[/caption]
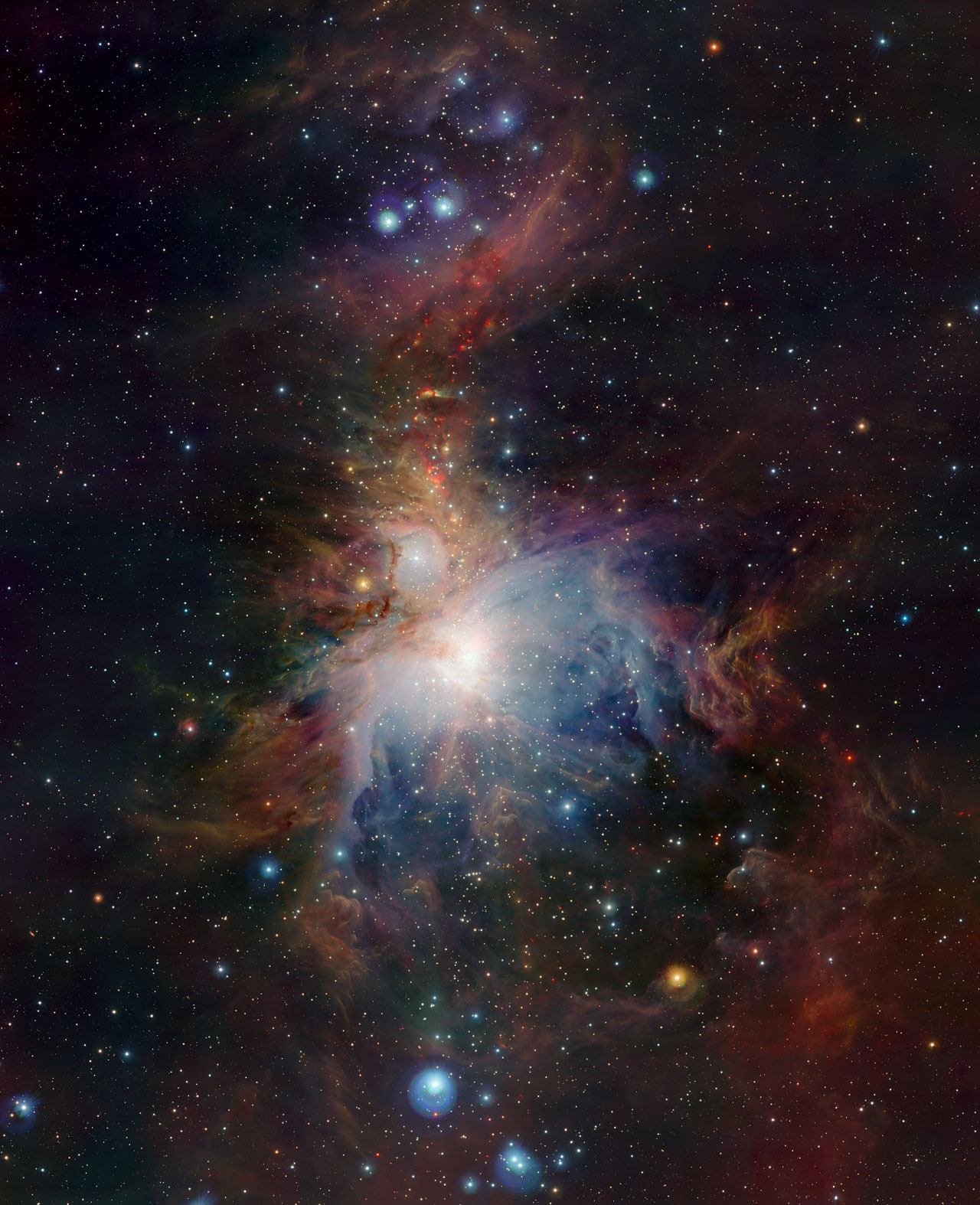
Oh-oh-oh Orion! The new VISTA (Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy) infrared survey telescope has used its huge field of view to show the full splendor of the Orion Nebula. With its infrared eyes, it has peered deeply into dusty regions that are normally hidden to expose the curious behavior of the very active young stars buried there.
VISTA is the latest addition to ESO’s Paranal Observatory. It is the largest survey telescope in the world and is dedicated to mapping the sky at infrared wavelengths. The large (4.1-metre) mirror, wide field of view and very sensitive detectors make VISTA a unique instrument. This dramatic new image of the Orion Nebula illustrates VISTA’s remarkable powers.
The Orion Nebula is about 1,350 light-years from Earth. Although spectacular when seen through an ordinary telescope, what can be seen using visible light is only a small part of a cloud of gas in which stars are forming. Most of the action is deeply embedded in dust clouds and to see what is really happening astronomers need to use telescopes with detectors sensitive to the longer wavelength radiation that can penetrate the dust. VISTA has imaged the Orion Nebula at wavelengths about twice as long as can be detected by the human eye.
