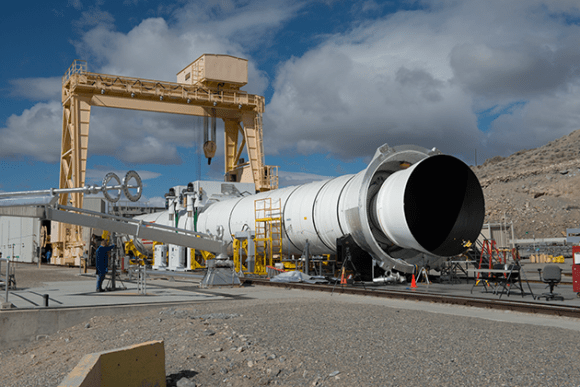
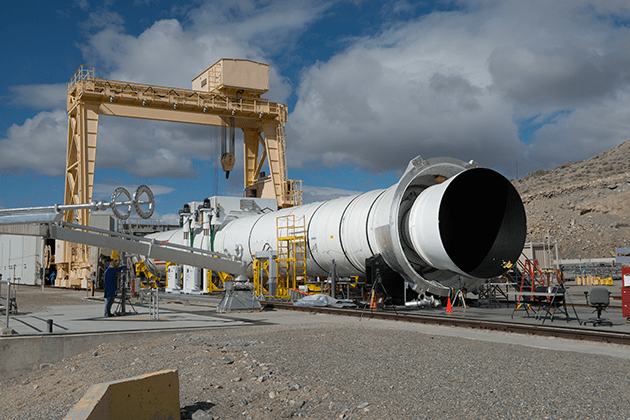
The world’s most powerful booster that will one day propel NASA astronauts on exciting missions of exploration to deep space destinations including the Moon and Mars was successfully ignited this morning, June 28, during an awesome ground test firing on a remote mountainside in Utah, that qualifies it for an inaugural blastoff in late 2018.
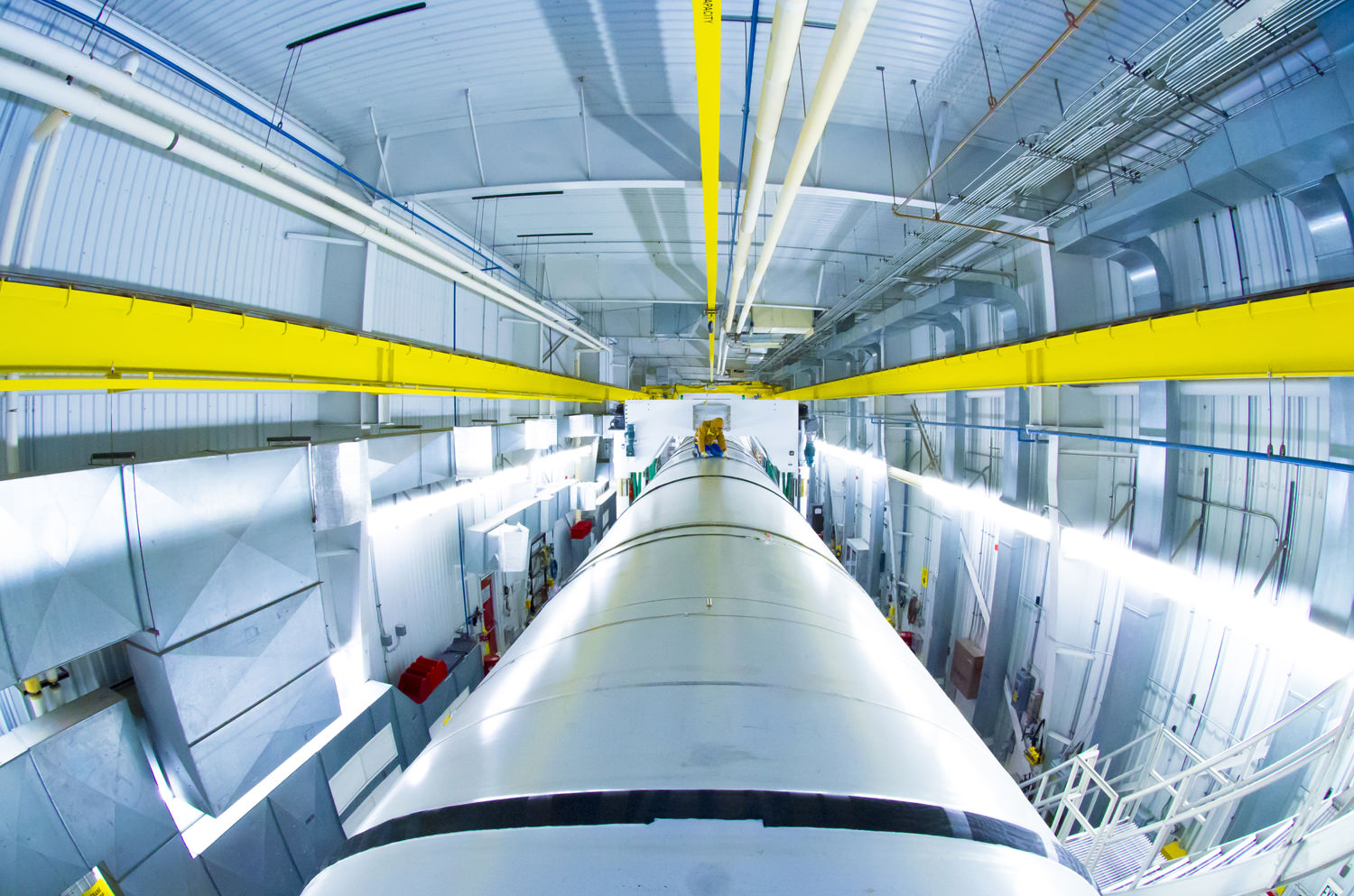
The two-minute-long, full-duration static test for NASA’s mammoth Space Launch System (SLS) rocket involved firing the new five-segment solid rocket booster for its second