We have known that water ice exists on the Moon since 1998. These large deposits are found in the permanently shadowed craters around the polar region. The challenge is how to get it since shadowed craters are not the best place for solar powered vehicles to operate. A team of engineers have identified a design for an ice-mining vehicle powered by americium-241. With a half-life of 432 years, this element is an ideal power source for a vehicle to operate in the dark for several decades.
Continue reading “A New Rover Design Could Crawl Across the Moon for Decades Harvesting Water”Lighting Up the Moon’s Permanently Shadowed Craters

The Moon’s polar regions are home to permanently shadowed craters. In those craters is ancient ice, and establishing a presence on the Moon means those water ice deposits are a valuable resource. Astronauts will likely use solar energy to work in these craters and harvest water, but the Sun never shines there.
What’s the solution? According to one team of researchers, a solar collector perched on the crater’s rim.
Continue reading “Lighting Up the Moon’s Permanently Shadowed Craters”Ice Deposits on Ceres Might Only Be a Few Thousand Years Old
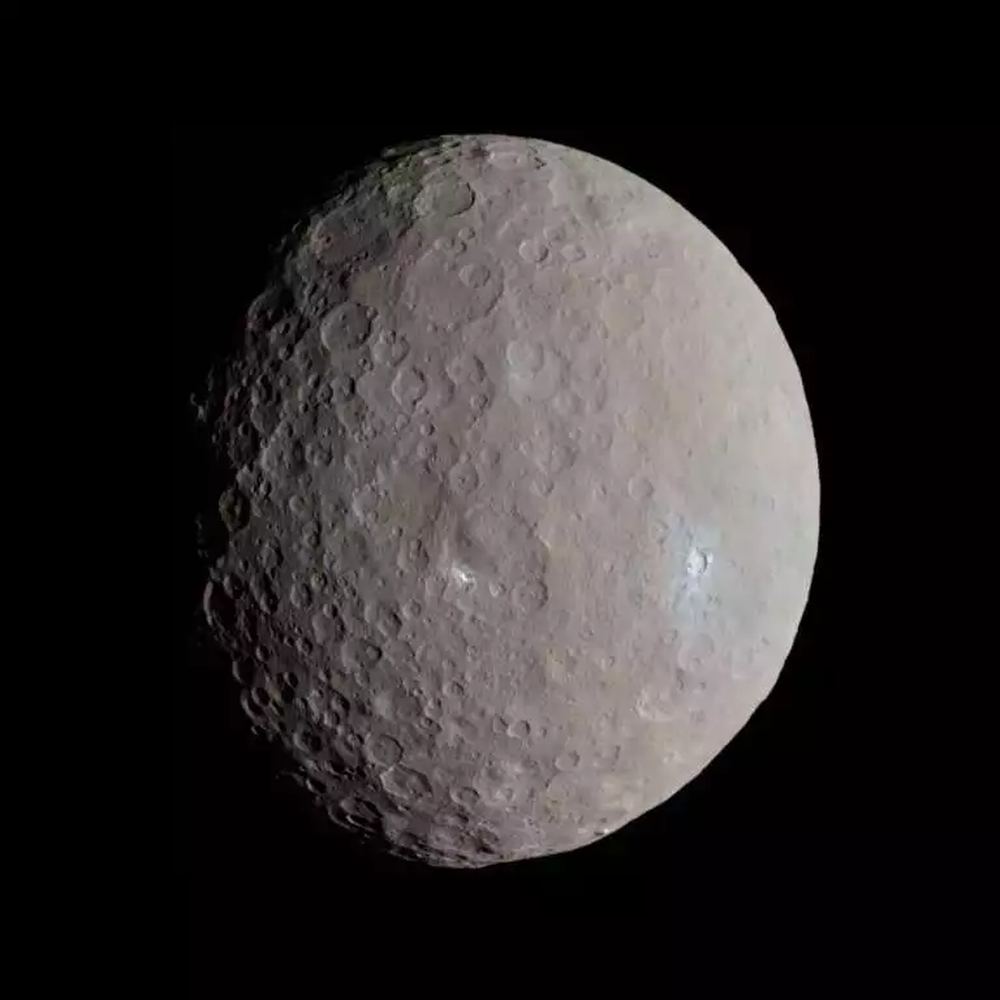