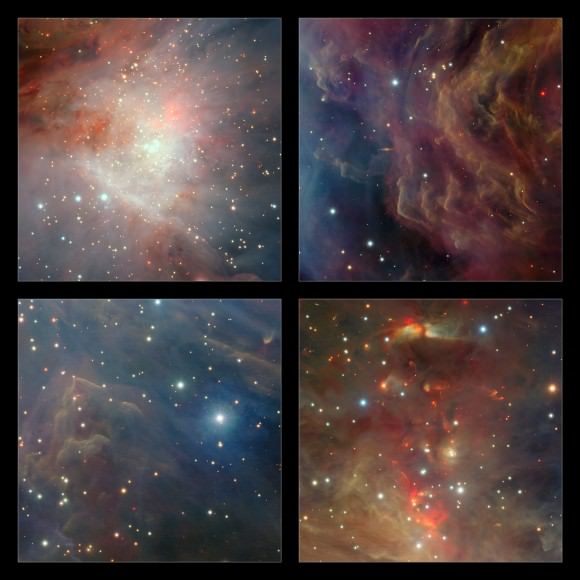

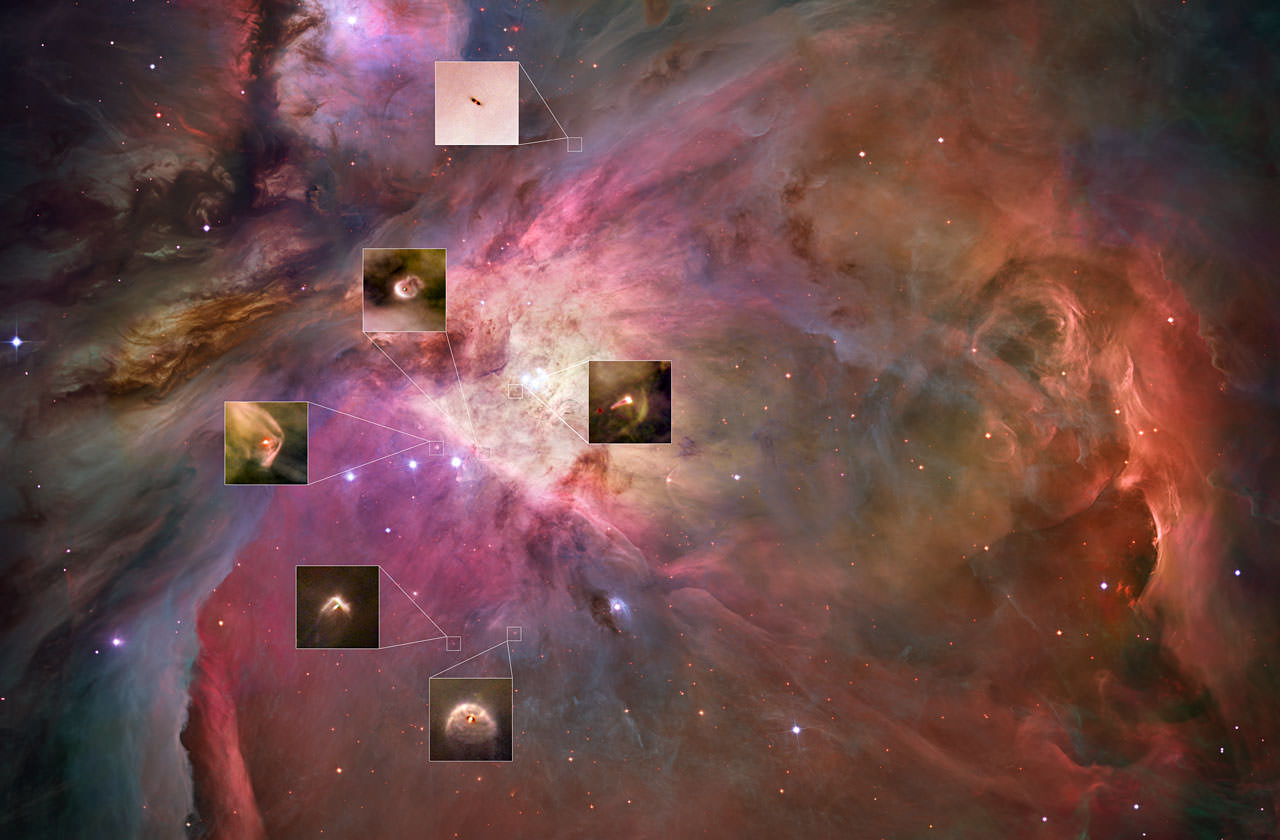
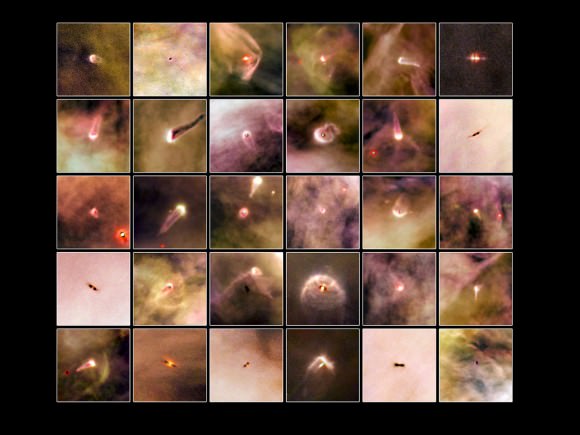
On the upper-left, the central region of VISTA’s view of the Orion Nebula is shown, centered on the four dazzling stars of the Trapezium. A rich cluster of young stars can be seen here that is invisible in normal, visible light images. In the lower-right panel the part of the nebula to the north of the center is shown. Here there are many young stars embedded in the dust clouds that are only apparent because their infrared glow can penetrate the dust and be detected by the VISTA camera. Many outflows, jets and other interactions from young stars are apparent, seen in the infrared glow from molecular hydrogen and showing up as red blobs. On the upper-right, a region to the west of center is shown. Here the fierce ultraviolet light from the Trapezium is sculpting the gas clouds into curious wavy shapes. A distant edge-on spiral galaxy is also seen shining right through the nebula. At the lower-left a region south of the center is shown. Each extract covers a region of sky about nine arcminutes across.
All these features are of great interest to astronomers studying the birth and youth of stars.
Source: ESO