and final qualification ground test as it sat restrained in a horizontal configuration at Orbital ATK’s test facilities at a desert site in Promontory, Utah.
The purpose was to provide NASA and prime contractor Orbital ATK with critical data on 82 qualification objectives. Engineers will use the data gathered by more than 530 instrumentation channels on the booster to certify the booster for flight.
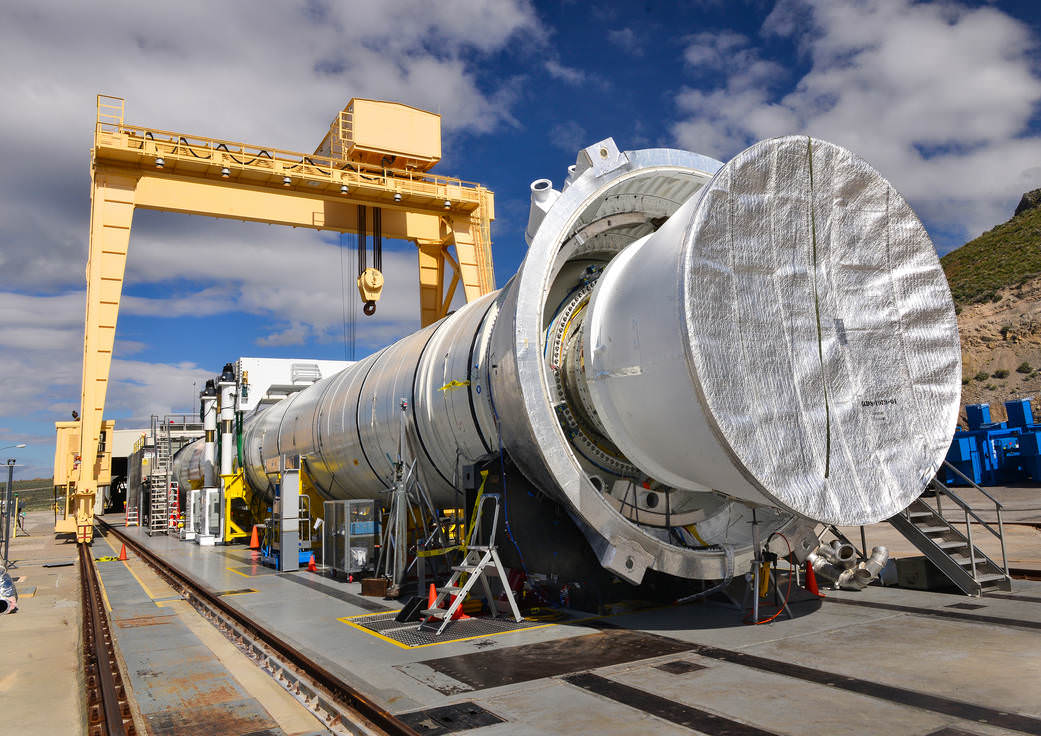
The 154-foot-long (47-meter) booster was fired up on the test stand by the Orbital ATK operations team at 11:05 a.m. EDT (9:05 a.m. MT) for what is called the Qualification Motor-2 (QM-2) test.
“We have ignition of NASA’s Space Launch System motor powering us on our Journey to Mars,” said NASA commentator Kim Henry at ignition!
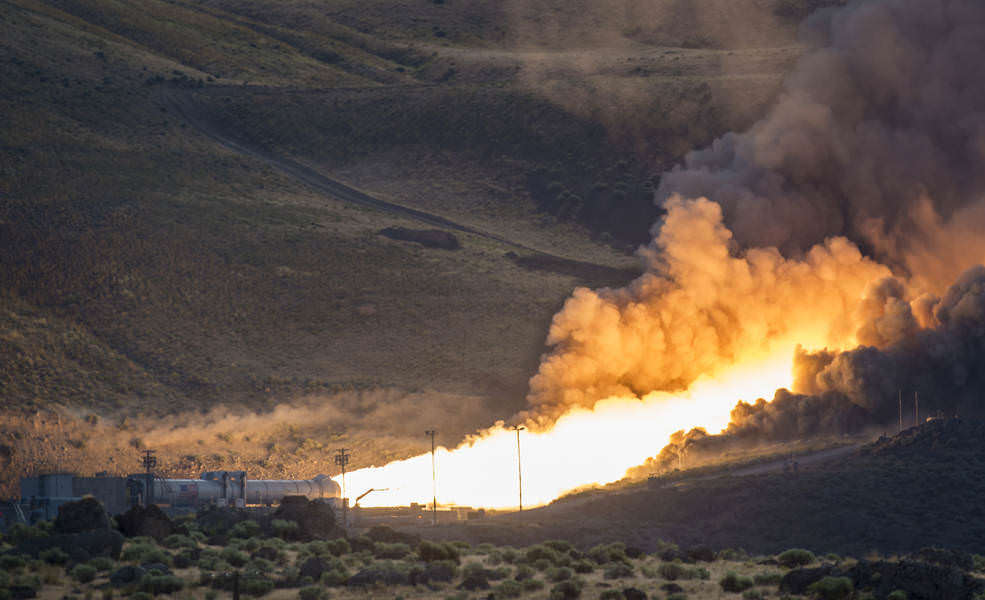
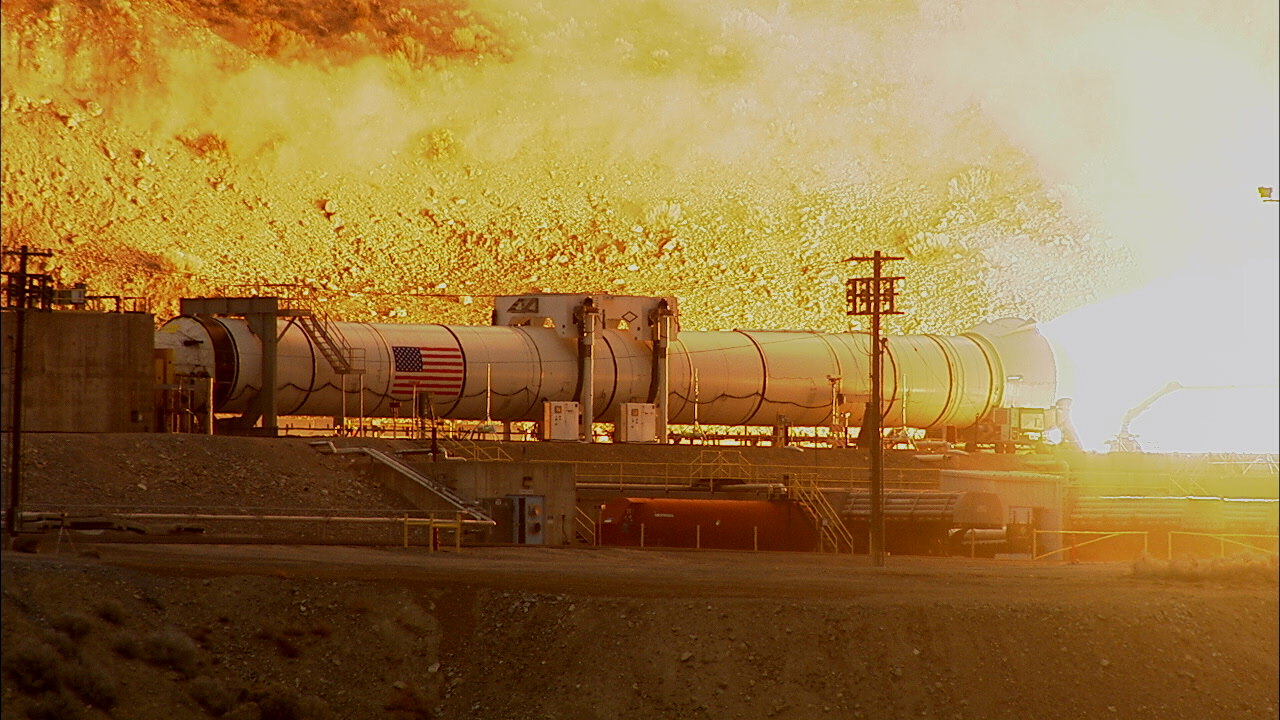
A gigantic plume of black smoke and intense yellow fire erupted at ignition spewing a withering cloud of ash into the Utah air and barren mountainside while consuming propellant at a rate of 5.5 tons per second.
It also sent out a shock wave reverberating back to excited company, NASA and media spectators witnessing the event from about a mile away as well as to another 10,000 or so space enthusiasts and members of the general public gathered to watch from about 2 miles away.

“What an absolutely amazing day today for all of us here to witness this test firing. And it’s not just a test firing. It’s really a qualification motor test firing that says this design is ready to go fly and ready to go do the mission which it’s designed to go do,” said William Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, during the post QM-2 test media briefing today.

The critically important test marks a major milestone clearing the path to the first SLS launch that could happen as soon as September 2018, noted Gerstenmaier
“The team did a tremendous professional job to get all this ready for the firing. We will get over 500 channels of data on this rocket. They will pour over the data to ensure it will perform exactly the way we intended it to at these cold conditions.”

The QM-2 booster had been pre-chilled for several weeks inside a huge test storage shed to conduct this so called ‘cold motor test’ at approximately 40 degrees Fahrenheit (5 C) – corresponding to the colder end of its accepted propellant temperature range.
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with lift off using two of the five segment solid rocket motors and four RS-25 engines to power the maiden launch of SLS and NASA’s Orion deep space manned spacecraft in late 2018.
