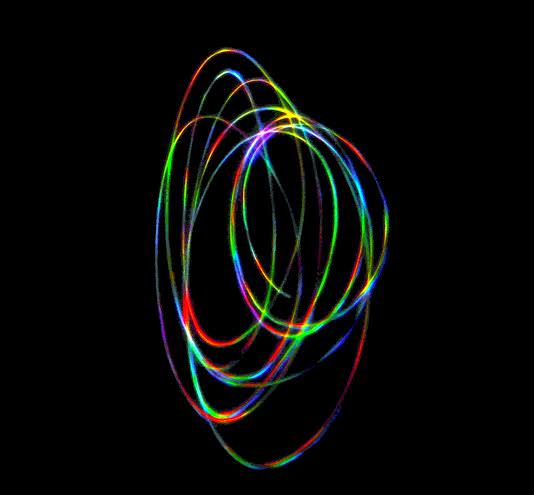
Ever notice how the brilliant star Sirius appears to change colors right before your eyes? Astrophotographer Roshaan Bukhari from Pakistan wanted to see for himself how this twinkling star changes in color due to the effects of our atmosphere as its light gets refracted and he did a little experiment with his telescope and camera. What resulted was a unique and colorful astrophoto!
“I pointed my telescope to sharply focus on Sirius and put my DSLR camera to 2 second exposure while holding it near the eyepiece and focusing Sirius from the camera viewfinder as well,” Roshaan told Universe Today via email. “I started shaking the telescope in a circular manner by holding it from the eyepiece so that Sirius was dancing all over the eyepiece in an ‘O’ shape. That’s when I pressed the camera shutter button and the shutter remained open for 2 seconds, recording the colours and the pattern of Sirius within the eyepiece.”
Roshaan said he did enhance the contrast to bring the trails out more clearly, but the color saturation and hues have not been altered in any way. The changes in color in just a two-second exposure are really amazing!
Roshaan shared how astronomy and astrophotography in Pakistan is becoming a “blooming field now” — which we are very happy to hear! “And I’m very happy to say that I am a part of it!” he said, adding, “I’m one of the biggest fans of Universe Today and have been listening to it’s podcasts on iTunes since i got my first iPhone back in 2008.”
Here are few more images from Roshaan Bukhari under Pakistan skies:
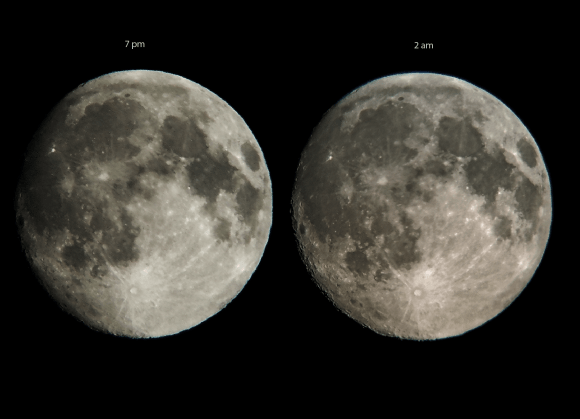

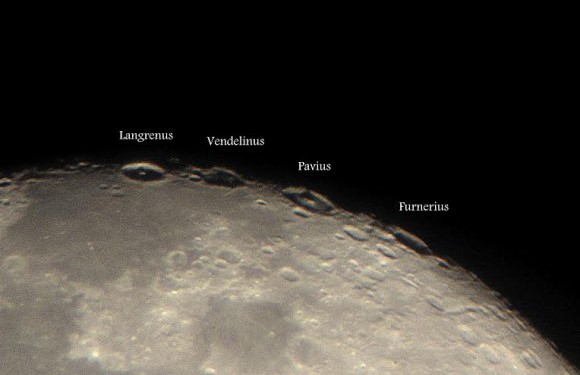
How does the look of the Moon change during the night? These images of the Moon — taken 7 hours apart — were shot through Roshaan’s telescope with his mobile phone camera using the handheld afocal method!
Phase of the moon at 7 pm was 96.8%, while at 2 am it was 97.5% (rate of change of lunar phase turns out to be 0.7% in 7 hours, figures estimated from Stellarium).
Roshaan said the quality of the images is not that great since he took them while there a lot of dust was up in the atmosphere due to some strong winds, but we think they look great!

Thanks to Roshaan for sharing his images from Pakistan.
Want to get your astrophoto featured on Universe Today? Join our Flickr group or send us your images by email (this means you’re giving us permission to post them). Please explain what’s in the picture, when you took it, the equipment you used, etc.




