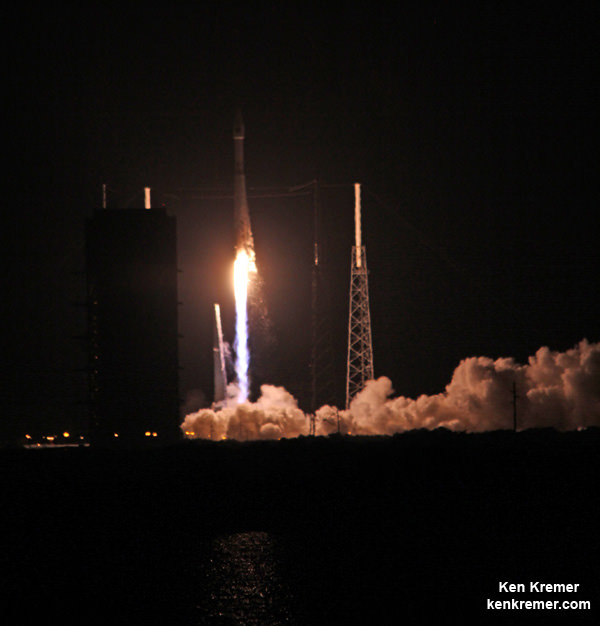
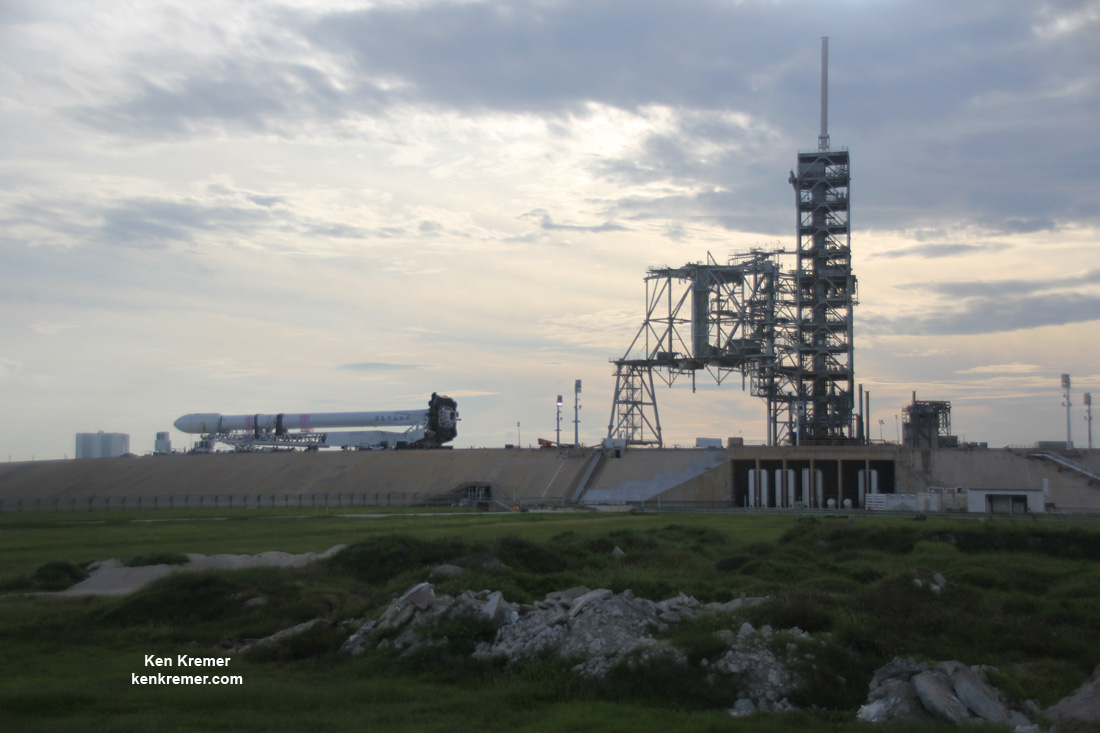
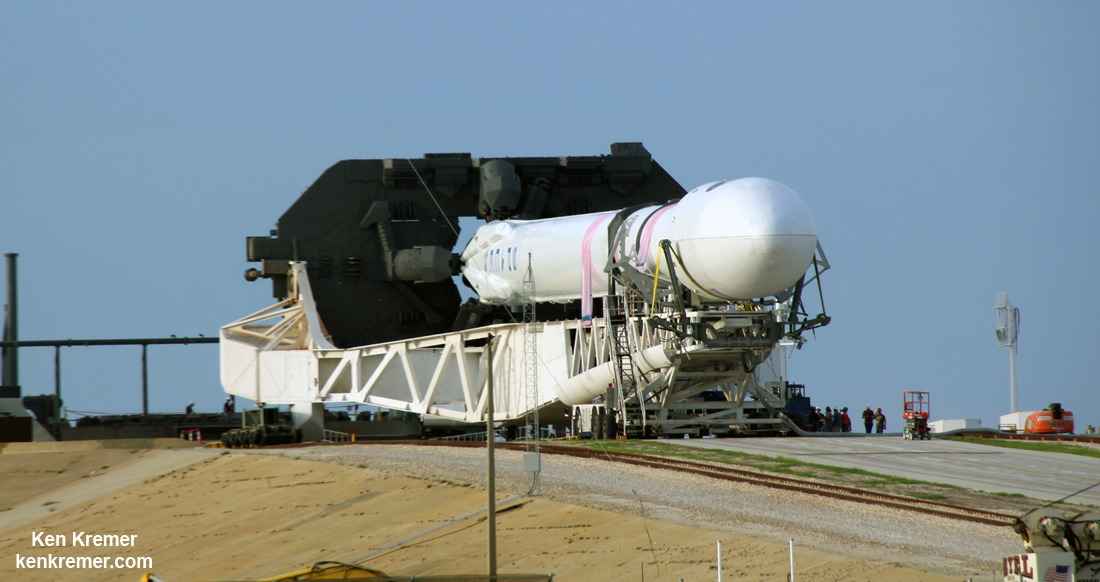
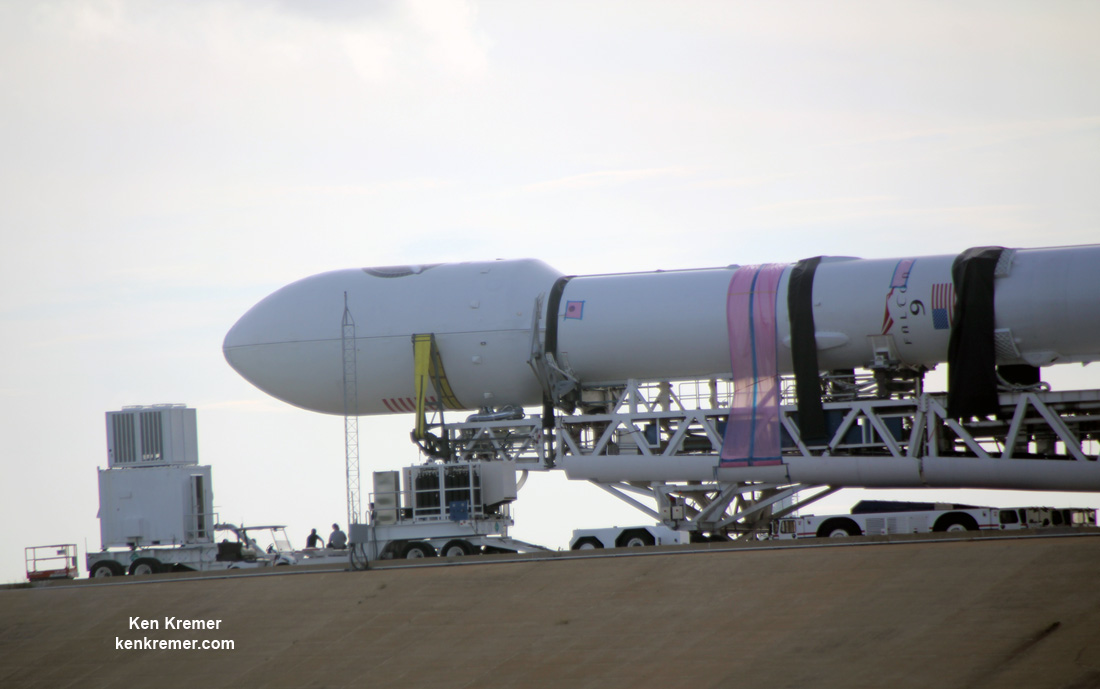
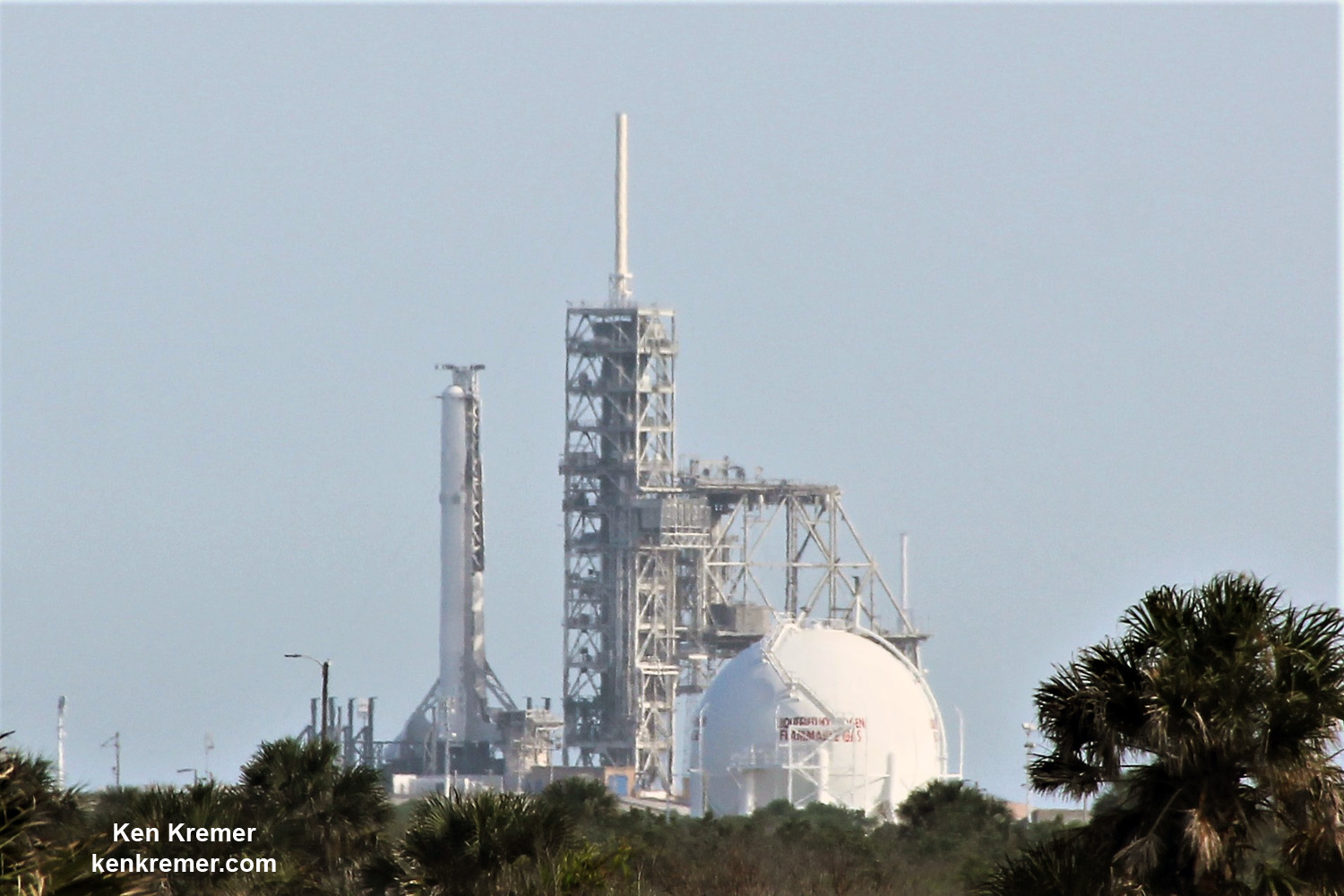
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – The super secret ‘Zuma’ spysat mission claimed by no U.S. government entity – not even the elusive NRO spy agency ! – and whose goals are veiled in virtually complete darkness– is poised for a dark of night blastoff on a SpaceX Falcon rocket Thursday evening, Nov. 16, from the Florida Space Coast. Update: Delayed to Friday 8 PM
