[/caption]
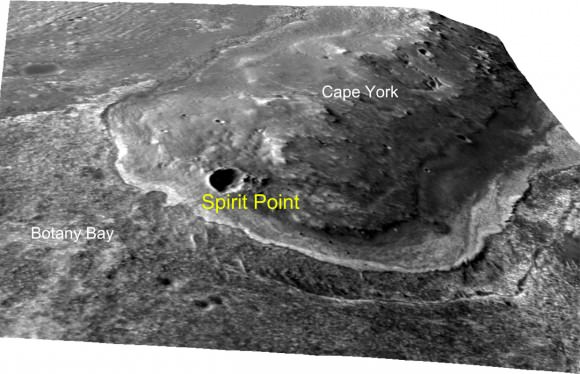
Scientists leading NASA’s Mars rover team have selected “Spirit Point” as the name for the spot where the “Opportunity” Mars rover will arrive at her next destination – Endeavour Crater. The site was named in honor of the death of the “Spirit” Mars Exploration Rover, which NASA recently declared has ceased all communications with Earth.
Spirit’s passing comes after more than six highly productive years roving the surface of the red planet as humankind’s surrogate. NASA concluded the last attempt to communicate with Spirit in a transmission on May 25, 2011.
“First landfall at Endeavour will be at the southern end of Cape York [at Spirit Point],” Steve Squyres told me. Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., is principal investigator for the rovers.
Read tributes from the Spirit rover science team below.
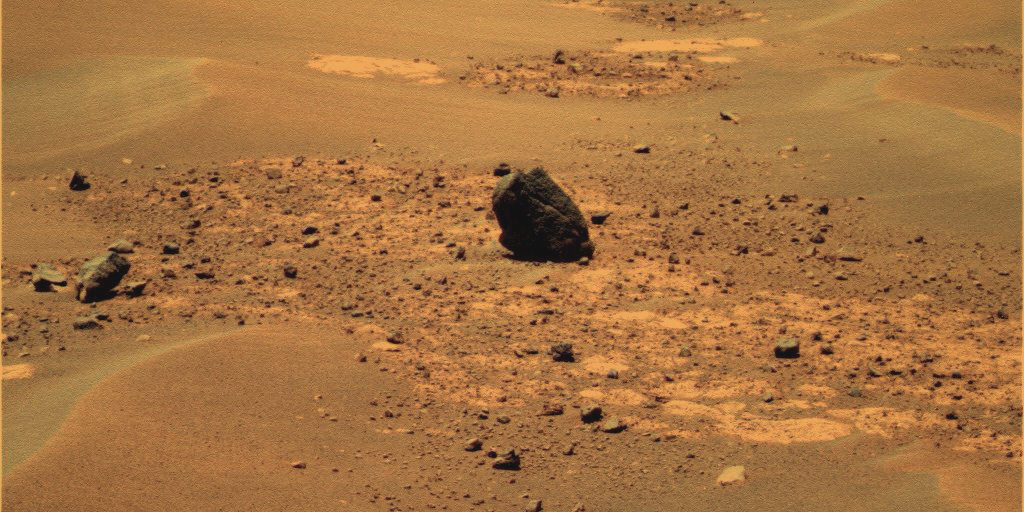
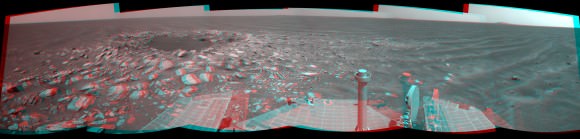
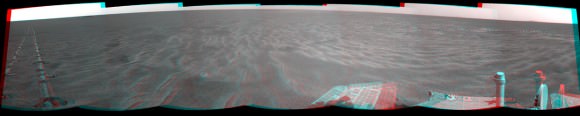
In memory of Spirit, the last panorama she snapped on Sol 2175 in February 2010 was featured on Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on May 30, 2011 and is the lead image here. The photo mosaic was created by Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer and shows some of the last scenes that Spirit ever photographed.

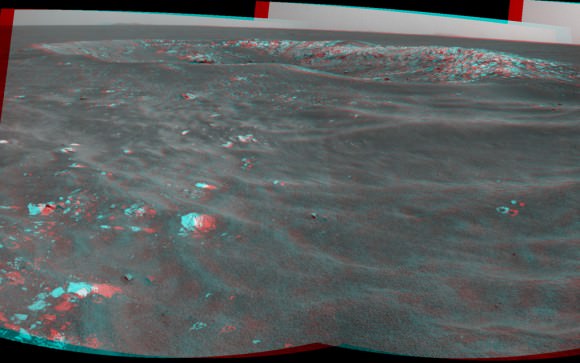
This mosaic of images was collected on Sol 1869 in April 2009 as Spirit approached a mysterious circular volcanic mound known as Von Braun, at left. Foreground at center, left ahead shows where Spirit became stuck in a concealed sand trap of slippery, water related sulfate minerals lying adjacent to the eroded volcanic plateau named Home Plate. Columbia Hills in the background.