The dwarf planet Ceres has some permanently dark craters that hold ice. Astronomers thought the ice was ancient when they were discovered, like in the moon’s permanently shadowed regions. But something was puzzling.
Why did some of these shadowed craters hold ice while others did not?
Continue reading “Ice Deposits on Ceres Might Only Be a Few Thousand Years Old”Wireless Power Transmission Could Enable Exploration of the Far Side of the Moon
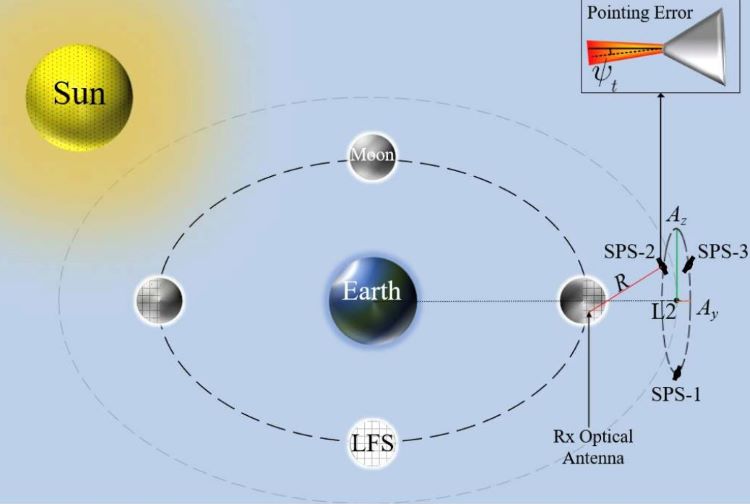
How can future lunar exploration communicate from the far side of the Moon despite never being inline with the Earth? This is what a recent study submitted to IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems hopes to address as a pair of researchers from the Polytechnique Montréal investigated the potential for a wireless power transmission method (WPT) comprised of anywhere from one to three satellites located at Earth-Moon Lagrange Point 2 (EMLP-2) and a solar-powered receiver on the far side of the Moon. This study holds the potential to help scientists and future lunar astronauts maintain constant communication between the Earth and Moon since the lunar far side of the Moon is always facing away from Earth from the Moon’s rotation being almost entirely synced with its orbit around the Earth.
Continue reading “Wireless Power Transmission Could Enable Exploration of the Far Side of the Moon”The Darkest Parts of the Moon are Revealed with NASA’s New Camera
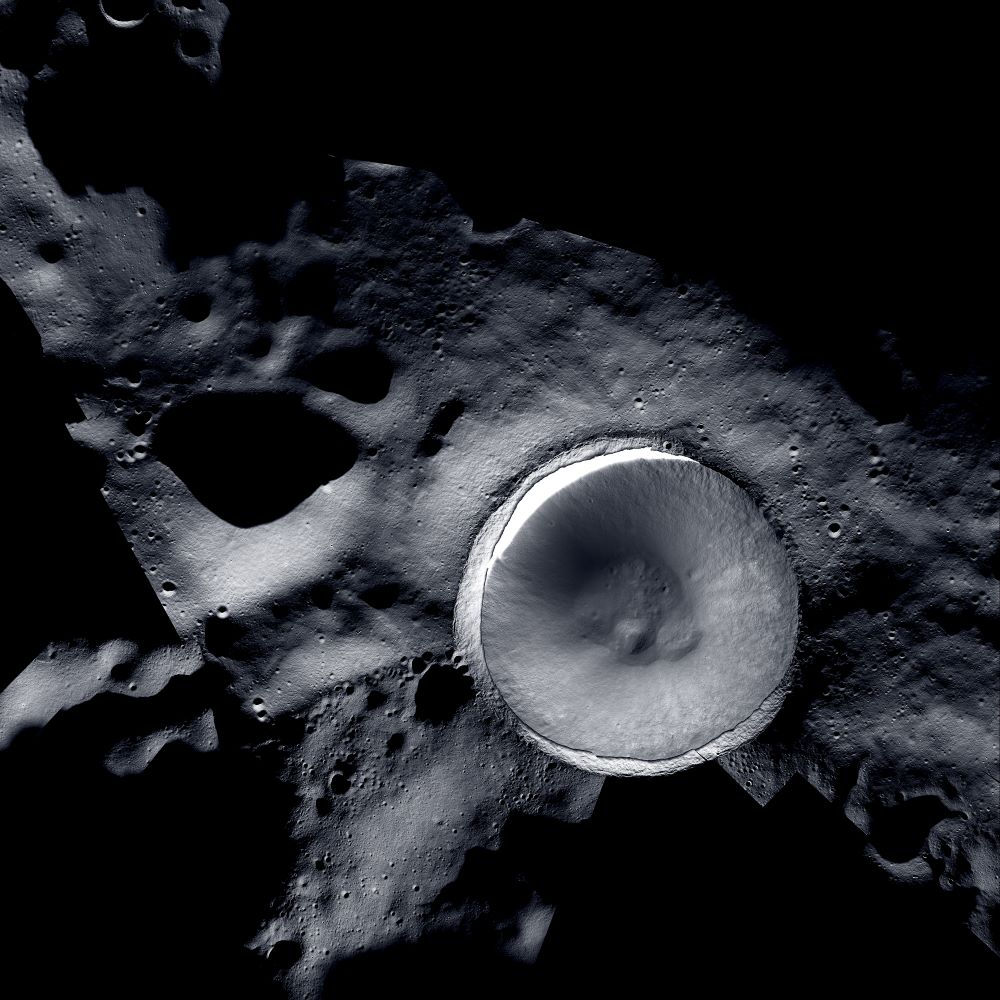
While the surface of the Moon has been mapped in incredible detail over the last several decades, one region has eluded orbital cameras due to the lack of sunlight, which are aptly called the permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon. However, two cameras operating on two different lunar orbiters have recently worked in tandem to produce a stunning mosaic image of the lunar south pole’s Shackleton Crater, a portion of which resides directly on the lunar south pole and whose depths have been shrouded in complete darkness for possibly the last few billion years. As a result, scientists hypothesize that water ice could have accumulated within its dark depths that future astronauts could use for fuel and life support.
Continue reading “The Darkest Parts of the Moon are Revealed with NASA’s New Camera”The Moon's Southern Ice is Relatively Young