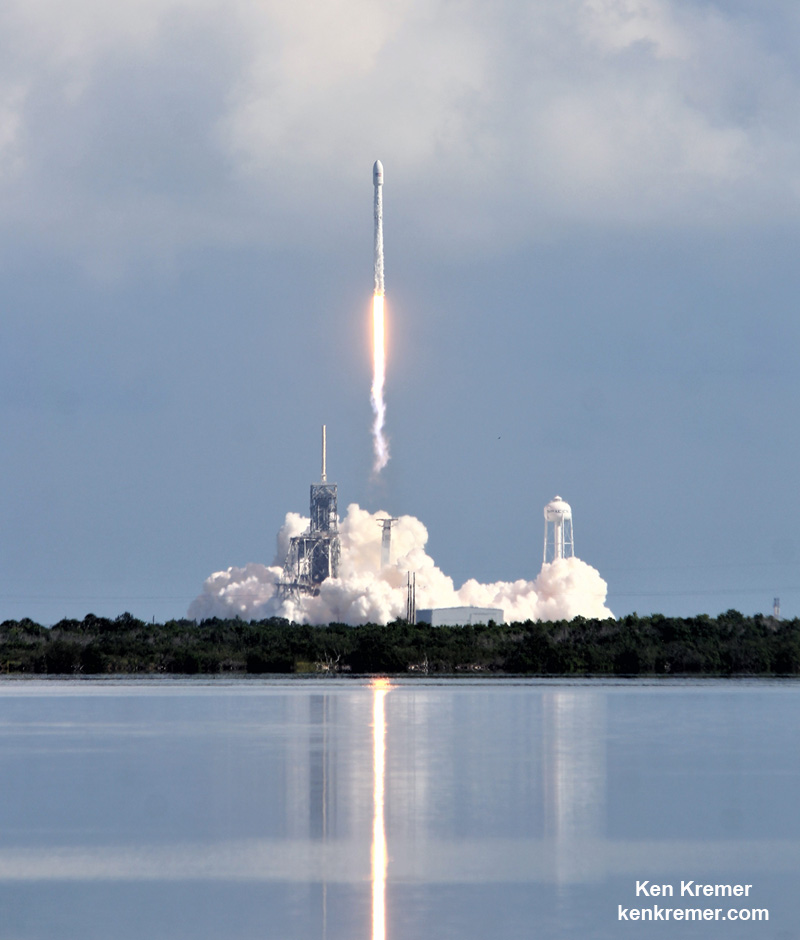
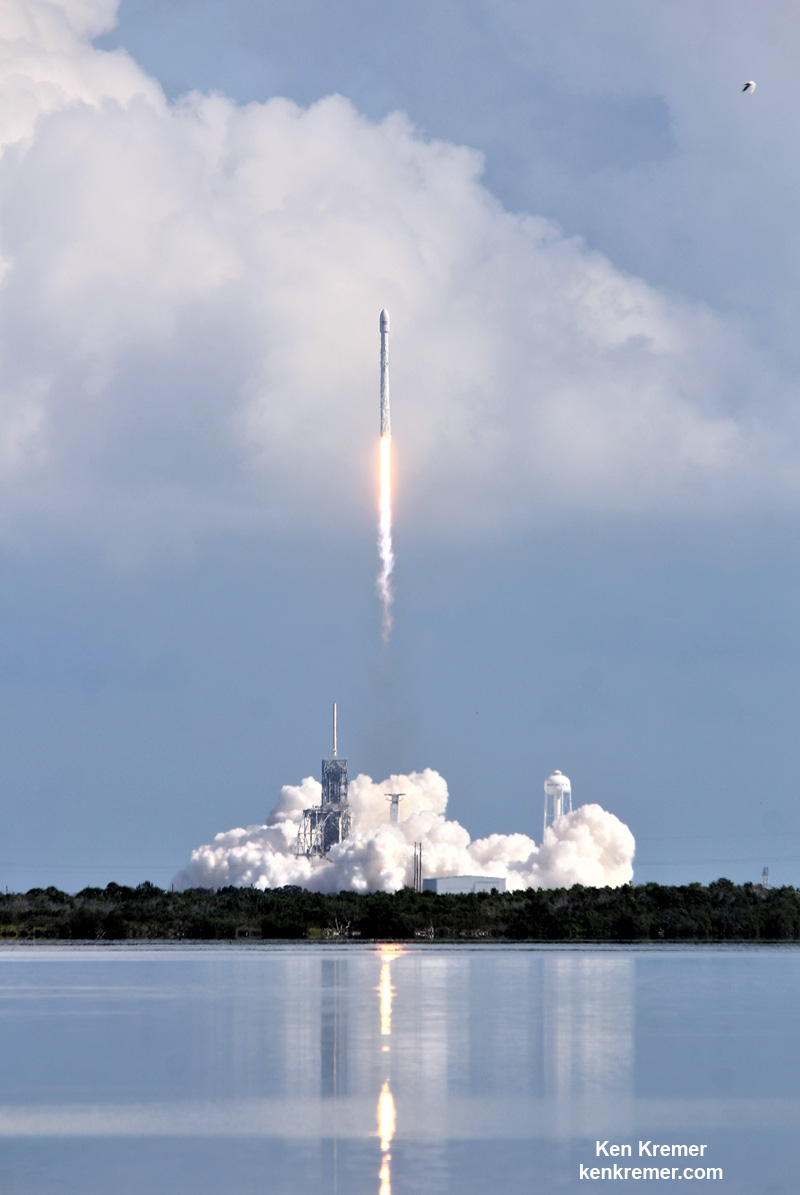
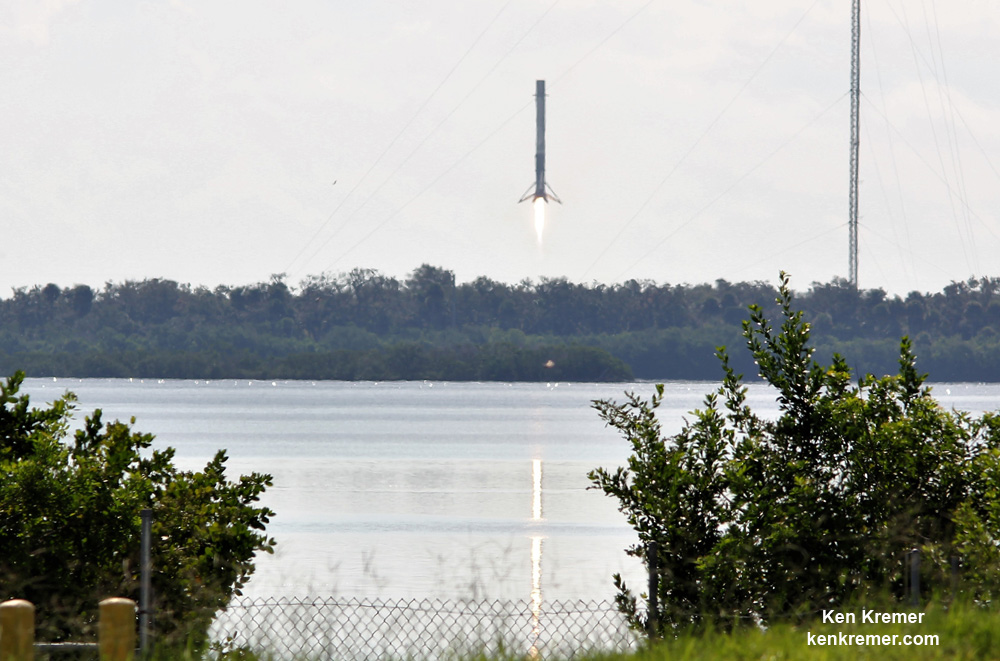
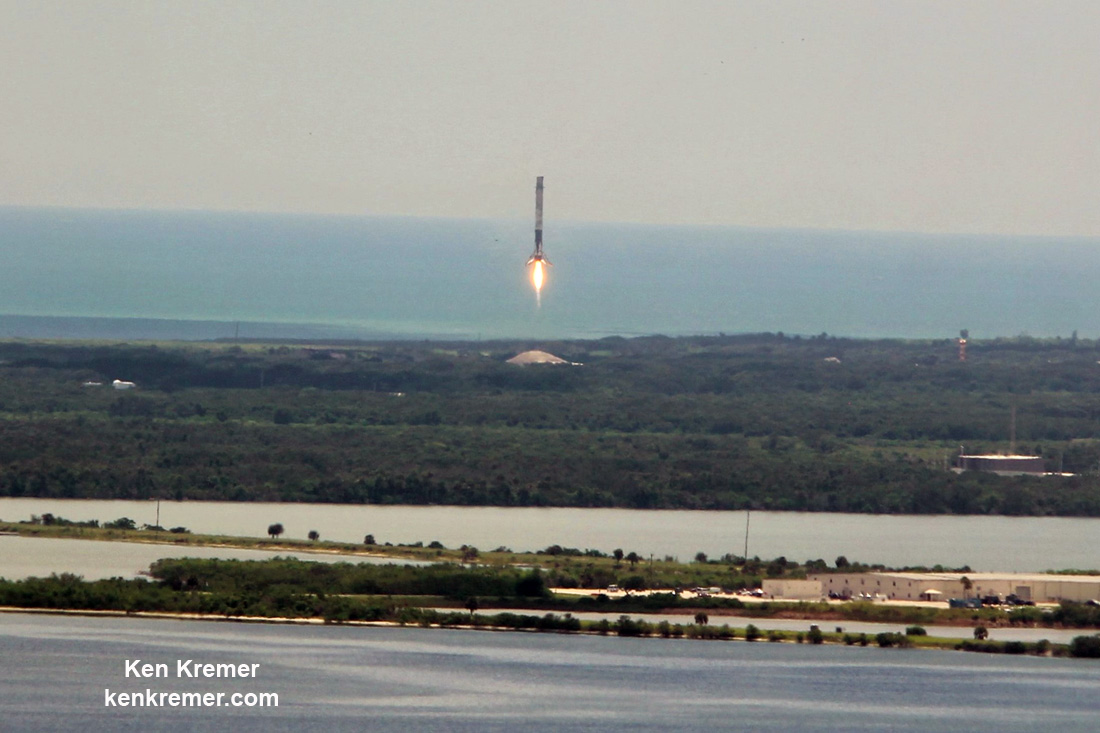
An unclassified aspect of the mission codenamed ‘Zuma’ is that SpaceX will also attempt to recover the 16 story tall first stage booster with a soft landing on the ground back at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. So expect some extremely loud sonic booms to rock the space coast region about eight minutes after liftoff.
