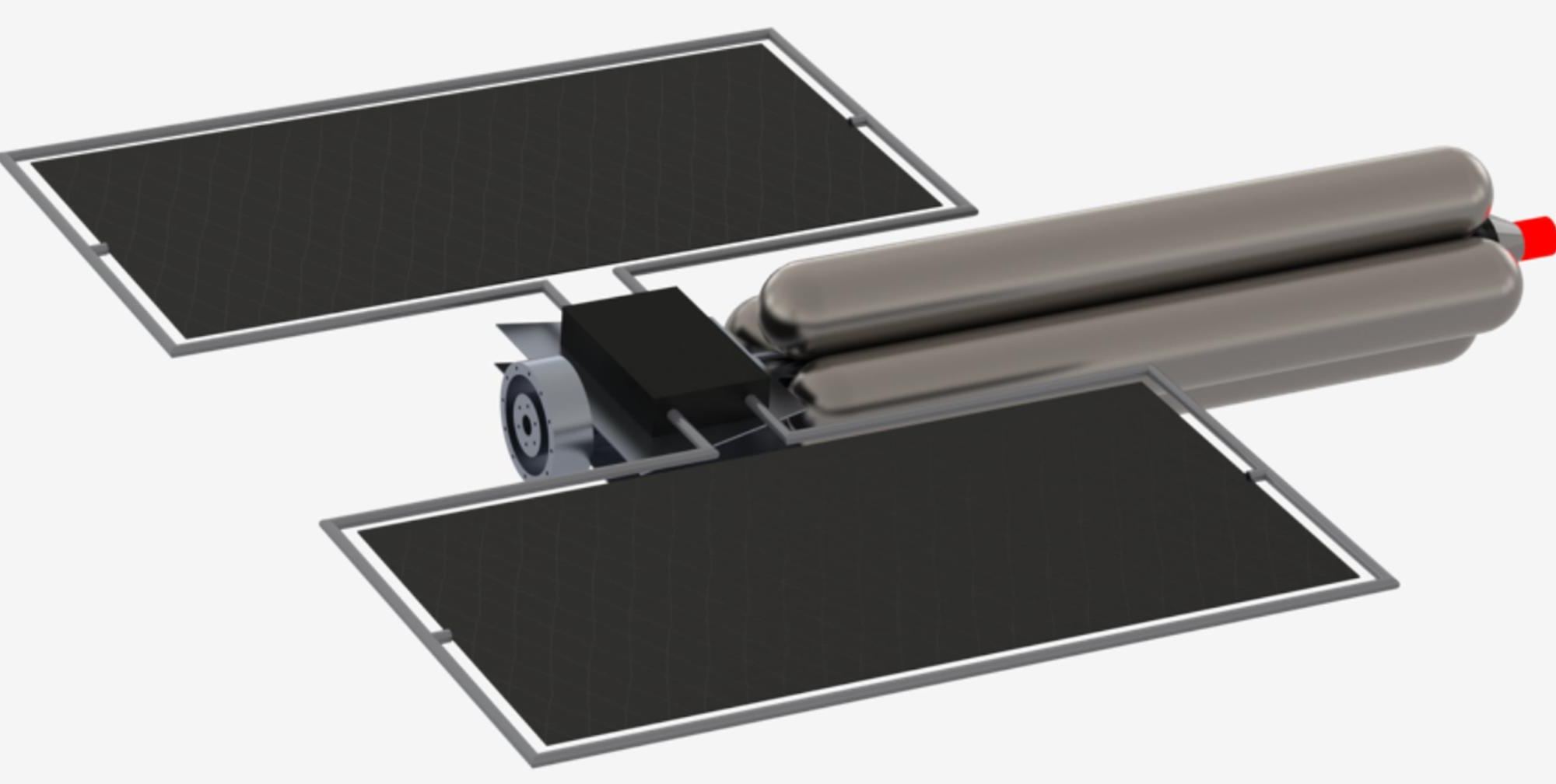
Artificial gravity remains the stuff of science fiction. But dealing with no gravity causes significant problems in many astronauts, ranging from bone deterioration to loss of sight. An alternative method that might eliminate some of these problems is “simulated gravity,” which uses a spinning structure to create centrifugal force that would have the same effect on the body as gravity would. Whether or not this would solve the problems caused by lack of gravity remains to be seen. Still, NASA seems keen on the idea – to the tune of a $600,000 NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Phase II grant to a team from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and the University of Washington (UW) who is looking to develop a structure that can simulate full Earth gravity and be launched in a single rocket.
