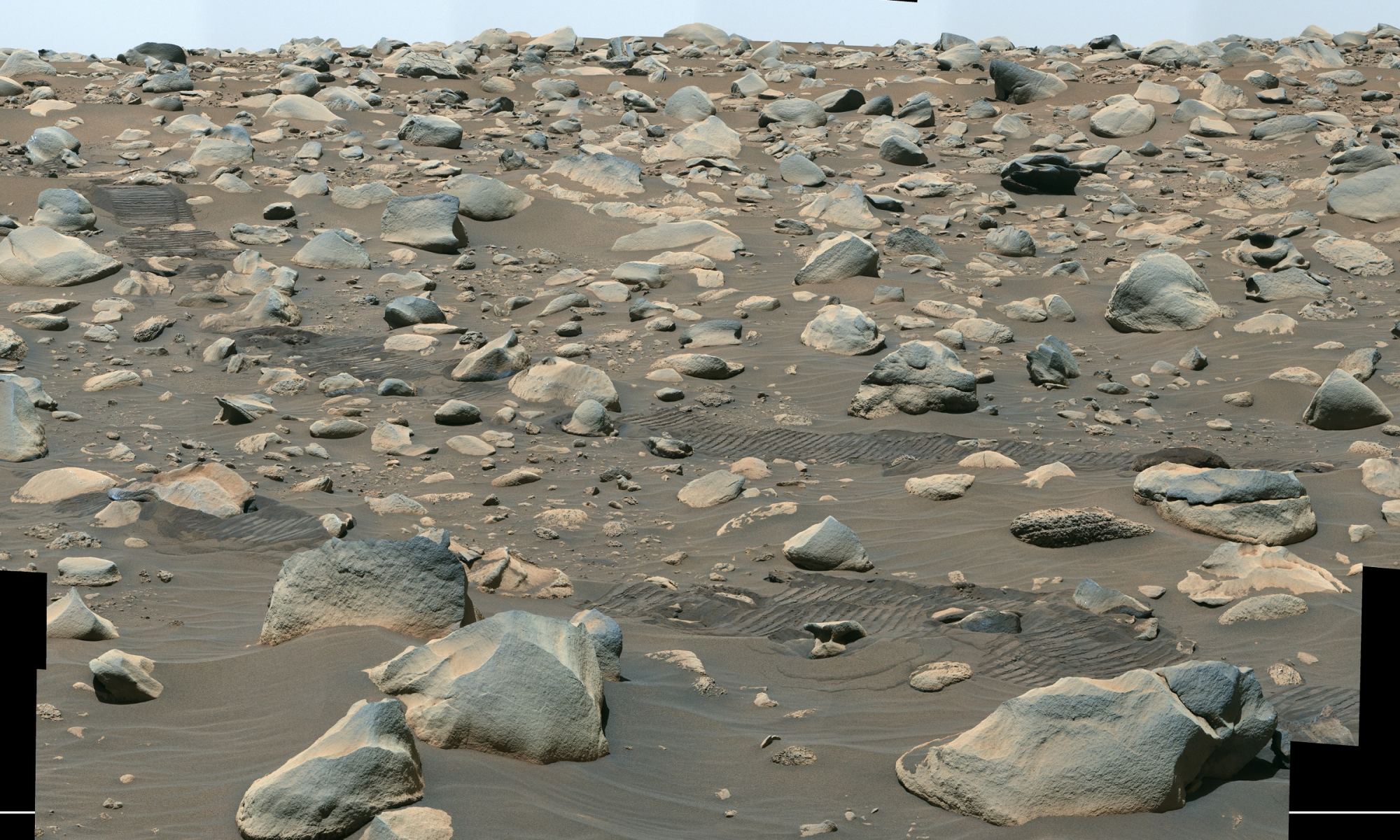
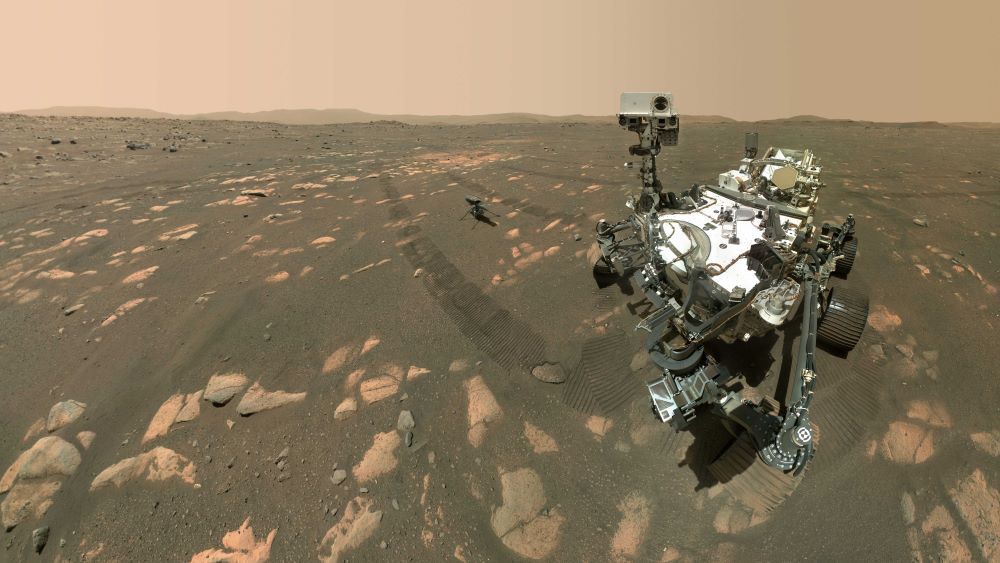
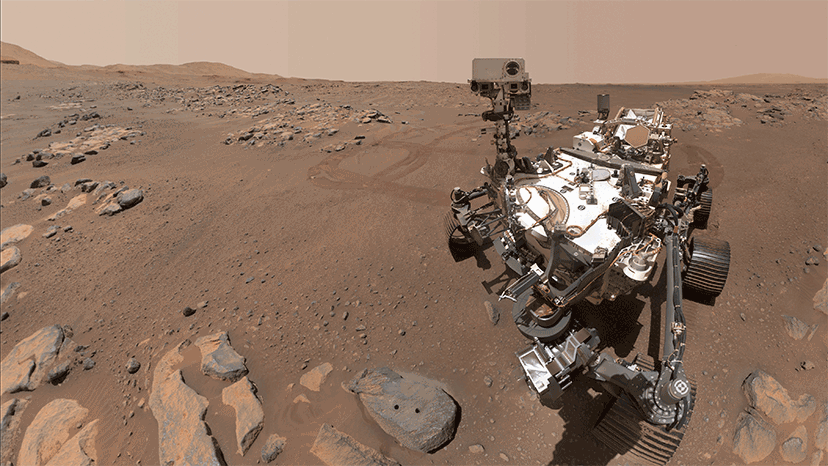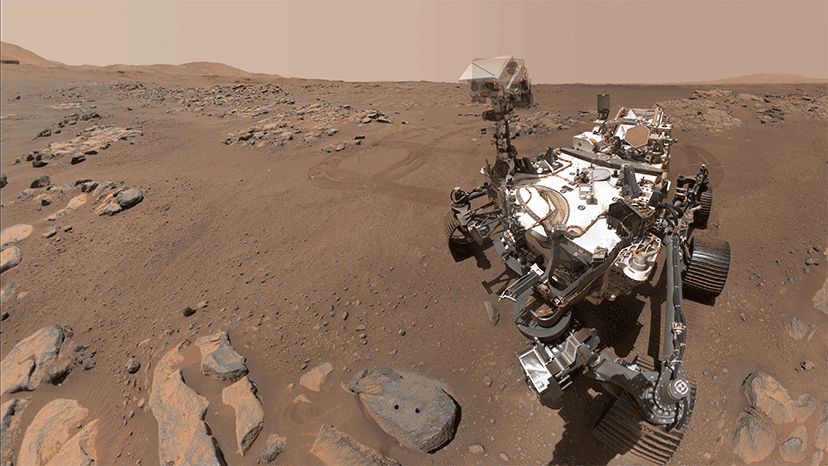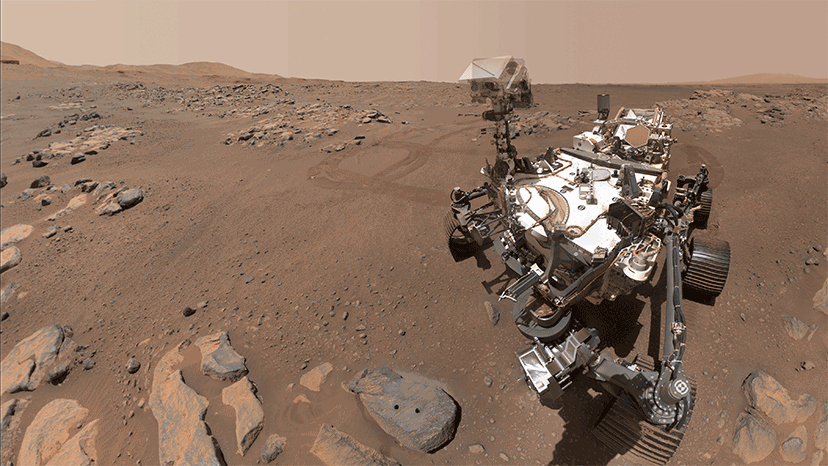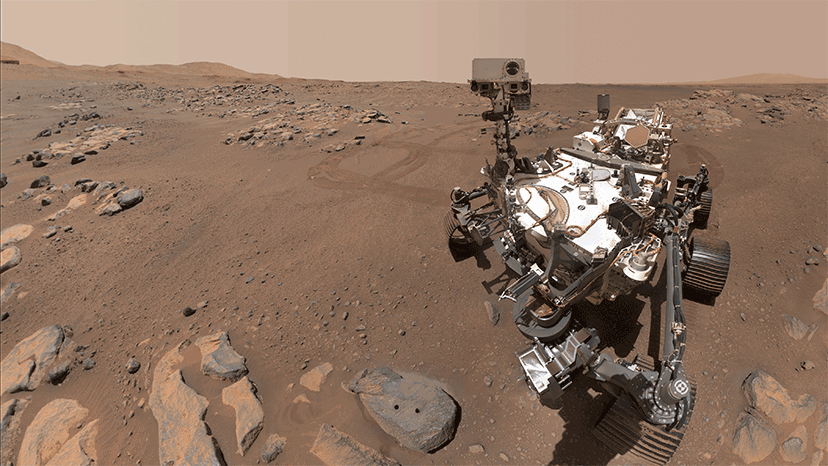
On August 30th, 2023, on the 899th Martian day (sol 899) of its mission, NASA’s Perseverance rover spotted a dust devil while exploring the Jezero Crater. The images taken by one of the rover’s Navigation Cameras (NavCams) were used to make a video (shown below), which is composed of 21 frames taken four seconds apart and sped up 20 times. Similar to small, short-lived whirlwinds on Earth, these vertical columns of wind form when pockets of hot air near the surface rise quickly through cooler air above it. By studying them, scientists hope to learn more about Mars’ atmosphere and improve their weather models.
Continue reading “Perseverance Watches a Dust Devil Whirl Past”Perseverance Watches a Dust Devil Whirl Past