When we look out into space, we’re also looking back into time. Just how far back can we see?
The Universe is a magic time window, allowing us to peer into the past. The further out we look, the further back in time we see. Despite our brains telling us things we see happen at the instant we view them, light moves at a mere 300,000 kilometers per second, which makes for a really weird time delay at great distances.
Let’s say that you’re talking with a friend who’s about a meter away. The light from your friend’s face took about 3.336 nanoseconds to reach you. You’re always seeing your loved ones 3.336 nanoseconds into the past. When you look around you, you’re not seeing the world as it is, you’re seeing the world as it was, a fraction of a second ago. And the further things are, the further back in time you’re looking.
The distance to the Moon is, on average, about 384,000 km. Light takes about 1.28 seconds to get from the Moon to the Earth. If there was a large explosion on the Moon of a secret Nazi base, you wouldn’t see it for just over a second. Even trying to communicate with someone on the Moon would be frustrating as you’d experience a delay each time you talked.
Let’s go with some larger examples. Our Sun is 8 minutes and 20 seconds away at the speed of light. You’re not seeing the Sun as it is, but how it looked more than 8 minutes ago.
On average, Mars is about 14 light minutes away from Earth. When we were watching live coverage of NASA’s Curiosity Rover landing on Mars, it wasn’t live. Curiosity landed minutes earlier, and we had to wait for the radio signals to reach us, since they travel at the speed of light.
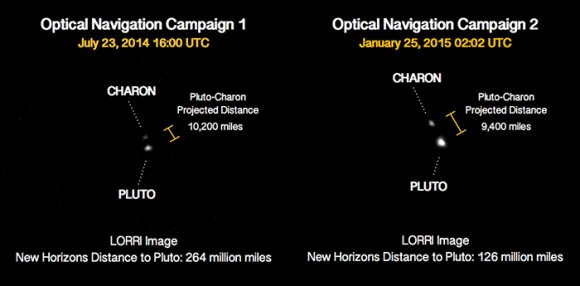
When NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft reaches Pluto next year, it’ll be 4.6 light hours away. If we had a telescope strong enough to watch the close encounter, we’d be looking at events that happened 4.6 hours ago.

The closest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4.2 light-years away. This means that the Proxima Centurans don’t know who won the last US Election, or that there are going to be new Star Wars movies. They will, however, as of when this video was produced, be watching Toronto make some questionable life choices regarding its mayoral election.
The Eagle Nebula with the famous Pillars of Creation, is 7,000 light-years away. Astronomers believe that a supernova has already gone off in this region, blasting them away. Take a picture with a telescope and you’ll see them, but mostly likely they’ve been gone for thousands of years.
The core of our own Milky Way galaxy is about 25,000 light-years away. When you look at these beautiful pictures of the core of the Milky Way, you’re seeing light that may well have left before humans first settled in North America.

And don’t get me started on Andromeda. That galaxy is more than 2.5 million light-years away. That light left Andromeda before we had Homo Erectus on Earth. There are galaxies out there, where aliens with powerful enough telescopes could be watching dinosaurs roaming the Earth, right now.
Here’s where it gets even more interesting. Some of the brightest objects in the sky are quasars, actively feeding supermassive black holes at the cores of galaxies. The closest is 2.5 billion light years away, but there are many much further out. Earth formed only 4.5 billion years ago, so we can see quasars shining where the light had left before the Earth even formed.
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation, the very edge of the observable Universe is about 13.8 billion light-years away. This light left the Universe when it was only a few hundred thousand years old, and only now has finally reached us. What’s even stranger, the place that emitted that radiation is now 46 billion light-years away from us.
So crack out your sonic screwdrivers and enjoy your time machine, Whovians. Your ability to look out into space and peer into the past. Without a finite speed of light, we wouldn’t know as much about the Universe we live in and where we came from. What moment in history do you wish you could watch? Express your answer in the form of a distance in light-years.