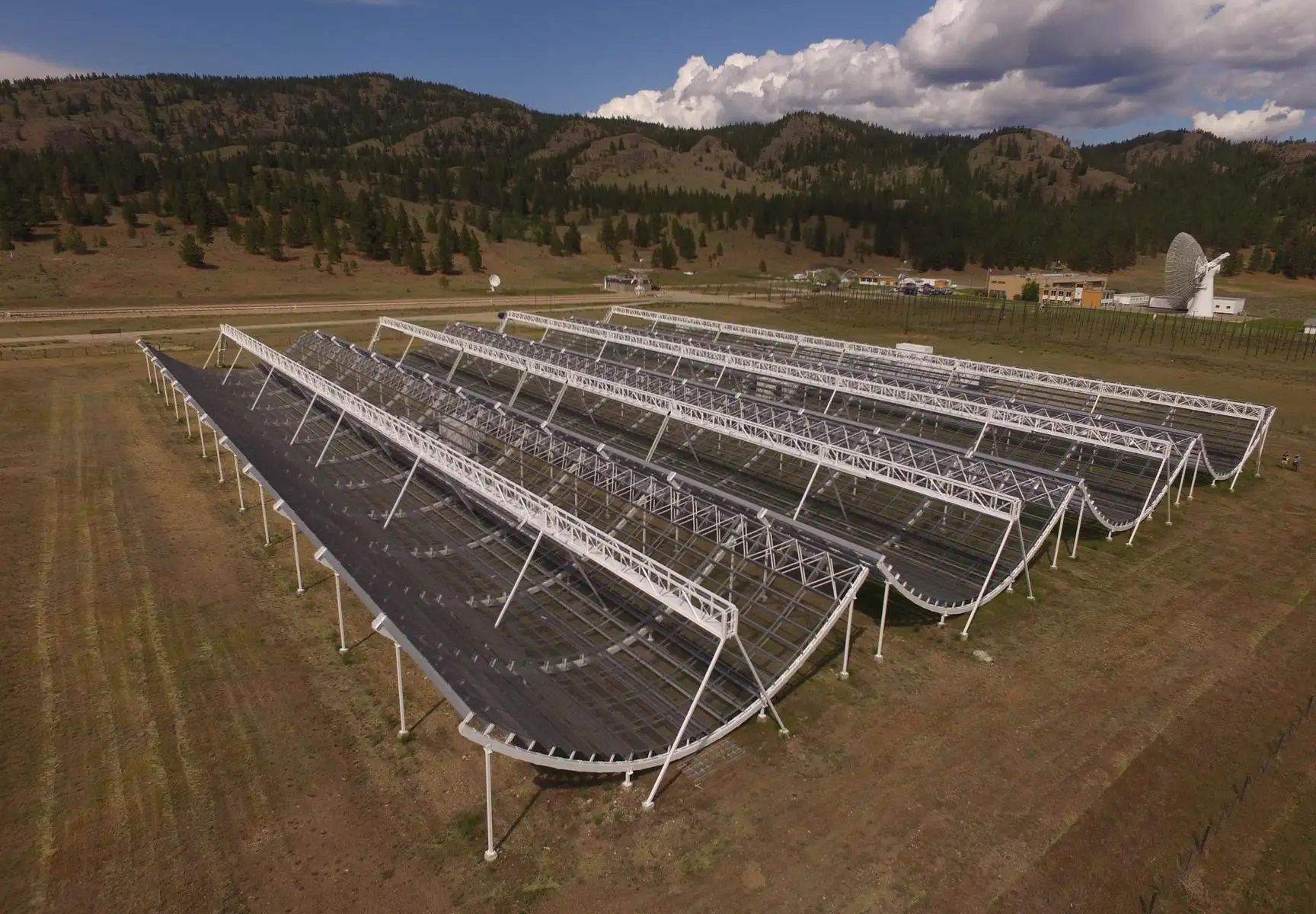
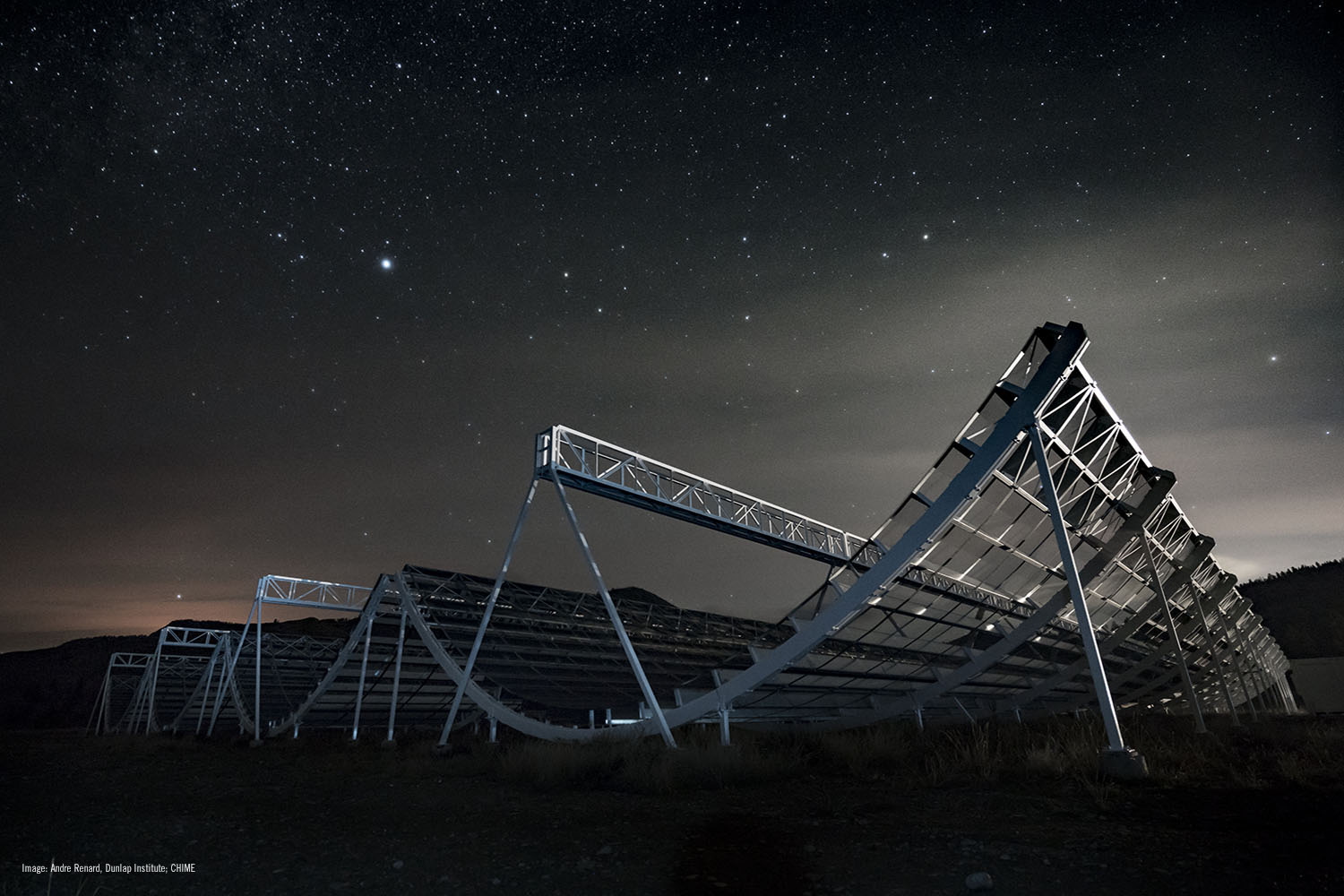
Located in the Okanagan Valley outside of Penticton, British Columbia, there is a massive radio observatory dedicated to observing cosmic radio phenomena. It’s called the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME), a cylindrical parabolic radio telescope that looks like what snowboarders would call a “half-pipe.” This array is part of the Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory (DRAO), overseen by the National Research Council (NRC).