The SLS boosters are derived from the four segment solid rocket boosters (SRBs) originally delevoped for NASA’s space shuttle program and used for 3 decades.
“This final qualification test of the booster system shows real progress in the development of the Space Launch System,” said NASA associate administrator Gerstenmaier.
“Seeing this test today, and experiencing the sound and feel of approximately 3.6 million pounds of thrust, helps us appreciate the progress we’re making to advance human exploration and open new frontiers for science and technology missions in deep space.”
Despite being cooled to 41 F (5 C) for the cold motor test the flames emitted by the 12-foot-diameter (3.6-meter) booster are actually hot enough at some 6000 degrees Fahrenheit to boil steel.
The internal pressure reaches about 900 psi.

The first ground test called QM-1 was conducted at 90 degrees Fahrenheit, at the upper end of the operating range, in March 2015 as I reported earlier here.
This second ground test firing took place about 1 hour later than originally planned due to a technical issue with the ground sequencing computer control system.
The next time one of these solid rocket boosters fire will be for the combined SLS-1/Orion EM-1 test flight in late 2018.
Each booster generates approximately 3.6 million pounds of thrust. Overall they will provide more than 75 percent of the thrust needed for the rocket and Orion spacecraft to escape Earth’s gravitational pull, says NASA.
“It was awesome to say the least,” space photographer and friend Julian Leek who witnessed the test first hand told Universe Today.
“Massive fire power released over the Utah mountains. There was about a five second delay before you could hear the sound – that really got everyone’s attention!”
“It was absolutely magnificent,” space photographer friend Dawn Taylor told me. “Can’t wait to see it at the Cape when it goes vertical.”