Mosaic Credit: Kenneth Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo/NASA/JPL/Cornell
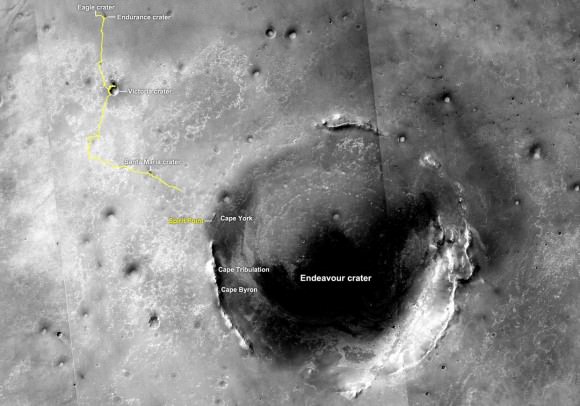
Endeavour’s massive rim consists of a series of ridges. Cape York is a 400 foot wide (120 meters) rim fragment at the western edge of Endeavour. Opportunity should reach “Spirit Point” before the end of this year, 2011.
“Spirit Point” was chosen as the site at Endeavour to commemorate the scientific achievements of Opportunity’s twin sister “Spirit”. Endeavour Crater was determined to be Opportunity’s long term destination nearly three ago after she departed the environs of Victoria crater.
“The Initial exploration plan will be decided when we get closer. The [science] priorities will depend on what we find,” Squyres added.
Since August 2008, the blistering pace of Opportunity’s long overland trek of about 11 miles (18 kilometers) has brought the golf cart sized robot to within about 2 miles (3 kilometers) of the rim of the humongous Endeavour crater – some 14 miles (22 kilometers) in diameter. Endeavour is more than 20 times wider than Victoria crater and by far the largest feature the Opportunity will ever explore – see route maps below.
“Spirit achieved far more than we ever could have hoped when we designed her,” according to Squyres in a NASA statement. “This name will be a reminder that we need to keep pushing as hard as we can to make new discoveries with Opportunity. The exploration of Spirit Point is the next major goal for us to strive for.”
The imaging team of Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer created a series of Spirit photomosaics from publically available images to illustrate the location and hazardous nature of Spirits final resting place – which fortuitously turned out to be a scientific goldmine revealing new insights into the flow of liquid water on Mars billions of years ago.

Mosaic shows predicament of being stuck at Troy with wheels buried in the sulfate-rich Martian soil. This false color mosaic has been enhanced and stretched to bring out additional details about the surrounding terrain and embedded wheels and distinctly shows a pointy rock perhaps in contact with the underbelly.
Mosaic Credit: Marco Di Lorenzo/ Kenneth Kremer/NASA/JPL/Cornell
The western rim of Endeavour possesses geological deposits far older than any Opportunity has investigated before and which may feature environmental conditions that were more conducive to the potential formation of ancient Martian life forms.
Spirits last transmissions to Earth took place in March 2010, before she entered hibernation mode due to ebbing solar power and succumbed to the likely damaging effects of her 4th Martian winter.
Spirit was closing in on her next science target, a mysterious volcanic feature named Von Braun, when she became mired in a sand trap named “Troy” on the outskirts of the eroded volcano named “Home Plate, just about 500 feet away. See our mosaics.

Numerous attempts by the rover team failed to extricate Spirit from the sand trap at Troy in which she became mired in May 2009 on the western edge of Home Plate. Mosaic shows last robotic arm maneuver before hibernation and above bright toned soil containing hydrated sulfates. Mosaic Credit: Marco Di Lorenzo/ Kenneth Kremer/ NASA/JPL/Cornell
Unable to escape and absent of sufficient power to run critical survival heaters, Spirit experienced temperatures colder than ever before that probably crippled fragile electronics components and connections and prevented further communications – although no one knows for sure.
NASA’s twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity have been exploring the Martian terrain on opposite sides of the red planet since the dynamic duo successfully landed over 7 years ago in January 2004.
Both robots were expected to last just three months but have accumulated a vast bonus time of exploration and discovery in numerous extended mission phases.
