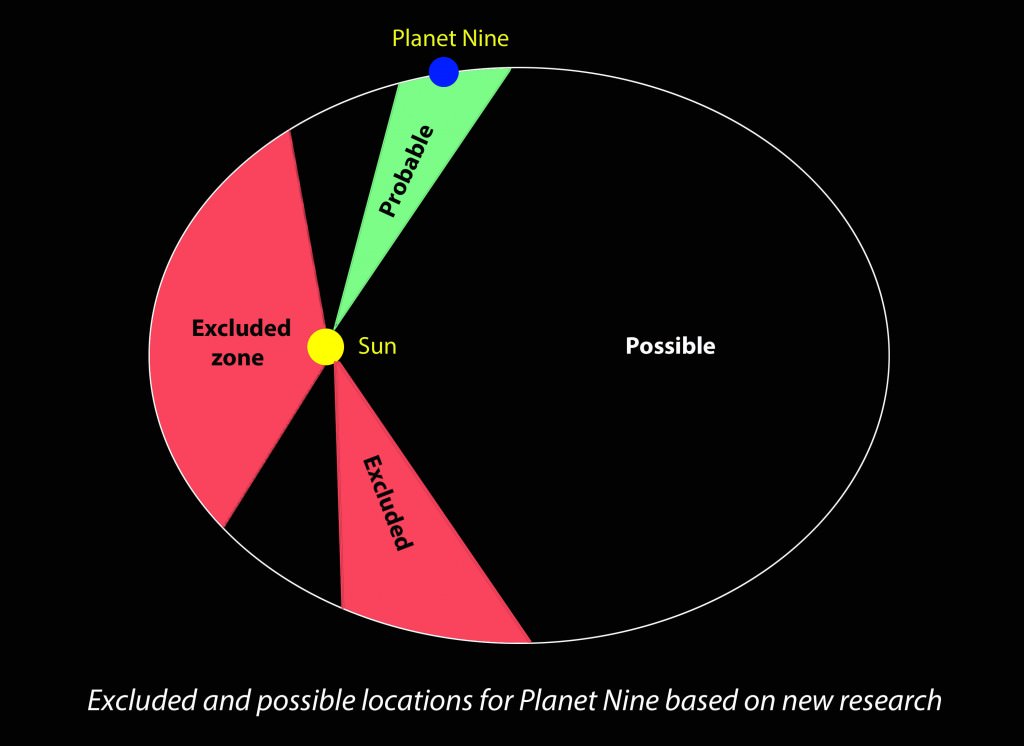
Planet Nine, the massive orb proposed to explain the clustered orbits of a half dozen remote Kuiper Belt asteroids, may have a darker side. Periodic mass extinctions on Earth, as indicated in the global fossil record, could be linked to the hypothetical planet according to research published by Daniel Whitmire, a retired professor of astrophysics and faculty member of the University of Arkansas Department of Mathematical Sciences.

Planet Nine is estimated to be 10 times more massive than Earth and currently orbiting about 1,000 times farther away from the Sun. Astronomers have been searching for a potential large planet — for years called “Planet X” — that might be implicated in a handful of major mass extinctions over the past 500 million years. During those times, between 50 and more than 90% of species on Earth perished in a geological heartbeat. The worst, dubbed the Permian-Triassic event or the Great Dying, occurred 250 million years ago and saw the disappearance of more than 90% of the planet’s life in a geological heartbeat.
Whitmire and his colleague, John Matese, first published research on the connection between Planet X and mass extinctions in the journal Nature in 1985 while working as astrophysicists at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. They proposed that perturbations from a 10th planet (Pluto was considered a planet back then) could fling a shower of comets from the Kuiper Belt beyond Neptune in Earth’s direction every 28 million years in sync with recorded mass extinctions.
Two other ideas also proposed at the time they wrote their paper — a sister star to the Sun and vertical oscillations of the Sun as it orbits the galaxy — have since been ruled out because the timing is inconsistent with the extinction record. Only Planet X remained as a viable theory, and it’s now gaining renewed attention.
Neil deGrasse Tyson explains precession and Mercury’s orbit
Whitmire and Matese proposed that as Planet X orbits the Sun, its tilted orbit slowly rotates, causing the location of its perihelion (closest point to the Sun) to slowly precess or shift position along its orbit instead of remaining in the same place. Every planet precesses, so no surprises here.

But location can make a huge difference. The team proposed that Planet X’s slow orbital gyration directs it into the Kuiper Belt approximately every 27 million years, knocking comets into the inner Solar System. The dislodged comets not only smash into the Earth, they also vaporize and break apart in the inner Solar System as they get nearer to the Sun, reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth. Add it up, and you have a recipe for cyclic destruction.
One thing to keep in mind is that their research led them to conclude that Planet X was only 5 times as massive as Earth and 100 times farther from the Sun. This doesn’t jive with the size and mass particulars for Planet Nine inferred by researchers Konstantin Batygin and Michael E. Brown at Caltech earlier this year, but until someone tracks the real planet down, there’s room for argument.
Comet and asteroid showers are often cited as possible bad guys in extinction episodes. And why not? We have hard evidence of the asteroid impact that sealed the dinosaurs’s fate 65 million years ago and have seen some six impacts at Jupiter since 1994. It’s cosmic billiards out there folks, and the game’s not over.



