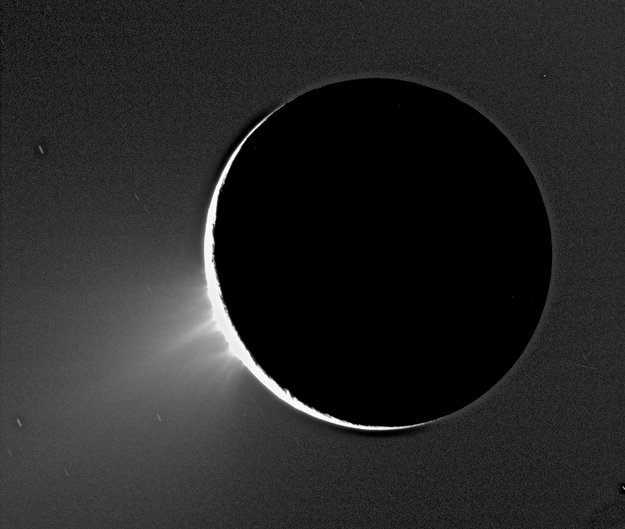
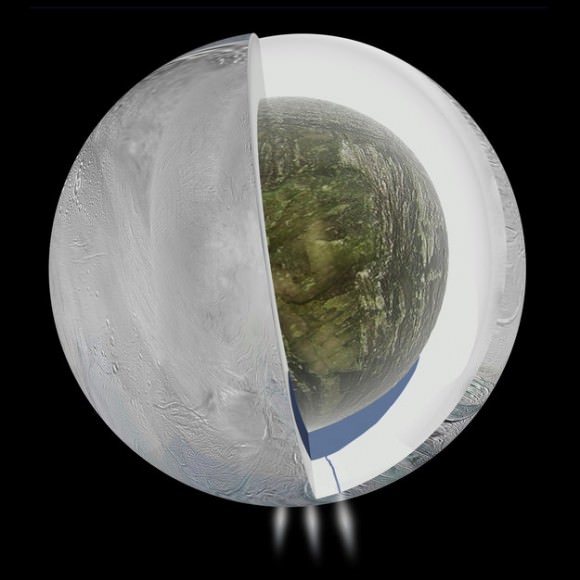
Ever since the Cassini spacecraft first spied water vapor and ice spewing from fractures in Enceladus’ frozen surface in 2005, scientists have hypothesized that a large reservoir of water lies beneath that icy surface, possibly fueling the plumes. Now, gravity measurements gathered by Cassini have confirmed that this enticing moon of Saturn does in fact harbor a large subsurface ocean near its south pole.
“For the first time, we have used a geophysical method to determine the internal structure of Enceladus, and the data suggest that indeed there is a large, possibly regional ocean about 50 kilometers below the surface of the south pole,” says David Stevenson from Caltech, a coauthor on a paper on the finding, published in the current issue of the journal Science. “This then provides one possible story to explain why water is gushing out of these fractures we see at the south pole.”
On three separate flybys in 2010 and 2012, the spacecraft passed within 100 km of Enceladus, twice over the southern hemisphere and once over the northern hemisphere.
During the flybys, the gravitational tug altered a spacecraft’s flight path ever so slightly, changing its velocity by just 0.2–0.3 millimeters per second.
As small as these deviations were, they were detectable in the spacecraft’s radio signals as they were beamed back to Earth, providing a measurement of how the gravity of Enceladus varied along the spacecraft’s orbit. These measurements could then be used to infer the distribution of mass inside the moon.
For example, a higher-than-average gravity ‘anomaly’ might suggest the presence of a mountain, while a lower-than-average reading implies a mass deficit.
On Enceladus, the scientists measured a negative mass anomaly at the surface of the south pole, accompanied by a positive one some 30-40 km below.
“By analyzing the spacecraft’s motion in this way, and taking into account the topography of the moon we see with Cassini’s cameras, we are given a window into the internal structure of Enceladus,” said lead author Luciano Iess.
“This is really the only way to learn about internal structure from remote sensing,” Stevenson added.
The only way to get more precise measurements would be to put seismometers on Enceladus’s surface. And that’s not going to happen anytime soon.
Stevenson said the key feature in the gravity data was the negative mass anomaly at Enceladus’s south pole. This happens when there is less mass in a particular location than would be expected in the case of a uniform spherical body. Since there is a known depression in the surface of Enceladus’s south pole, the scientists expected to find a negative mass anomaly. However, the anomaly was quite a bit smaller than would be predicted by the depression alone.
“The perturbations in the spacecraft’s motion can be most simply explained by the moon having an asymmetric internal structure, such that an ice shell overlies liquid water at a depth of around 30–40 km in the southern hemisphere,” Iess said.
While the gravity data cannot rule out a global ocean, a regional sea extending from the south pole to 50 degrees S latitude is most consistent with the moon’s topography and high local temperatures observed around the fractures – called ‘tiger stripes’ at Enceladus south pole.
Many have said Enceladus is one of the best places in the Solar System to look for life. Noted scientist Carolyn Porco and Chris McKay have a recent paper out titled, “Follow the Plume: The Habitability of Enceladus,” where they say that since analysis of the plume by the Cassini mission indicates that the “steady plume derives from a subsurface liquid water reservoir that contains organic carbon, biologically available nitrogen, redox energy sources, and inorganic salts” that samples from the plume jetting out into space are accessible with a low-cost flyby mission. “No other world has such well-studied indications of habitable conditions.”
These latest findings by Cassini make a mission to Enceladus even more enticing.
Paper in Science (paywall) “The Gravity Field and Interior Structure of Enceladus.”
Sources: ESA, Caltech

