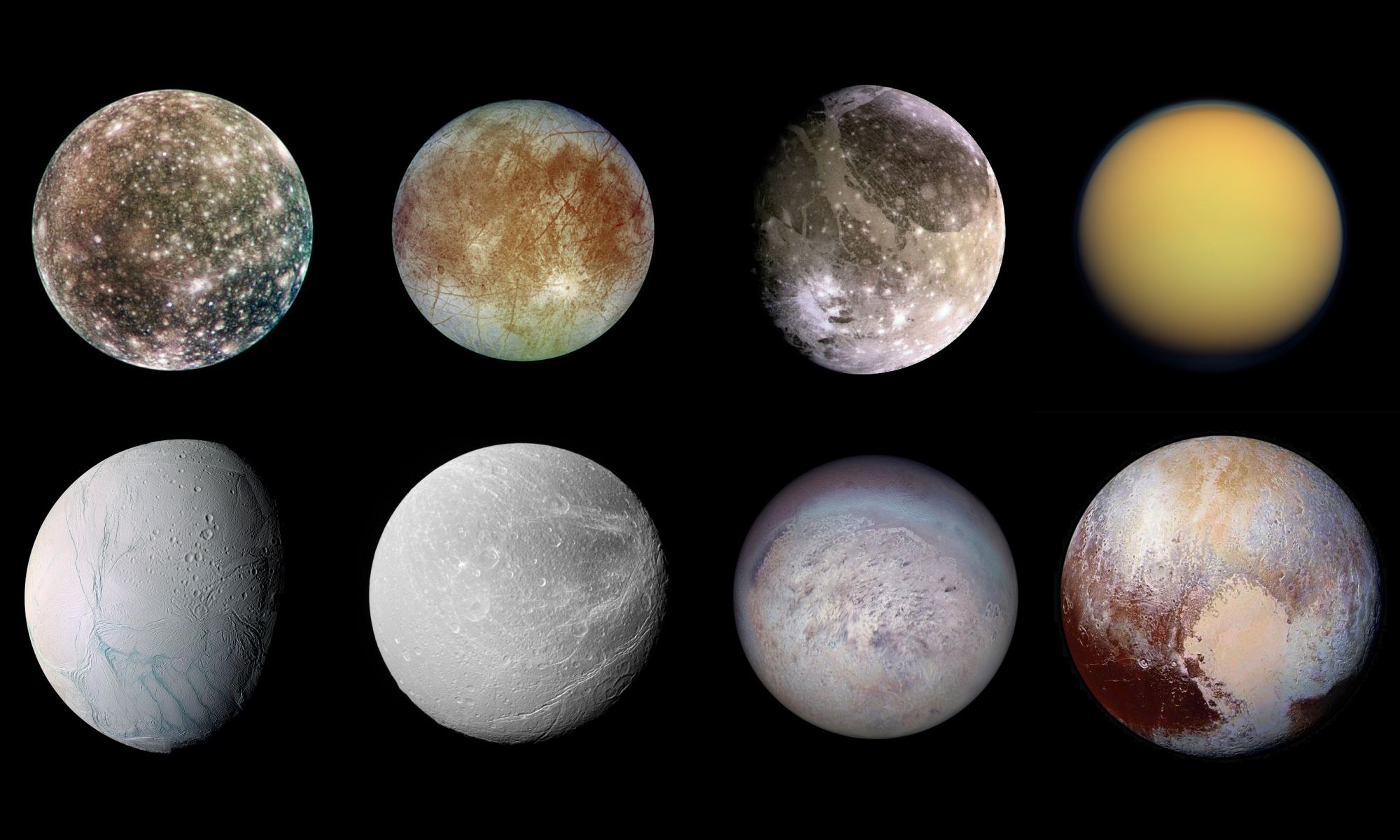
As of December 19th, 2022, 5,227 extrasolar planets have been confirmed in 3,908 systems, with over 9,000 more awaiting confirmation. While most of these planets are Jupiter- or Neptune-sized gas giants or rocky planets many times the size of Earth (Super-Earths), a statistically significant number have been planets where water makes up a significant part of their mass fraction – aka. “water worlds.” These planets are unlike anything we’ve seen in the Solar System and raise several questions about planet formation in our galaxy.
In a recent study, an international team led by researchers from the University of Montreal’s Institute for Research on Exoplanets (iREx) found evidence of two water worlds in a single planetary system located about 218 light-years away in the constellation Lyra. Based on their densities, the team determined that these exoplanets (Kepler-138c and Kepler-138d) are lighter than rocky “Earth-like” ones but heavier than gas-dominated ones. The discovery was made using data from NASA’s now-retired Spitzer Space Telescope and the venerable Hubble Space Telescope.
Continue reading “Hubble and Spitzer Team up to Find a Pair of Waterworld Exoplanets”