Zuma is a total mystery, to the delight of the spymasters.
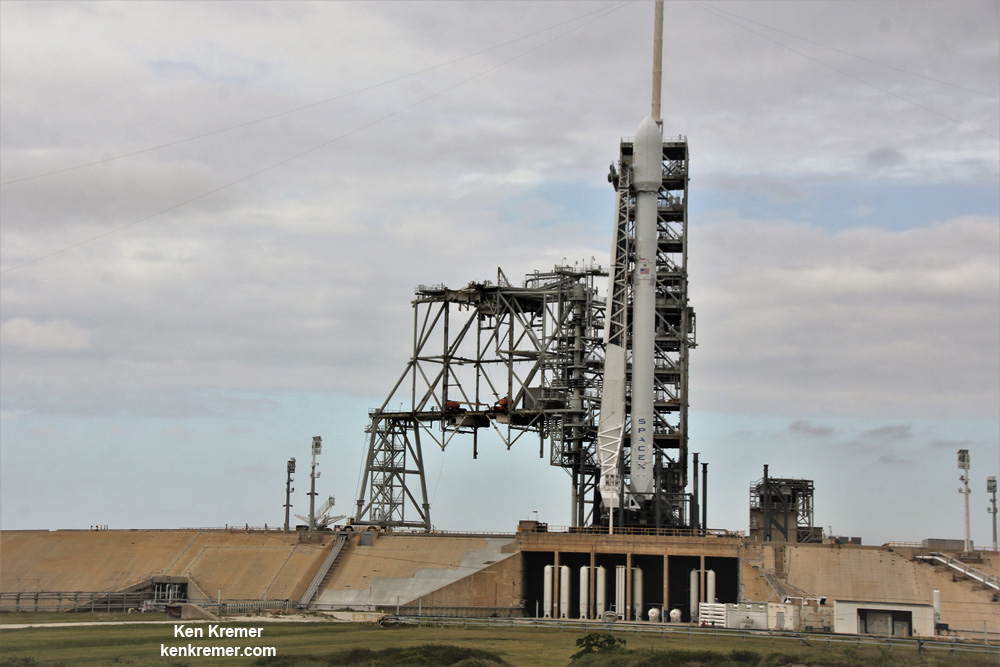
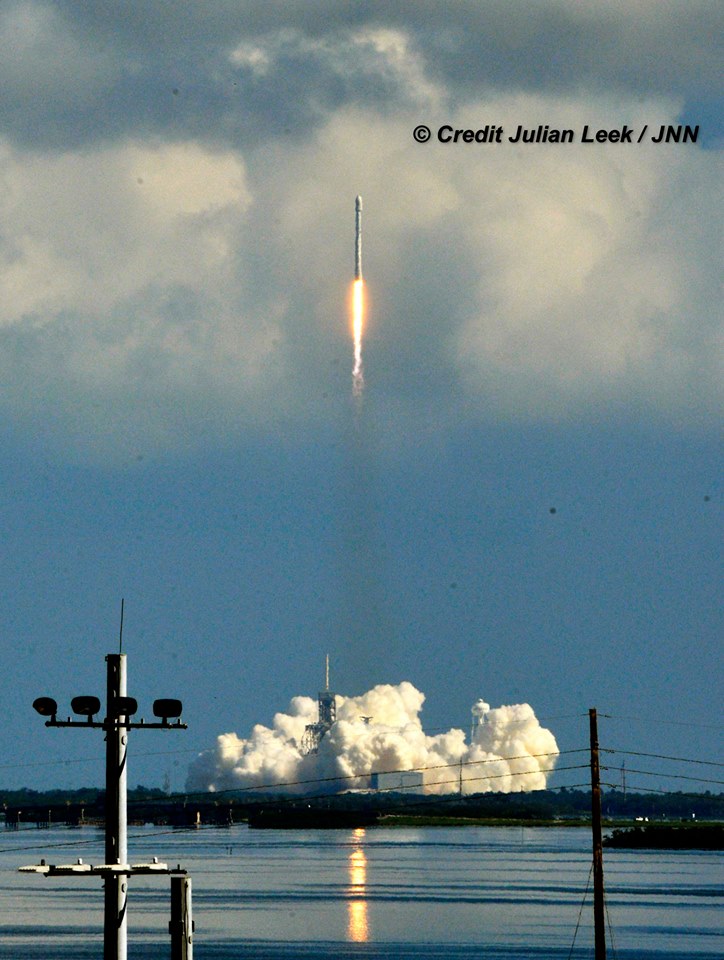
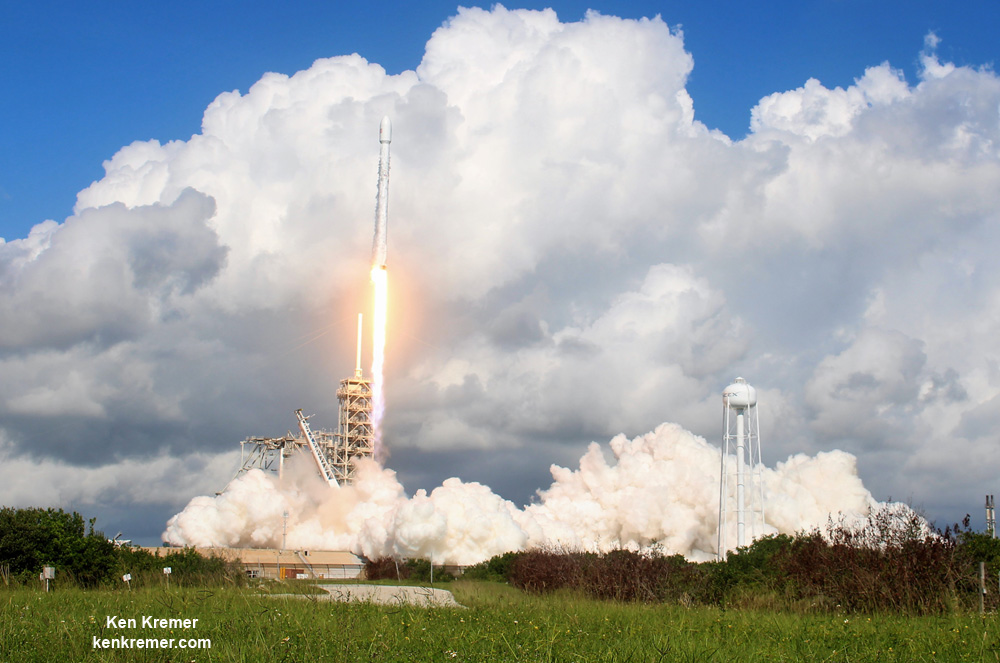
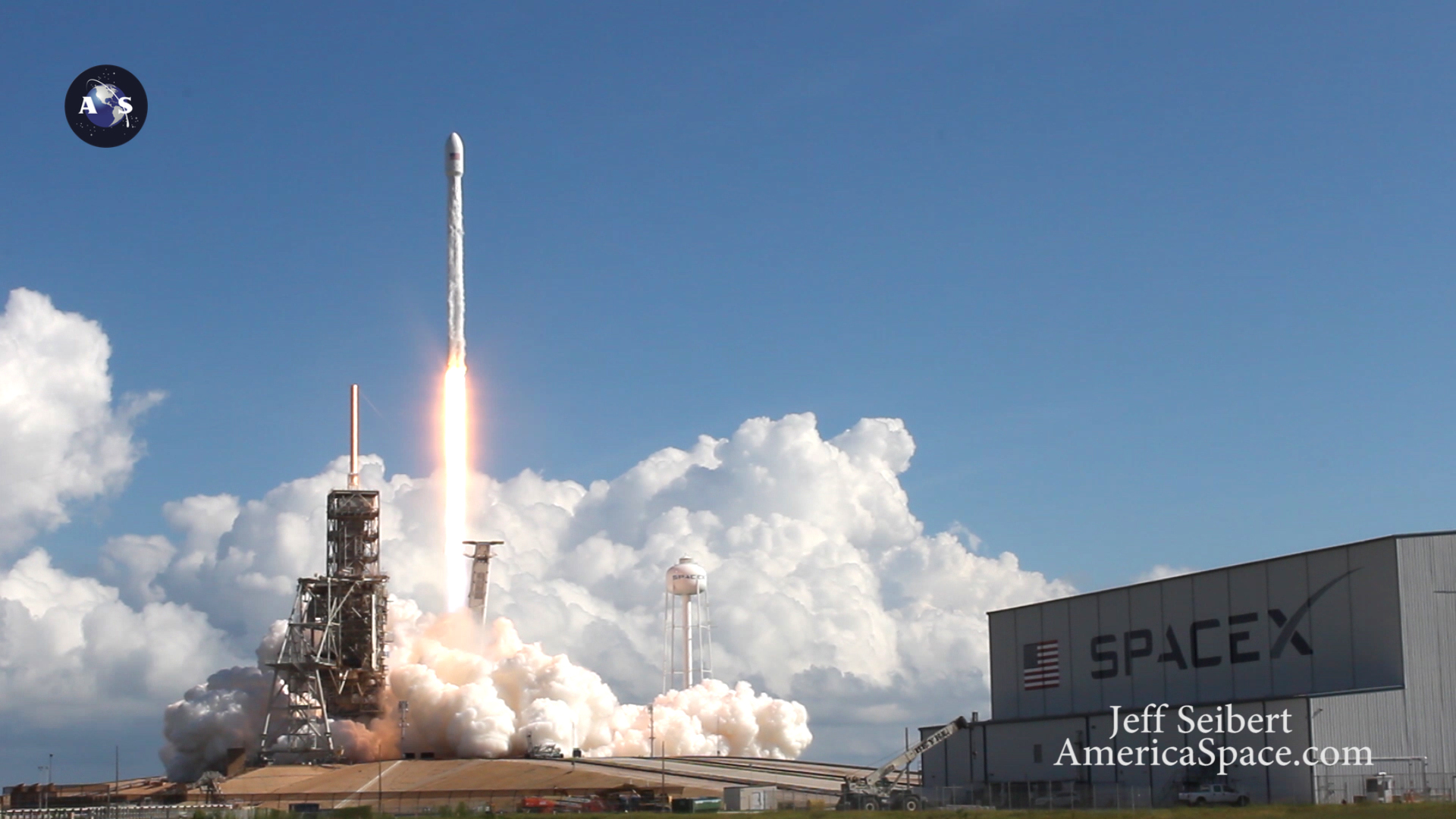
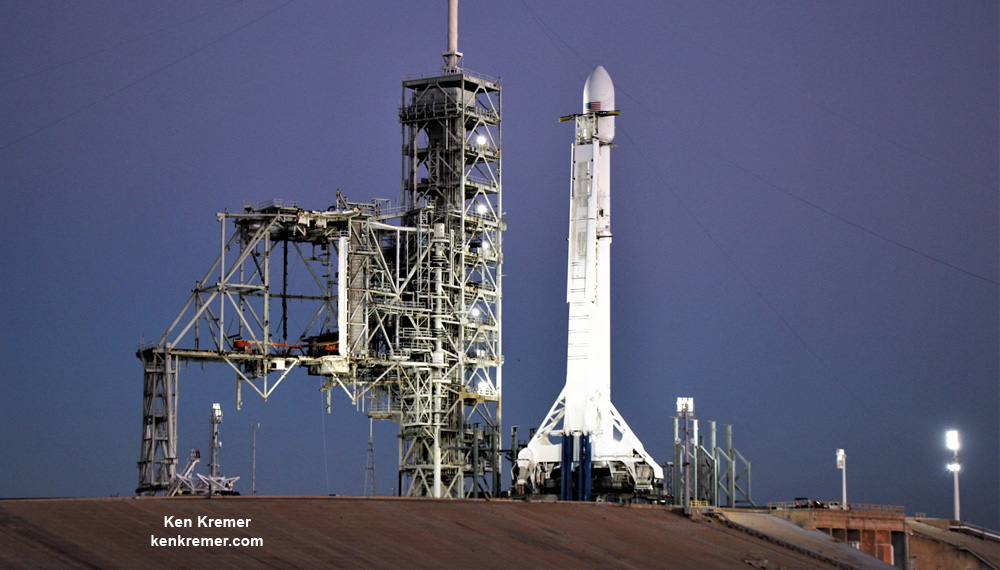
One of the very few tidbits of information we can absolutely confirm (and not deny) is that the clandestine and ownerless ‘Zuma’ Spysat is now targeted for a nighttime launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from seaside Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a lengthy 2 hour window.