Continue reading “A Huge Rotating Kilometer-Scale Space Station Could be Launched From a Single Rocket”The Best way to Leave the Solar System Might be to fly Uncomfortably Close to the Sun
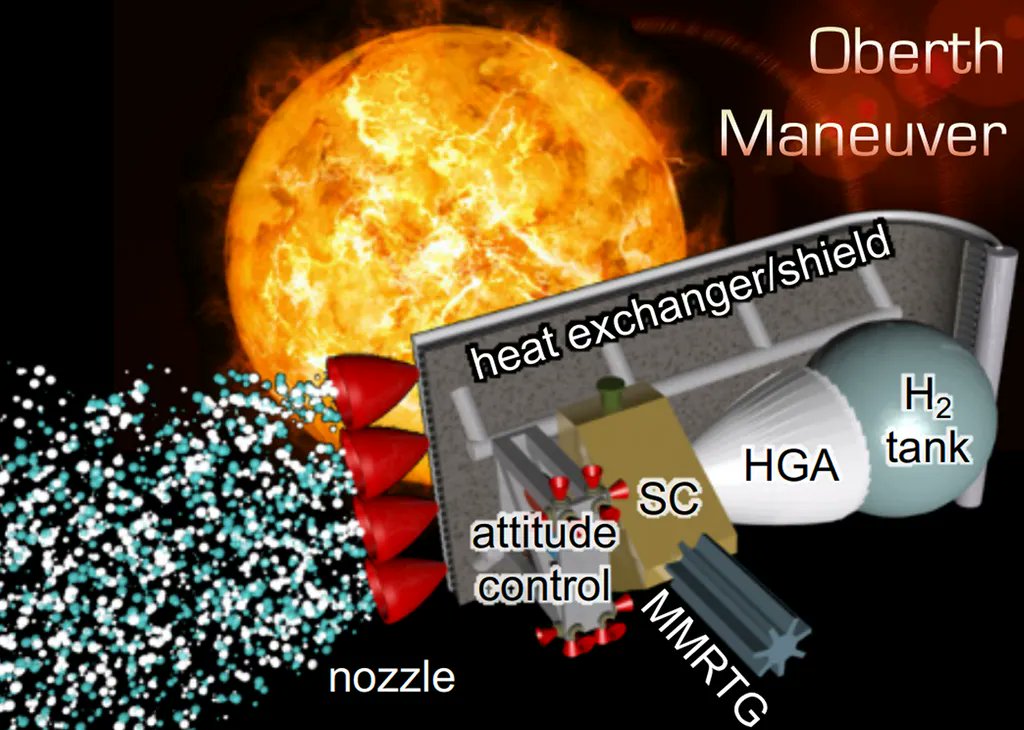
We’ve reported before on the conceptual mission known as the Interstellar Probe. This ambitious mission would visit the interstellar medium about 1,000 AU away from the Sun. But how exactly would the probe get there in a reasonable time frame? It has taken Voyager 35 years to travel less than 10% of that distance. The answer might lie in an old technology that has been given new life by advances in material science – the solar thermal propulsion system.
Continue reading “The Best way to Leave the Solar System Might be to fly Uncomfortably Close to the Sun”The new NIAC Awards are out! New Spacesuits, Breathing Martian air, Advanced Telescopes, and More
The NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) has been a significant funder of pie in the sky research for a long time now. From extrasolar object interceptors to beaming power into a lunar crater, we love reporting about NIAC funded concepts here at UT. Now, a new crop of Phase I and a smaller but more focused crop of Phase II fellows are funded to push the boundaries of space exploration forward.
Continue reading “The new NIAC Awards are out! New Spacesuits, Breathing Martian air, Advanced Telescopes, and More”Extrasolar Object Interceptor Would be Able to Chase Down the Next Oumuamua or Borisov and Actually Return a Sample
What if we had the ability to chase down interstellar objects passing through our Solar System, like Oumuamua or Comet Borisov? Such a spacecraft would need to be ready to go at a moment’s notice, with the capacity to increase speed and change direction quickly.