Around the Moon’s southern polar region lies the South Pole-Aitken Basin, the single-largest impact basin on the lunar surface. Within this basin, there are numerous permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) that are thought to have trapped water ice over time. These deposits are crucial to future missions like the Artemis Program that will lead to the creation of permanent infrastructure. This water ice will supply crews with a steady source of water for drinking and irrigation and the means for chemically producing oxygen gas and rocket fuel.
For scientists, these PSRs are believed to have emerged when the Moon began migrating away from Earth roughly 2.5 billion years ago. Over time, these regions acted as “cold sinks” and trapped water ice that existed on the lunar surface at the time. However, according to a recent study led by the Planetary Science Institute (PSI), the Moon’s permanently shadowed areas arose less than 2.2 billion years ago and trapped ice even more recently than that. These findings could significantly impact future crewed missions as they indicate that the water ice found in lunar craters could be of more recent origin.
Continue reading “The Moon's Southern Ice is Relatively Young”China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese National Space Administration recently published a study in the journal Space: Science & Technology outlining how the upcoming Chang’e-7 mission, due to launch in 2026, will use a combination of orbital observations and in-situ analyses to help identify the location, amount, and dispersion of water-ice in the permanently-shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon, specifically at the lunar south pole.
Continue reading “China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice”New Spacecraft Can See Into the Permanently Shadowed Craters on the Moon

Shackleton Crater at the lunar south pole is one of the locations on NASA’s shortlist for human exploration with the future Artemis missions. But because craters at the lunar poles — like Shackleton — at have areas that are perpetually in shadow, known as permanently shadowed regions (PSRs), we don’t know for sure what lies inside the interior. However, a new spacecraft with a specialized instrument is about to change all that.
Continue reading “New Spacecraft Can See Into the Permanently Shadowed Craters on the Moon”‘TransFormers’ Could Beam Light Into Permanently Shadowed Craters
Permanently shadowed craters on the moon or Mercury are one of the most exciting locations to search for water. Because the walls of these craters protect certain spots inside from the rays of the sun, it’s quite possible for ice to lurk inside of there.
We’ve found ice on so-called airless worlds because of this trick of geometry. So how about exploring them? What’s the best way to do so?
The NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts office suggests using TransFormers to get inside these places. No, not the awesome robots you see in the movies, but still something that has a certain degree of complication: “multifunctional platforms that can change their shape and function”, according to the agency.
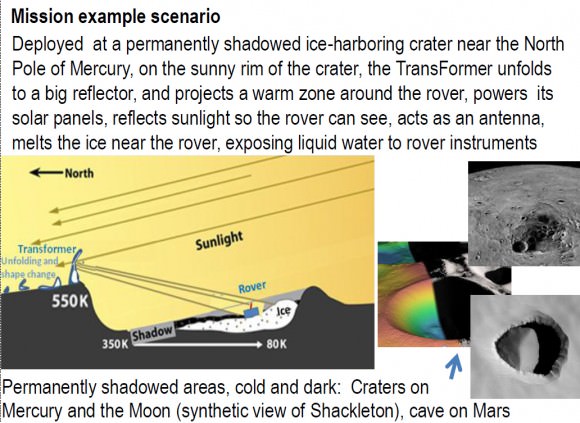
Like the iconic science fiction heroes, however, the TransFormers would be able to unfold and change their shape. These machines could relay information between a rover and an orbiting satellite, or reflect solar energy on to a target (say, a solar-powered rover).
The challenge with putting a rover in a permanently shadowed crater is figuring out how to power it. Nuclear power sources have special handling considerations during preparation and launch that must be taken into account for safety reasons. Solar power, however, would not be possible in these craters given there is no sunlight.
Putting a TransFormer at the crater’s edge, however, could make the environment a friendly one for a rover powered by the sun. It could reflect light inside and provide a power source for the rover to keep moving.

And once that rover starts running around, it would have immense scientific benefits, NASA stated.
“For example, water found in the permanently shadowed areas of craters on the Moon or Mercury can reveal clues about planetary formation and history, and could be used as a resource for astronauts,” the agency wrote.
This could even be extended to the Red Planet, which offers the enticing possibility of stumbling across life.
“Cave exploration on Mars offers the possibility of finding extraterrestrial life; furthermore, caves are time capsules preserving geochemical traces and may safely shelter future human explorers.”
Source: NIAC