*** Several top members of the rover science team kindly provided me some comments (below) to sum up Spirits achievements and legacy and what’s ahead for Opportunity at Endeavour.
Ray Arvidson of Washington University, St Louis, Deputy Principal Investigator for the rovers:
“Spirit’s last communication with Earth was in March 2010 as the southern hemisphere winter season began to set in, the sun was low on the horizon, and the rover presumably stopped communicating to use all available solar power to charge the batteries.
Von Braun was one of the two destinations Spirit was traveling to when the rover became embedded in soft sands in the valley to the west of Home Plate.
Von Braun is a conically-shaped hill to the south of Home Plate, Inner Basin, Columbia Hills. Goddard is an oval-shaped shallow depression to the west of von Braun and was the second area to be visited by Spirit. Both von Braun and Goddard are suspected to be volcanic features.

During Spirit’s six year and two month mission the vehicle acquired remote sensing and in-situ observations that conclusively demonstrated that the ancient Columbia Hills in Gusev Crater expose materials that have been altered in water-related environments, including ground water corrosion and generation of sulfate and opaline minerals in volcanic steam vents and perhaps hydrothermal pools.
Together with its sister rover, Opportunity, the Mars Exploration Rover Mission, was designed to “follow the water” and return data that would allow us to test the hypothesis that water was at and near the surface during previous epochs.
Opportunity is still exploring the evidence in Meridiani for ancient shallow lakes and is on the way to outcrops on the rim of Endeavour crater, a ~20 km wide crater that exposes the old Noachian crust that shows evidence from orbital data for hydrated clay minerals.
These two rovers have performed far beyond expectations, unveiled the early, wet history of Mars, and have made an enormous scientific return on investment.”
Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., Principal Investigator for the rovers:
“Our best hope for hearing from Spirit was last fall. When that didn’t happen, we began a long, careful process of trying every possible approach to re-establishing contact. But it slowly became clear that it was unlikely, and I personally got used to the idea that Spirit’s mission was probably over several months ago.
Once that right front wheel failed, Spirit’s days were numbered in that kind of terrain. It wouldn’t have made any difference if we had tried to move Spirit sooner. We were very lucky to have survived as long as we did.
One of the lessons learned is to try to keep the wheels from failing.
It’s very sad to lose Spirit. But two things have softened the blow. First we’ve had a long time to get used to the idea. Second, even though Spirit is dead, she died an honorable death. If we’d lost her early in the mission, before she accomplished so much, it would have been much harder. But she accomplished so much more than any of us expected, the sadness is very much tempered with satisfaction and pride.
The big scientific accomplishments are the silica deposits at Home Plate, the carbonates at Comanche, and all the evidence for hydrothermal systems and explosive volcanism. What we’ve learned is that early Mars at Spirit’s site was a hot, violent place, with hot springs, steam vents, and volcanic explosions. It was extraordinarily different from the Mars of today.
Opportunity is heading at high speed for the rim of Endeavour Crater. First landfall will be at the southern end of Cape York. She should be there in not too many more months.
It hasn’t yet been decided where Opportunity will attempt to climb up Endeavour… we’ll see when we get there.
The phyllosilicates are a high priority, but the top priority depends on what we find.

I hope Spirits legacy will be the inspiration that people, especially kids, will take away from Spirit’s mission. I have had long, thoughtful conversations about Spirit with kids who have had a rover on Mars as long as they can remember. And my fondest hope for Spirit is that somewhere there are kids who will look at what we did with her, and say to themselves “well, that’s pretty cool… but I bet when I grow up I can do better. That’s what we need for the future of space exploration.
Spirit existed, and did what she did, because of the extraordinary team of engineers and scientists who worked so hard to make it possible. It’s a team that I’m incredibly proud to have been a small part of. Working with them has been quite literally the adventure of a lifetime.”
Jim Bell of Arizona State University, lead scientist for the rovers Pancam stereo panoramic camera:
“It is with a bittersweet sense of both sadness and pride that NASA announced the official end of the mission for the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit.
The Spirit team has seen the end coming since communications were lost with the rover in March 2010. Mission engineers made heroic efforts to reestablish contact. In the end Spirit was conquered by the extremely cold Martian winter and its two broken wheels, which prevented its dusty solar panels from pointing toward the Sun.
But what a mission! Designed to last 90 days, Spirit kept going for more than six years, with the team driving the rover almost 5 miles (8 km) across rocky volcanic plains, climbing rugged ancient hills, and scurrying past giant sand-dune fields. It eventually spent most of the mission near the region known as Home Plate, which is full of layered, hydrated minerals.