We can also confirm that the launch contract was arranged as a commercial enterprise under the auspices of Northrop Grumman Corporation – as a means to significantly slash launch costs for whatever U.S government entity is responsible for Zuma.
That goal is completely in line with SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk’s entire company-wide goal in developing the Falcon and Dragon family of rockets and spaceships.
“The U.S. Government assigned Northrop Grumman the responsibility of acquiring launch services for this mission,” Lon Rains, Northrop Grumman Director of Communications, told Universe Today.
“We have procured the Falcon 9 launch service from SpaceX.”
The launch window at pad 39A opens at 8 p.m. EST (0100 GMT). It extends for two full hours until 10 p.m. EST (0300 GMT).
We can further confirm that the launch was postponed a day to Thursday from the originally slated Wednesday night target – ostensibly to deal with last minute ‘mission assurance issues to insure the rocket and payload are ready for a launch upon which SpaceX’s reputation is on the line for future high value national security payloads of the most critical importance to the US governments Defense and Spy agencies
“SpaceX is now targeting Thursday, Nov. 16 for launch of the Zuma mission,” said SpaceX spokesman John Taylor.
“Both Falcon 9 and the payload remain healthy; teams will use the extra day to conduct some additional mission assurance work in advance of launch.”
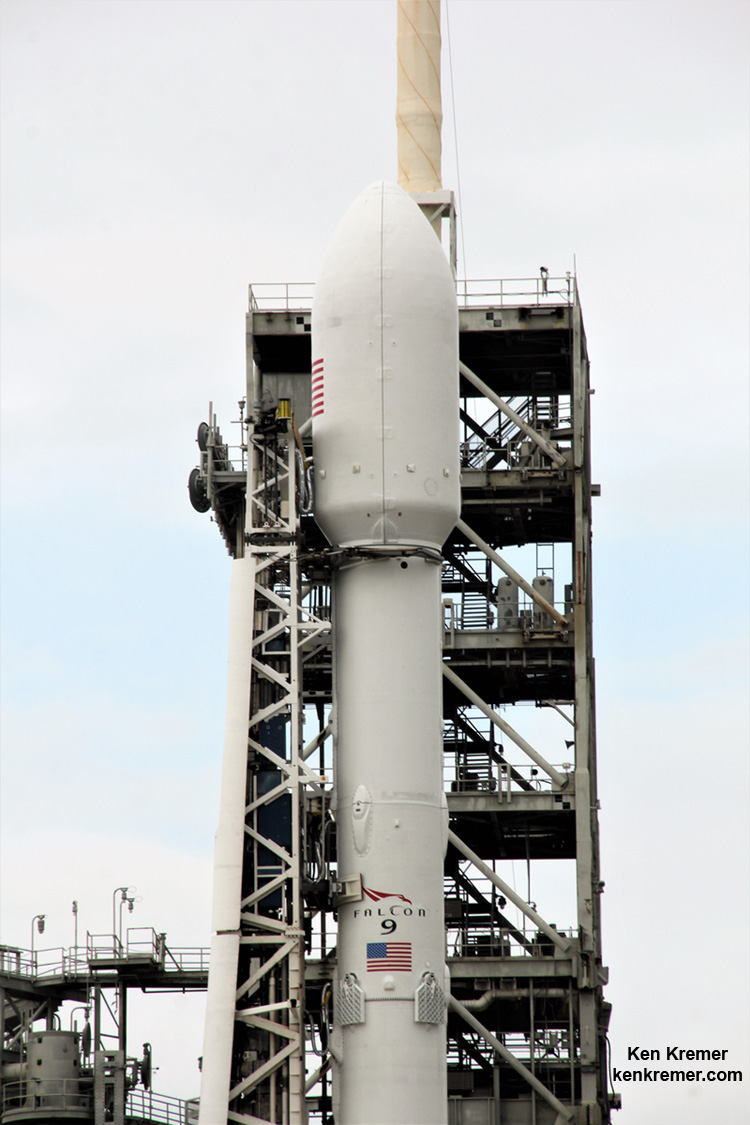

You can watch the launch live on a SpaceX dedicated webcast starting about 10 minutes prior to the 8 p.m. EDT (0100 GMT) liftoff time.
