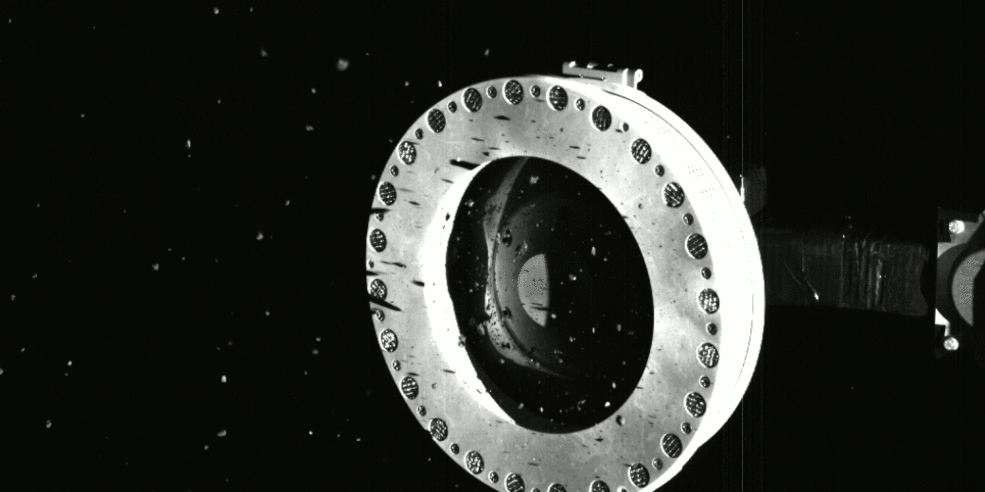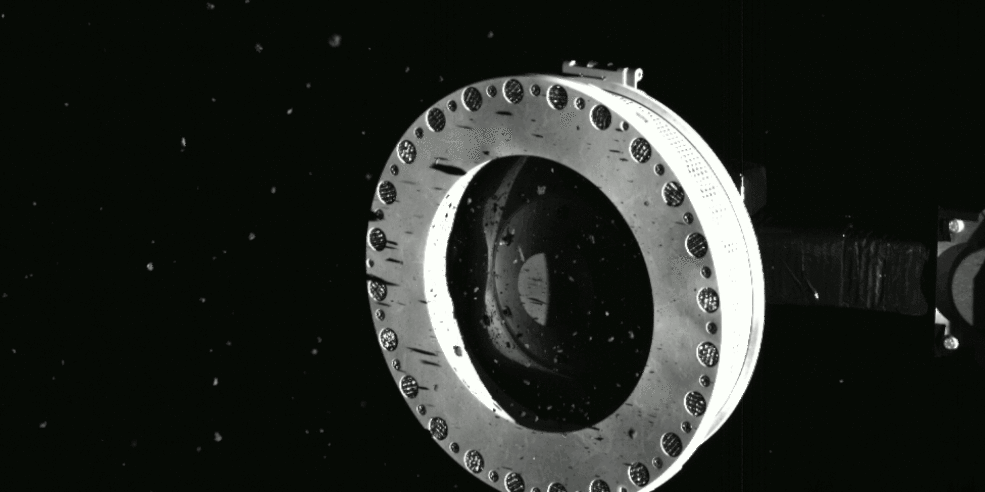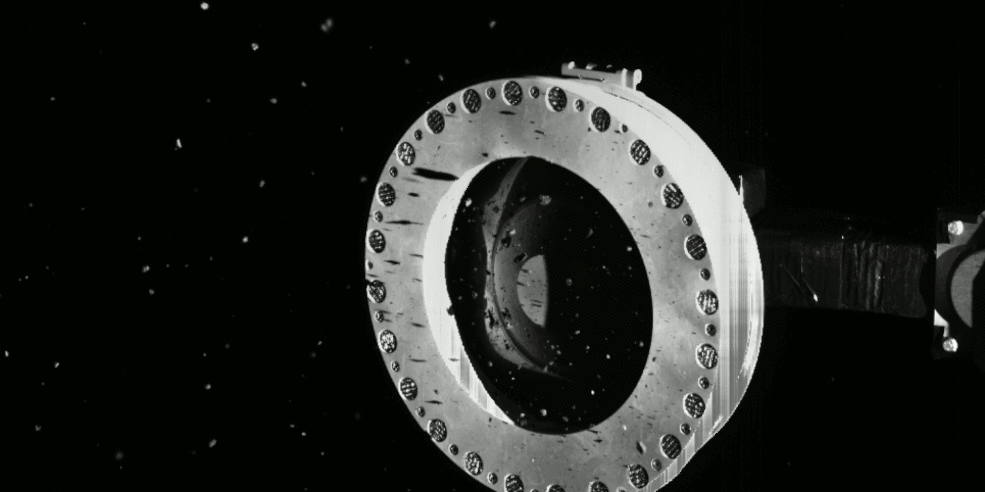
Is there such as thing as too much asteroid?
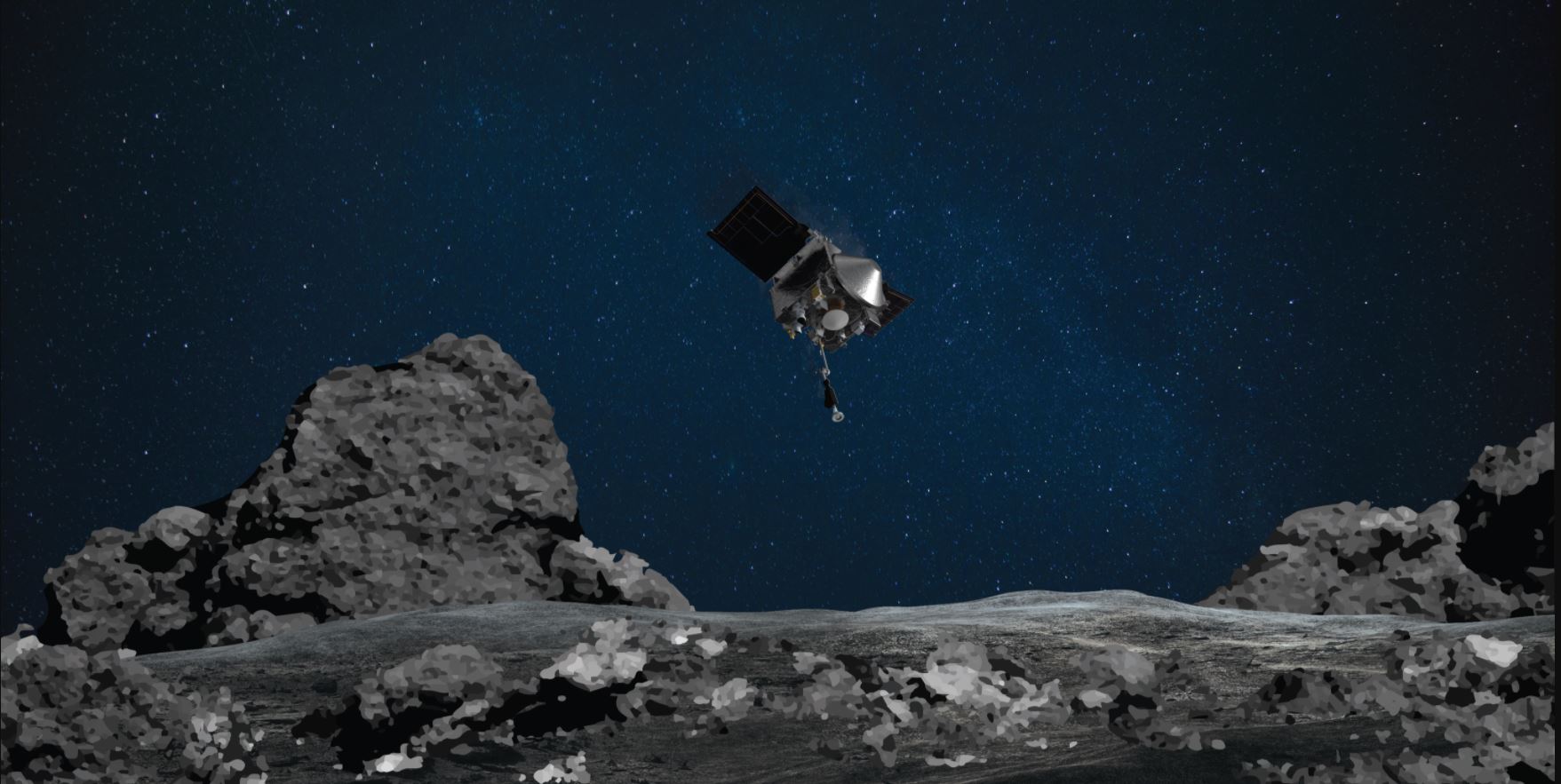
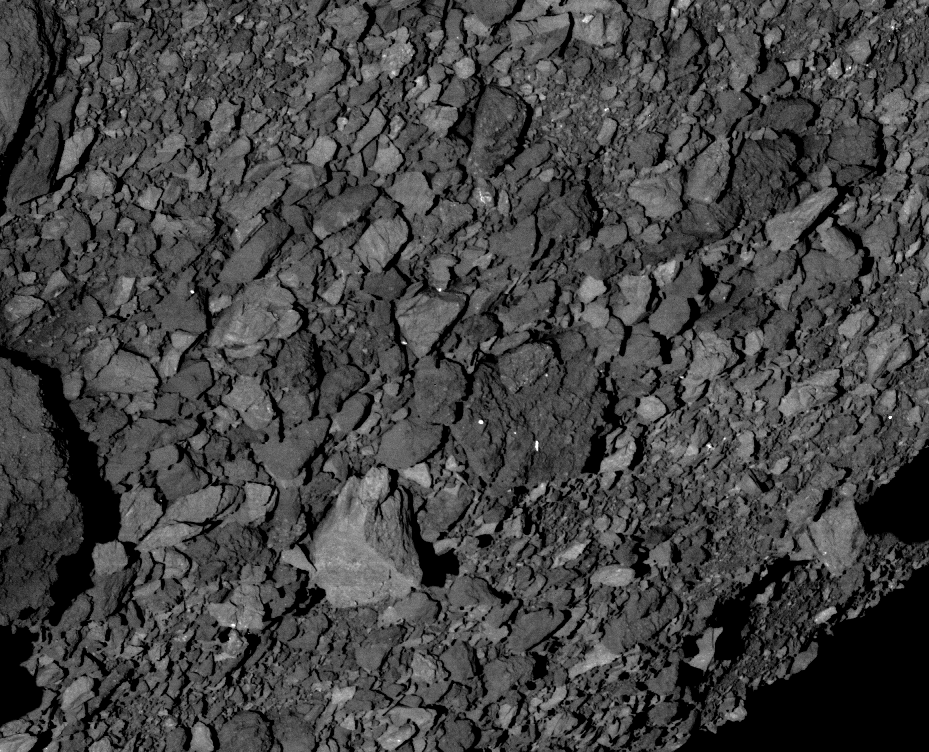
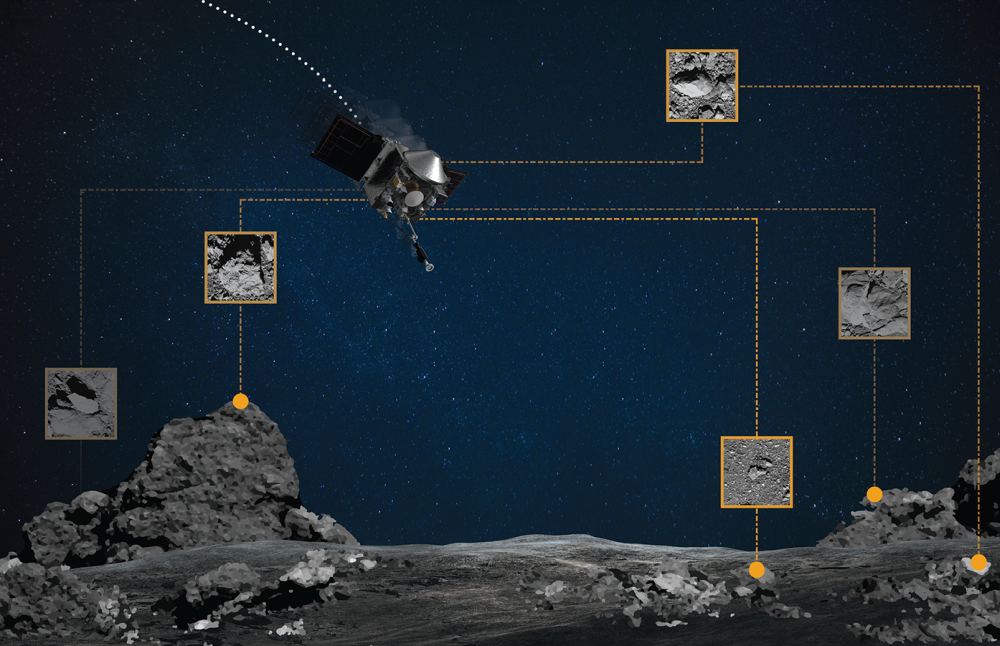
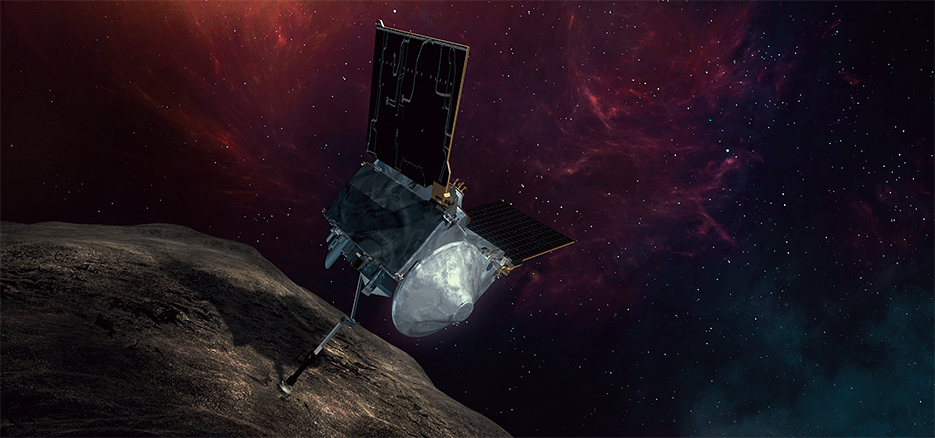
Scientists and engineers for NASA’s OSIRIS-REx decided to perform an “early stow” of the sample from Asteroid Bennu collected by the spacecraft on October 20, because the collection container is full-to-overflowing, possibly jamming the collector head from sealing shut.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Collected So Much Material, the Sample Capsule Overflowed. Time to Bring it All Home.”