Data from the rover enabled dozens of scientific discoveries, but three stand out to me as most important:
Hydrated sulfate and high-silica soils in the Columbia Hills and around Home Plate.
These minerals, and the environment in which they occur (Home Plate is a circular-shaped, finely layered plateau that may be the eroded remains of a volcanic cone or other hydrothermal deposit), tell us that at some point in the past history of Gusev there was liquid water and there were heat sources — two key ingredients needed to consider the area habitable for life as we know it.
Carbonate minerals in some of the rocks within the Columbia Hills.
Carbonates were expected on Mars, if indeed the climate was warmer and wetter in the past. However, their detection has been elusive so far. Indeed, the Spirit team had to work hard to uncover the signature of carbonates years after the rover made the measurements. As the analysis continues the results for Mars in general could be profound.
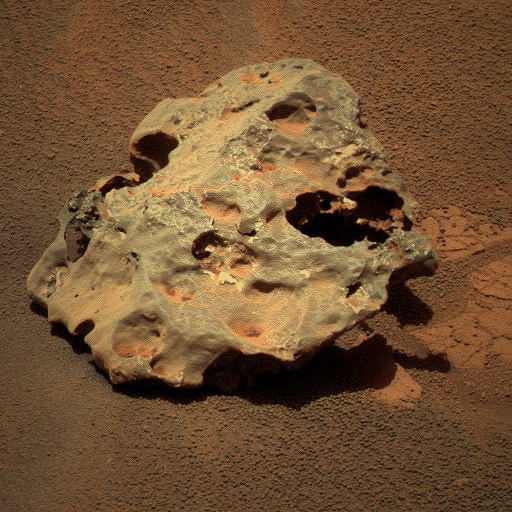
An incredible diversity of rock types, from all over Mars, that Spirit was able to sample in Gusev crater.
Some of the rocks appear to be from local volcanic lava flows or ash deposits. But others have likely been flung in to the area over time by distant impacts or volcanoes, and a few even appear to be meteorites, flung in from outer space. Spirit’s instruments provided the team with the ability to recognize this amazing diversity, and thus to learn much more about Mars in general, not just Gusev in particular.
Spirit also helped us test an experiment: If we put all the rover’s images out on the Web for everyone in the world to see, in near real-time, would people follow along? They did!
I wonder if, maybe 10 or 15 years from now, I’ll meet some young colleagues who were turned on to space exploration by being able to check out the latest Spirit images from Mars from their classroom, or living room, every day when they were a kid. That would be extremely satisfying — and a great testament to the power of openly sharing data from space exploration missions like Spirit’s.
Meanwhile, Opportunity continues to rove on to city-size Endeavour crater, where orbital measurements have identified, for the first time in either rover’s mission, the signatures of clay minerals in the crater’s rim. Clays are also formed in water, but in less acidic, perhaps more life-friendly water than the sulfates that Opportunity has been mapping thus far.”
Rob Manning, Jet Propulsion laboratory, Pasadena, CA., Mars Rover Spacecraft System Engineering team lead
“Although Opportunity has proven her endurance, Spirit was the one we struggled with the hardest to get what she earned. Suffering from late repair and modification, a blown fuse in her power system and with possibly damaged circuits, she was very late getting out the door and onto the pad in Florida.
Unlike Opportunity, whose Hematite-laden Meridiani destination had been established long before launch, Spirit was launched with a great deal of uncertainty on where she would find herself on Mars. Would it be the flat and safe plains of Elysium? Would the intriguing but rough ancient Gusev crater with what appears to have been an ancient river flowing into a giant but now dry lake?
If Opportunity failed to get on her way to Mars, would her destination become Meridiani? Would Spirit have also been as lucky to find herself bouncing into a tiny rock-outcropped crater as Opportunity had?
Only after the successful launch of Opportunity followed by further successful rocket and airbag tests to confirm that the landing system design would work in the rougher terrain inside Gusev crater allowed us to seal her fate and her permanent home.
She would go Gusev and test the Gusev lake hypothesis. Sadly the surface of Gusev where she came to rest revealed a meteor impact-tilled lake of ancient lava. Any signs of ancient water lake beds and other fantastic discoveries would have to wait until she surmounted many more obstacles including summiting a formidable hill her designers never intended her to attempt.
Spirit, her designers, her builders, her testers, her handlers and I have a lot to be thankful for.
That NASA, the congress and the public were willing to trust us with this daunting feat is perhaps a statement about the persistent spirit of discovery that remains in all of us.
I think that Spirit is alive and well.”

Mosaic Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Kenneth Kremer