That’s the idea behind a new mission concept called the Extrasolar Object Interceptor and Sample Return spacecraft. It has received exploratory funding from NASA through its Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program.
“Bringing back samples from these objects could fundamentally change our view of the universe and our place in it,” says Christopher Morrison, an engineer from the Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation-Tech (USNC-Tech) who submitted the proposal to NIAC.
Continue reading “Extrasolar Object Interceptor Would be Able to Chase Down the Next Oumuamua or Borisov and Actually Return a Sample”Exploring the Moon’s Shadowed Regions Using Beamed Energy
In less than three years, astronauts will return to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era. As part of the Artemis Program, the purpose is not only to send crewed missions back to the lunar surface to explore and collect samples. This time around, there’s also the goal of establishing vital infrastructure (like the Lunar Gateway and a Base Camp) that will allow for “sustained lunar exploration.”
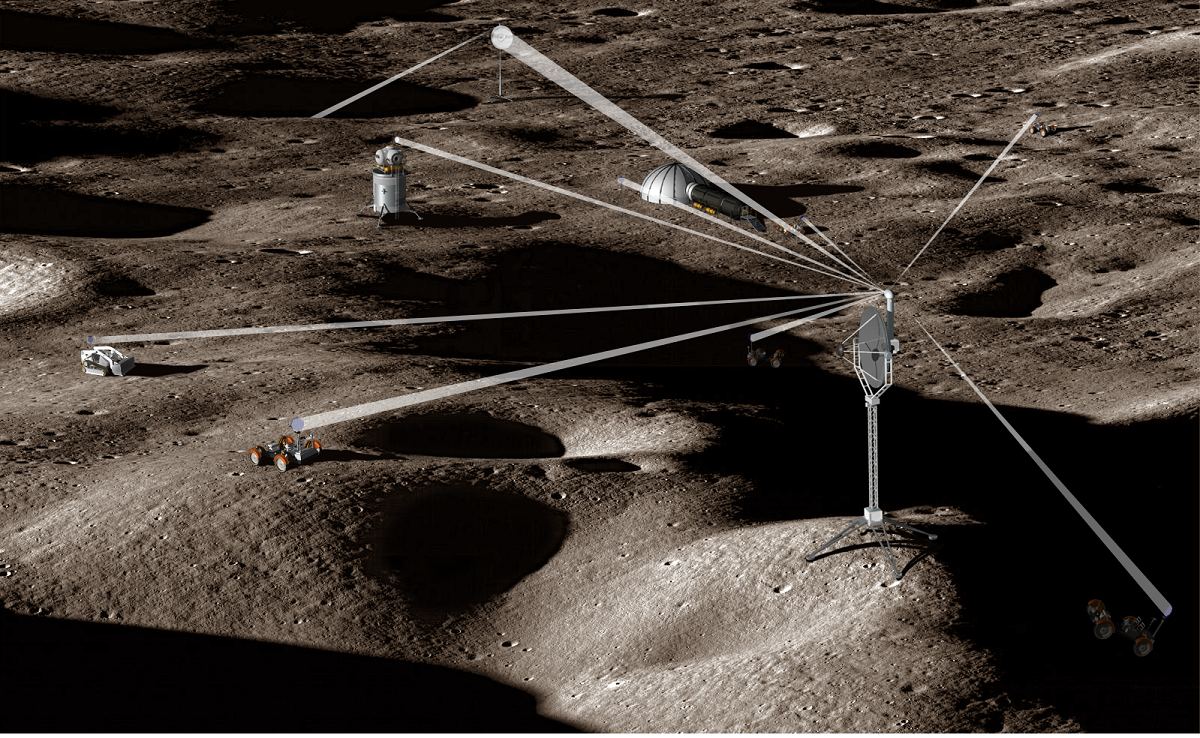
A key requirement for this ambitious plan is the provision of power, which can be difficult in regions like the South Pole-Aitken Basin – a cratered region that is permanently-shadowed. To address this, a researcher from the NASA Langley Research Center named Charles Taylor has proposed a novel concept known as “Light Bender.” Using telescope optics, this system would to capture and distribute sunlight on the Moon.