Watch the SpaceX broadcast live at: SpaceX.com/webcast
The launch window for the newly built booster extends for two hours until it closes at 10 p.m. EDT (0300 GMT).
The weather outlook is rather favorable along the Florida Space Coast with a 90% chance of favorable conditions at launch time according to U.S. Air Force meteorologists with the 45th Space Wing Weather Squadron at Patrick Air Force Base.
The primary concerns on Nov. 16 are only for the Cumulous Cloud Rule.
The odds get even high at greater than 90% favorable for the 24 hour scrub turnaround day Nov 17.
The launch window remains the same on Nov 17 at 8 to 10 p.m.
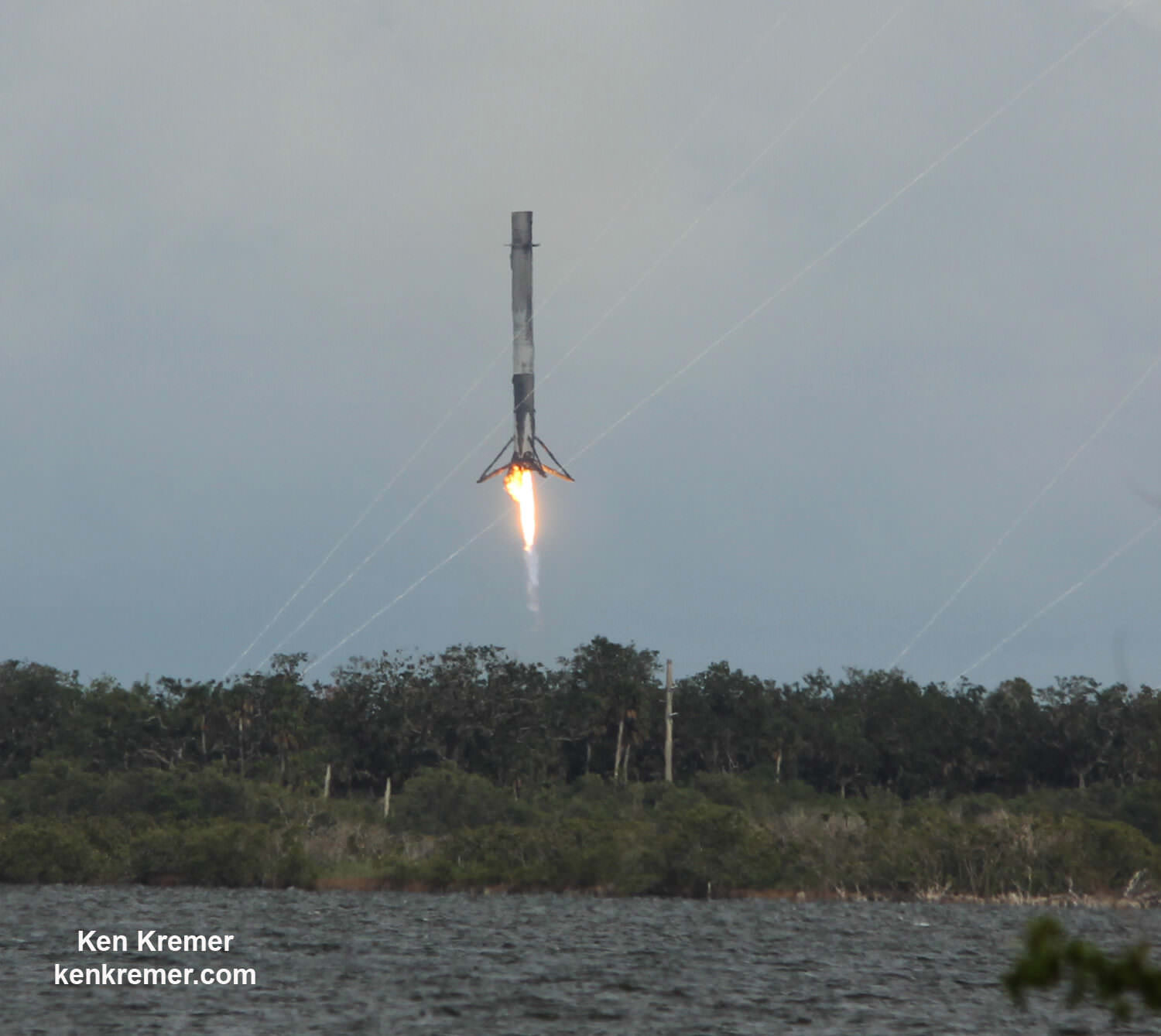

Furthermore the two stage 229-foot-tall (70-meter-tall) Falcon 9 rocket was raised to vertical launch position later today Wednesday afternoon Nov. 15 – so everything seems to be in place for a Thursday evening launch attempt.

However we don’t know anything about the ‘Zuma’ payloads characteristics and vital statistics – despite the seemingly endless leaks streaming out of Washington these days.
“The Zuma payload is a restricted payload,” Rains told me.
So quite naturally we’re all curious for any nugget of information from which we might draw some reasonable conclusions based on the scientific method of analysis.
The little bits we do know is that the launch services for the ownerless government payload are being procured by Northrop Grumman Corporation under a commercial contract with a stated goal to find a develop a “cost effective approach”
“Northrop Grumman is proud to be a part of the Zuma launch,” Rains added.
“This event represents a cost effective approach to space access for government missions.”