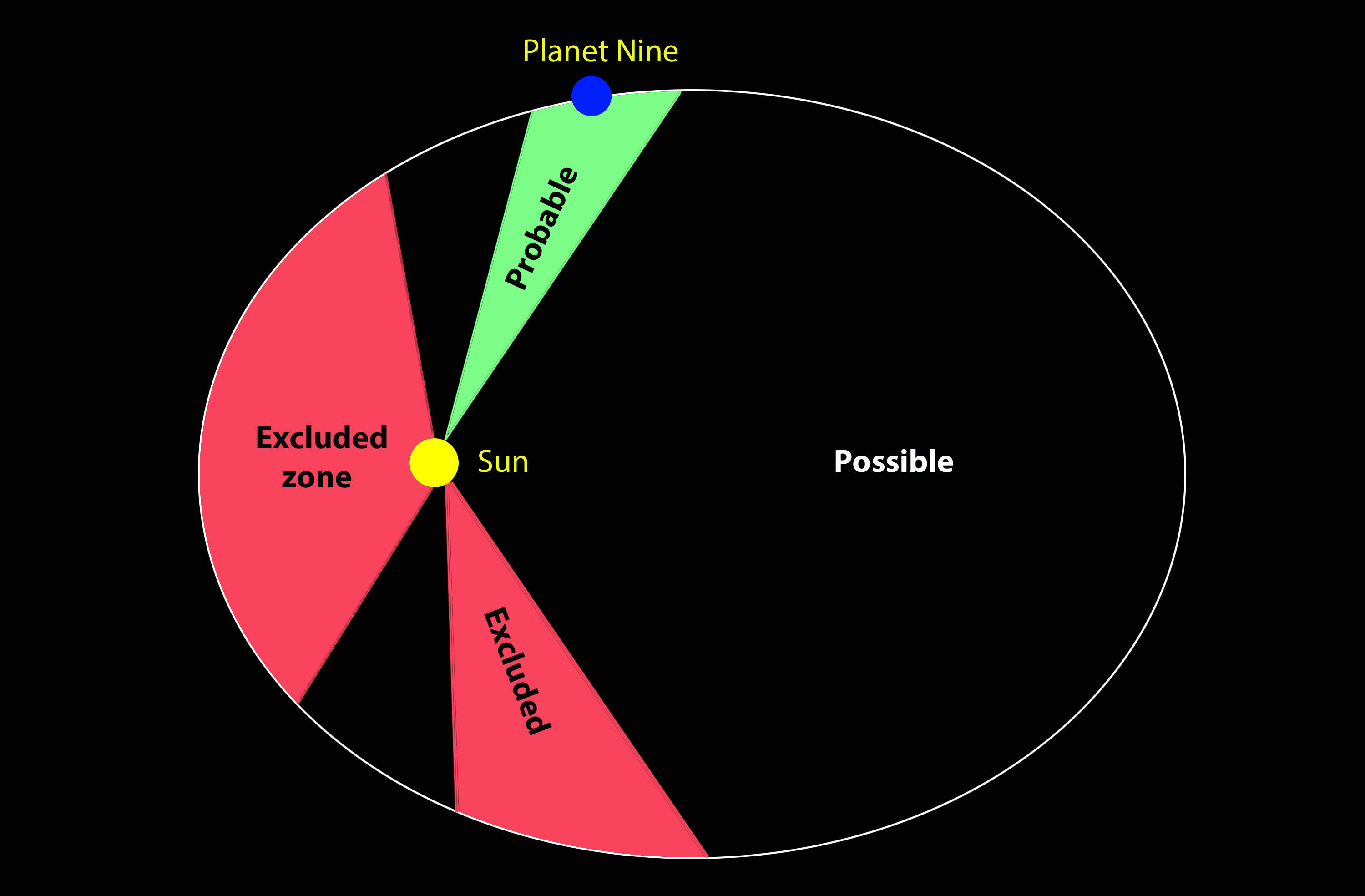

![The six most distant known objects in the solar system with orbits exclusively beyond Neptune (magenta) all mysteriously line up in a single direction. Also, when viewed in three dimensions, they tilt nearly identically away from the plane of the solar system. Batygin and Brown show that a planet with 10 times the mass of the earth in a distant eccentric orbit anti-aligned with the other six objects (orange) is required to maintain this configuration. Credit: Caltech/R. Hurt (IPAC); [Diagram created using WorldWide Telescope.]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/Planet-nine-1024x576.jpg)