Continue reading “Exploring the Moon’s Shadowed Regions Using Beamed Energy”NASA Invests in a Plan to Build Landing Pads and Other Structures on the Moon out of Regolith
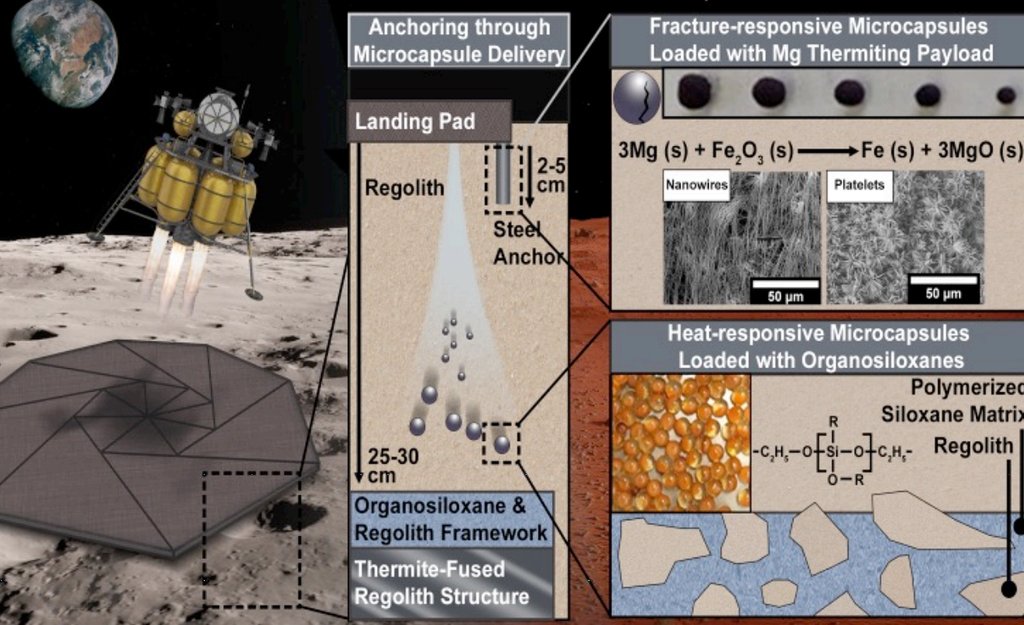
Materials are a crucial yet underappreciated component of any space exploration program. Without novel materials and ways to make them, things that are commonplace today, such as a Falcon 9 rocket or the Mars rovers, would never have been possible. As humanity expands into the solar system, it will need to make more use of the materials found there – a process commonly called in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). Now, the advanced concepts team at NASA has taken a step towards supporting that process by supporting a proposal from Dr. Sarbajit Banerjee, a chemist at Texas A&M. The proposal suggests using lunar regolith to build a stable landing pad for future moon missions.
Continue reading “NASA Invests in a Plan to Build Landing Pads and Other Structures on the Moon out of Regolith”Robotic asteroid mining spacecraft wins a grant from NASA
Back in April, NASA once again put out the call for proposals for the next generation of robotic explorers and missions. As part of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Program, this consisted of researchers, scientists, and entrepreneurs coming together to submit early studies of new concepts that could one-day help advance NASA’s space exploration goals.
One concept that was selected for Phase III of development was a breakthrough mission and flight system called Mini Bee. This small, robotic mining craft was designed by the Trans Astronautica (
NASA Invests In Radical Game-Changing Concepts For Exploration
Every year, the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program puts out the call to the general public, hoping to find better or entirely new aerospace architectures, systems, or mission ideas. As part of the Space Technology Mission Directorate, this program has been in operation since 1998, serving as a high-level entry point to entrepreneurs, innovators and researchers who want to contribute to human space exploration.
This year, thirteen concepts were chosen for Phase I of the NIAC program, ranging from reprogrammed microorganisms for Mars, a two-dimensional spacecraft that could de-orbit space debris, an analog rover for extreme environments, a robot that turn asteroids into spacecraft, and a next-generation exoplanet hunter. These proposals were awarded $100,000 each for a nine month period to assess the feasibility of their concept.