One juicy tidbit we do know is that it is intended for launch to low Earth orbit (LEO).
“It will be launched into Low Earth Orbit,” Rains informed me.
Low Earth Orbit extends upwards to roughly 1200 miles altitude and includes the ISS orbit for example at approx. 250 miles.
“As a company, Northrop Grumman realizes this is a monumental responsibility and we have taken great care to ensure the most affordable and lowest risk scenario for Zuma.”
In addition to launch services Northrop Grumman Corporation may have manufactured the Zuma payload – although that’s not even known.

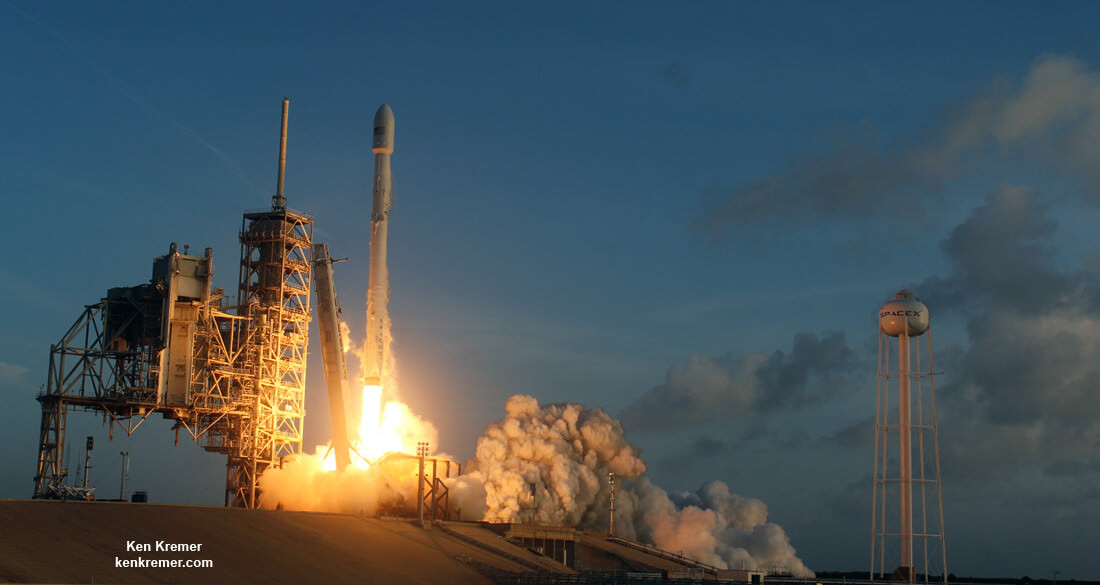
SpaceX has successfully launched a pair of diverse national security payloads this year already with identified customers. Namely the NROL-76 surveillance satellite for the NRO on May 1, 2017 and the OTV-5 military spaceplane for the USAF on Sept. 7.

The long launch window should significantly increase the chance of launching Zuma and removing any errant or intentional boaters and flyers from the restricted airspace around the launch pads.
That’s increasingly important these days given that a pair of critical NASA science mission this week and in the past 3 days were scrubbed near T Zero on both US East and West coast launch pads in Virginia for the Orbital ATK Antares rocket and in California for the ULA Delta II rocket.
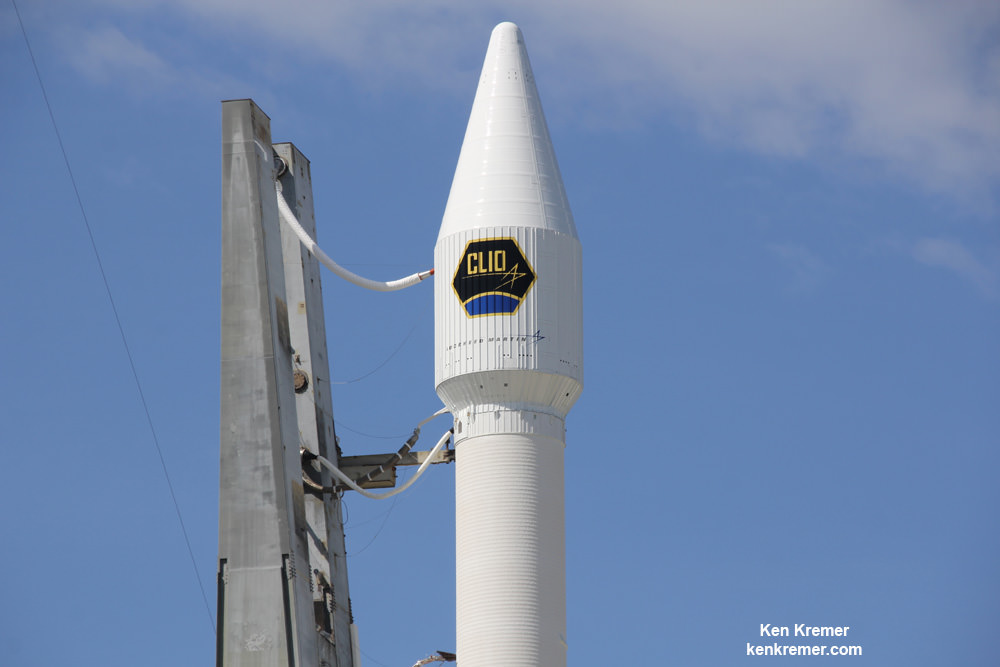
‘Homeless’ government satellites not even claimed by the NRO are rather rare.
A recent example is Clio, an unclaimed mission from Lockheed Martin.
Clio launched at night on a ULA Atlas V on September 16, 2014 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fl.

Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of SpaceX Zuma, KoreaSat-5A & SES-11, ULA NROL-52 and NASA and space mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Learn more about the upcoming SpaceX Falcon 9 Zuma launch on Nov 16, 2017, upcoming Falcon Heavy and CRS-13 resupply launches, NASA missions, ULA Atlas & Delta launches, SpySats and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events at Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL:
Nov 17: “SpaceX Falcon 9 Zuma launch, ULA Atlas NRO NROL-52 spysat launch, SpaceX SES-11, CRS-13 resupply launches to the ISS, Intelsat35e, BulgariaSat 1 and NRO Spysat, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew capsules from Boeing and SpaceX , Heroes and Legends at KSCVC, GOES-R weather satellite launch, OSIRIS-Rex, Juno at Jupiter, InSight Mars lander, SpaceX and Orbital ATK cargo missions to the ISS, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, Curiosity and Opportunity explore Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings