Star clusters tend to host more hot Jupiters than average, but why? A team of astronomers have proposed a new solution, and it involves a lot of swapping of stellar neighbors.
Continue reading “Trading Spaces: How Swapping Stars Create Hot Jupiters”Baby Gas Giants Cast Shadows on Their Siblings

A team of astronomers has caught glimpses of gas giants forming around a very young star.
The nascent giants are having a chilling effect on their potential siblings.
Continue reading “Baby Gas Giants Cast Shadows on Their Siblings”It’s Tough to Find Evidence of Stars Eating Planets
Tragically sometimes stars engulf their own planets. While most stars are able to quickly cover up the evidence for their crime, a new study by astronomers has revealed that in some cases the evidence can linger for up to two billion years.
Continue reading “It’s Tough to Find Evidence of Stars Eating Planets”A new way to Discover Planets? Astronomers Detect an Exoplanet by Seeing its Trojan Belts

Although we have found thousands of exoplanets in recent years, we really only have three methods of finding them. The first is to observe a star dimming slightly as a planet passes in front of it (transit method). The second is to measure the wobble of a star as an orbiting planet gives it a gravitational tug (Doppler method). The third is to observe the exoplanet directly. Now a new study in the Astrophysical Journal Letters has a fourth method.
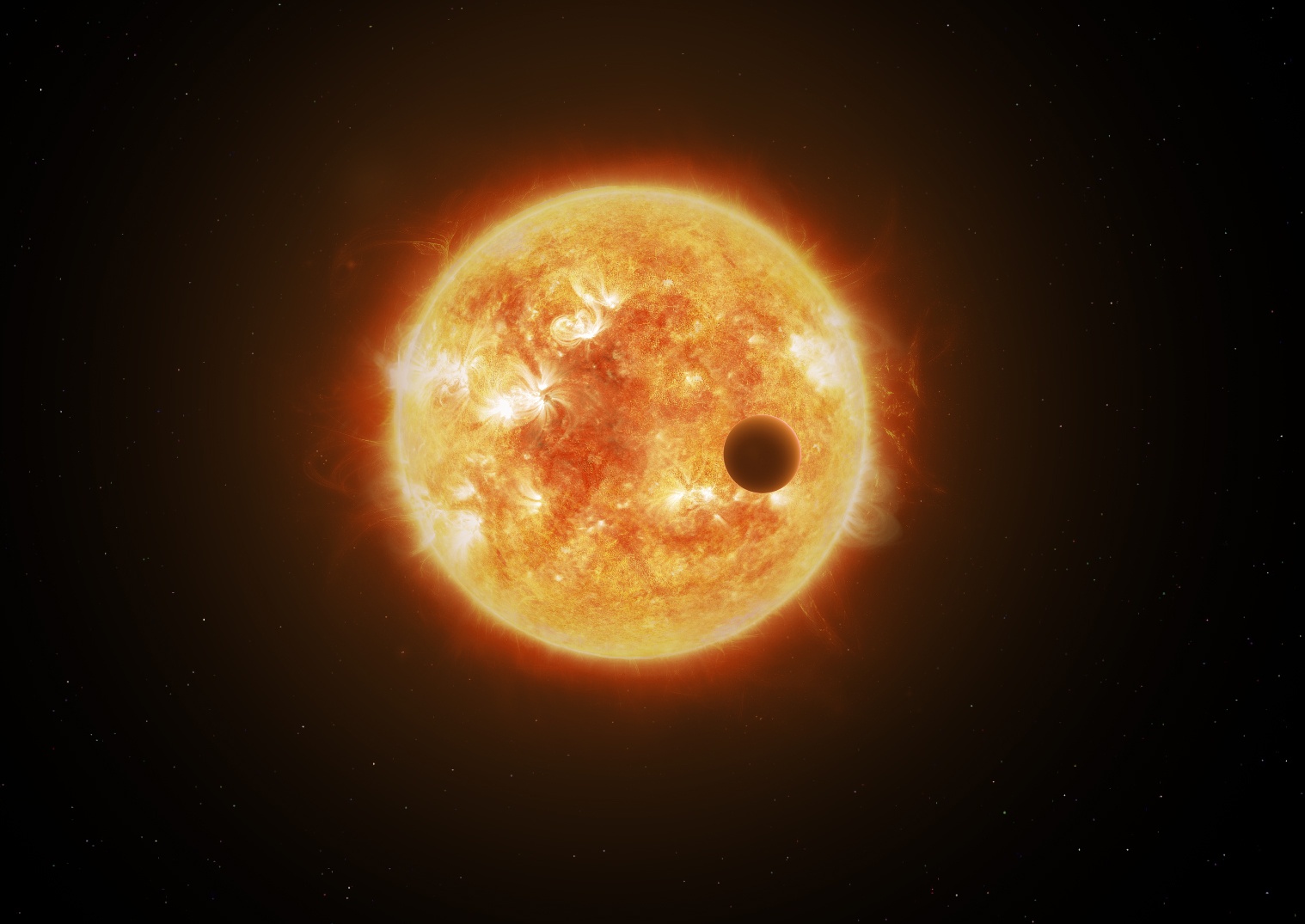
Continue reading “A new way to Discover Planets? Astronomers Detect an Exoplanet by Seeing its Trojan Belts”Hot Stars Blast Away at gas Giants Until Only Their Rocky Cores Remain

In our solar system, we have two types of planets. Small, warm, rocky worlds populate the inner region, while the outer region has cold gas giants. Intuitively this makes a lot of sense. When the solar system was forming, the Sun’s light and heat must have pushed much of the gas toward the outer system, leaving heavier dust and rock to form the inner worlds. Giants could only grow in the cold, dark outer solar system. But we now know our solar system is more the exception than the rule. Many star systems have large gas planets that orbit close to their stars. These hot Jupiters and hot Neptunes are unlike anything in our solar system, and astronomers are keen to understand what they may be like.
Continue reading “Hot Stars Blast Away at gas Giants Until Only Their Rocky Cores Remain”How Do Hot Jupiters Get So Close to Their Stars?

In this age of exoplanet discovery, we’ve discovered thousands of exoplanets of different types. The hot Jupiter is one of the most unusual types. There’s nothing like it in our Solar System.
Hot Jupiters are massive gas planets, and they attract a lot of attention because they’re so close to their stars and reach blistering temperatures. Their existence spawns a lot of questions about their formation and evolution. A new study is trying to answer some of those questions by determining hot Jupiters’ ages.
Continue reading “How Do Hot Jupiters Get So Close to Their Stars?”Digging Through Kepler Data Turns Up a Near Twin of Jupiter
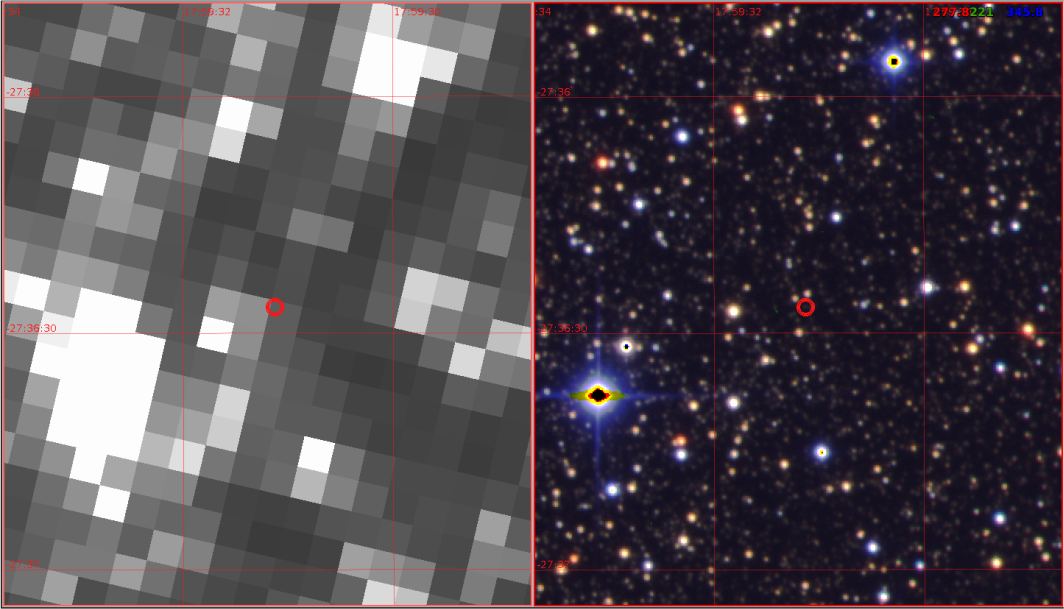

NASA’s Kepler planet-hunting spacecraft was deactivated in November 2018, about ten years after it launched. The mission detected over 5,000 candidate exoplanets and 2,662 confirmed exoplanets using the transit method. But scientists are still working with all of Kepler’s data, hoping to uncover more planets in the observations.
A team of researchers have announced the discovery of one more planet in the Kepler data, and this one is nearly a twin of Jupiter.
Continue reading “Digging Through Kepler Data Turns Up a Near Twin of Jupiter”Hubble Has Been Watching This Planet Form for 13 Years
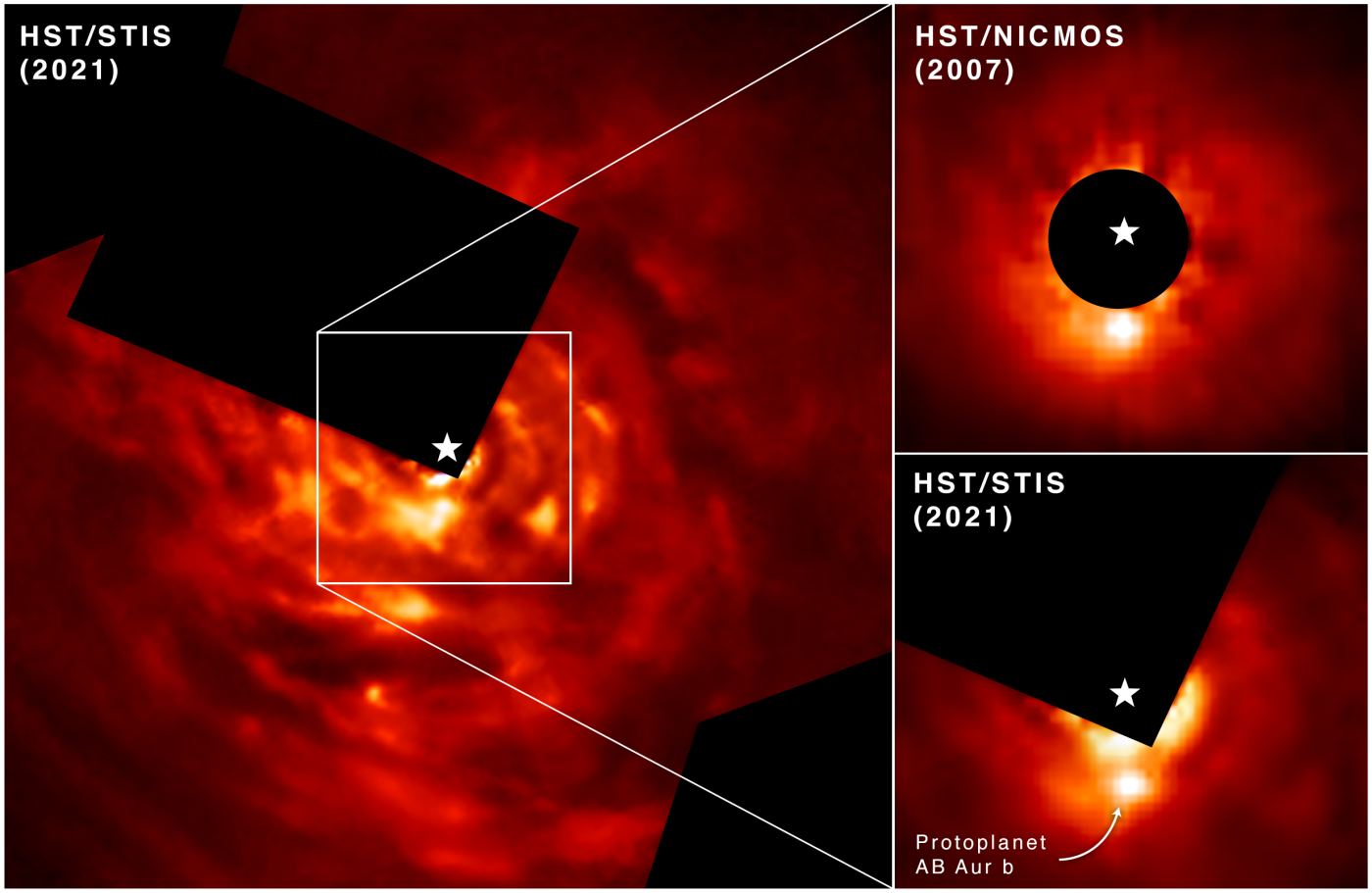
Hubble’s most remarkable feature might be its longevity. The Hubble has been operating for almost 32 years and has fed us a consistent diet of science—and eye candy—during that time. For 13 of its 32 years, it’s been checking in on a protoplanet forming in a young solar system about 530 light-years away.
Planet formation is always a messy process. But in this case, the planet’s formation is an “intense and violent process,” according to the authors of a new study.
Continue reading “Hubble Has Been Watching This Planet Form for 13 Years”A Second Generation of Planets can Form Around a Dying Star

When young stars coalesce out of a cloud of molecular hydrogen, a disk of leftover material called a protoplanetary disk surrounds them. This disk is where planets form, and astronomers are getting better at peering into those veiled environments and watching embryonic worlds take shape. But young stars aren’t the only stars with disks of raw material rotating around them.
Some old, dying stars also have disks. Can a second generation of planets form under those conditions?
Continue reading “A Second Generation of Planets can Form Around a Dying Star”Rings in the Early Solar System Kept our Planet From Becoming a Super-Earth
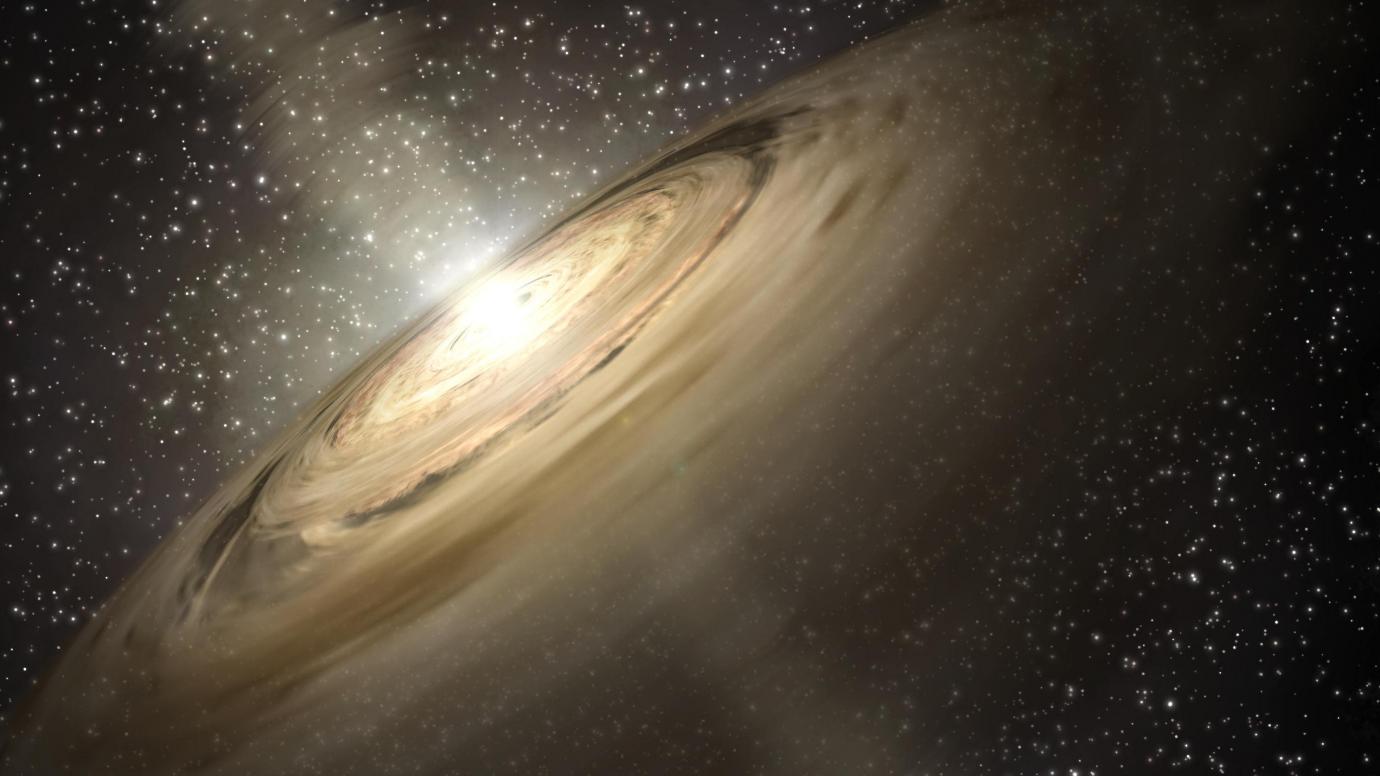

To date, a total of 4,884 extrasolar planets have been confirmed in 3,659 systems, with another 8,414 additional candidates awaiting confirmation. In the course of studying these new worlds, astronomers have noted something very interesting about the “rocky” planets. Since Earth is rocky and the only known planet where life can exist, astronomers are naturally curious about this particular type of planet. Interestingly, most of the rocky planets discovered so far have been many times the size and mass of Earth.
Of the 1,702 rocky planets confirmed to date, the majority (1,516) have been “Super-Earths,” while only 186 have been similar in size and mass to Earth. This raises the question: is Earth an outlier, or do we not have enough data yet to determine how common “Earth-like” planets are. According to new research by an international team led by Rice University, it may all have to do with protoplanetary rings of dust and gas in an early solar system.
Continue reading “Rings in the Early Solar System Kept our Planet From Becoming a Super-Earth”