Continue reading “NASA Invests In Radical Game-Changing Concepts For Exploration”
Robot Spacecraft Swarm Among Group Tapped For More NASA Funding
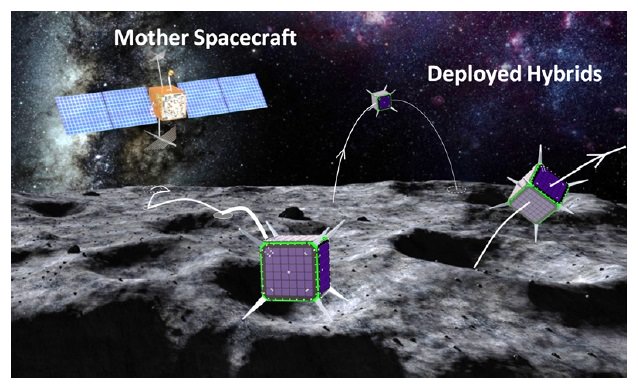
How do crazy but neat ideas such as the Mars crane make it to space? It’s through years, sometimes decades, of development to try to solve a problem in space exploration. NASA has an entire program devoted to far-out concepts that are at least a decade from making it into space, and has just selected five projects for a second round of funding.
One of them is a robotic swarm of spacecraft that we’ve written about before on Universe Today. Flying out from a mothership, these tiny spacecraft would be able to tumble across the surface of a low-gravity moon or asteroid.
“The systematic exploration of small bodies would help unravel the origin of the solar system and its early evolution, as well as assess their astrobiological relevance,” stated its principal investigator, Stanford University’s Marco Pavone, in a 2012 story. “In addition, we can evaluate the resource potential of small bodies in view of future human missions beyond Earth.”
The concept, called “Spacecraft/Rover Hybrids for the Exploration of Small Solar System Bodies“, is among the selectees in the second phase of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts program. Each will receive up to $500,000 to further develop their concept during the next two years. While Phase I studies are considered to show if a project is feasible, Phase II begins to narrow down the design.
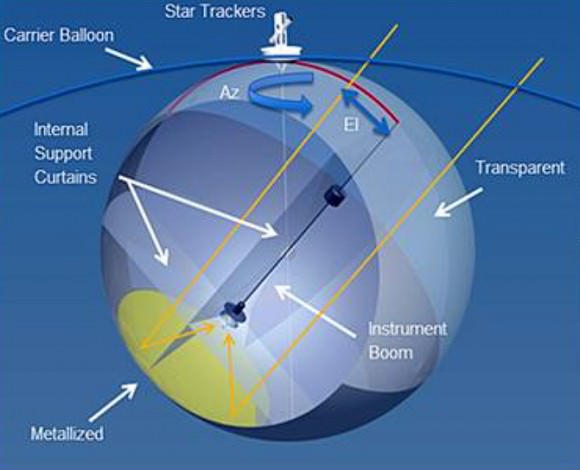
“This was an extremely competitive year for NIAC Phase II candidates,” stated Jay Falker, the program’s executive at NASA Headquarters. “But the independent peer review process helped identify those that could be the most transformative, with outstanding potential for future science and exploration.”
This is the rest of the selected concepts:
10 meter Sub-Orbital Large Balloon Reflector (Christopher Walker, University of Arizona): A telescope that uses part of a balloon as a reflector. The telescope would fly high in the atmosphere, perhaps doing examinations of Earth’s atmosphere or performing telecommunications or surveillance.
Deep mapping of small solar system bodies with galactic cosmic ray secondary particle showers (Thomas Prettyman, Planetary Science Institute): Using subatomic particles to map asteroids, comets and other smaller objects in the solar system.
Low-Mass Planar Photonic Imaging Sensor (Ben S.J. Yoo, University of California, Davis): A new way of thinking about telescopes that would use a low-mass planar photonic imaging sensor. This could be useful for missions to the outer solar system.
Orbiting Rainbows (Marco Quadrelli, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory): Using “an orbiting cloud of dust-like matter” for astronomical imaging by taking advantage of the spots where light passes through.
Source: NASA