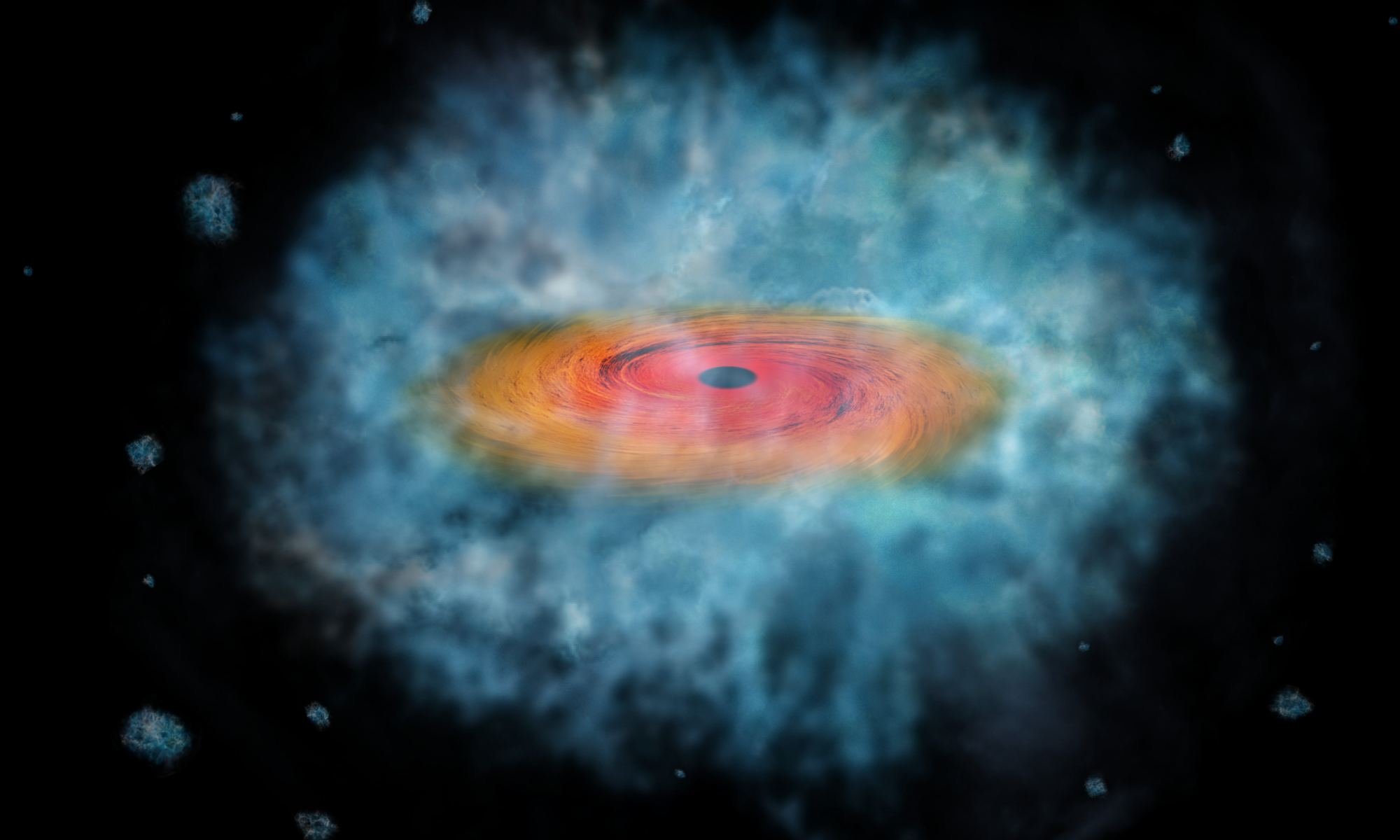
Originally, the observatory was meant to detect radio waves from neutral hydrogen gas in the early Universe. Today, it is used for other objectives, such as detecting and studying Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs). Since it became operational, CHIME scientists have been busy sorting through terabytes of data to pinpoint signals, often finding several in a single day. To assist with all this data-mining and coordinate CHIMEs efforts with other facilities worldwide, scientists from McGill University have developed a new system for sharing the enormous amount of data CHIME generates.
Continue reading “Fast Radio Bursts can now be Tracked in Real-Time”