To date Orbital ATK has cast 3 of the 10 booster segments required for the 2018 launch, said Charlie Precourt, vice president and general manager of Orbital ATK’s Propulsion Systems Division in Promontory, Utah.
I asked Precourt about the production timing for the remaining segments.
“All of the segments will be delivered to NASA at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida by next fall,” Precourt replied during the media briefing.
“They will be produced at a rate of roughly one a month. We also have to build the nozzles up and so forth.”
When will booster stacking begin inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at KSC?
Booster shipments start shipping from Utah this fall. Booster stacking in the VAB starts in the spring of 2018,” Alex Priskos, manager of the NASA SLS Boosters Office at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, told me.
Furthermore a preliminary look at the data indicates that all went well.
“What an outstanding test. After a look at some very preliminary data everything looks great so far,” Priskos said at the briefing. “We’re going to be digging into the data a lot more as we go forward.”

Meanwhile the buildup of US flight hardware continues at NASA and contractor centers around the US, as well as the Orion service module from ESA.
The maiden test flight of the SLS/Orion is targeted for no later than November 2018 and will be configured in its initial 70-metric-ton (77-ton) version with a liftoff thrust of 8.4 million pounds.
In February 2016 the welded skeletal backbone for the Orion EM-1 mission arrived at the Kennedy Space Center for outfitting with all the systems and subsystems necessary for flight.
The core stage fuel tank holding the cryogenic liquid oxygen and hydrogen propellants is being welded together at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA.
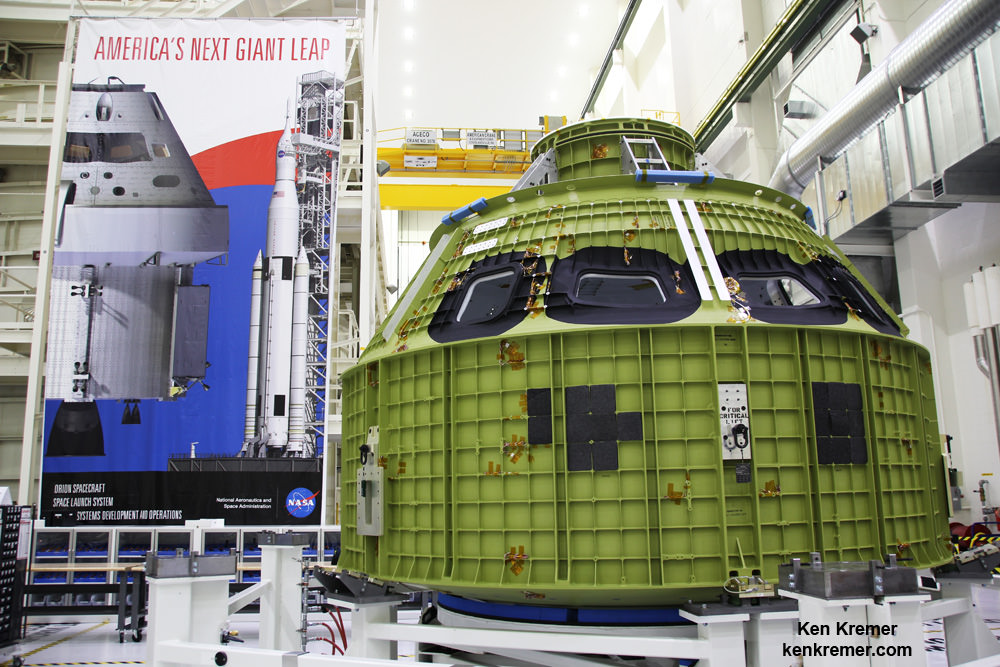
Although the SLS-1 flight in 2018 will be uncrewed, NASA plans to launch astronauts on the SLS-2/EM-2 mission slated for the 2021 to 2023 timeframe.
It all depends on the budget NASA receives from Congress and who is elected President in the election in November 2016.
“If we can keep our focus and keep delivering, and deliver to the schedules, the budgets and the promise of what we’ve got, I think we’ve got a very capable vision that actually moves the nation very far forward in moving human presence into space,” Gerstenmaier explained at the briefing.
“This is a very capable system. It’s not built for just one or two flights. It is actually built for multiple decades of use that will enable us to eventually allow humans to go to Mars in the 2030s.
One forerunner to the Mars mission could be a habitation module around the Moon perhaps five years from now.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.