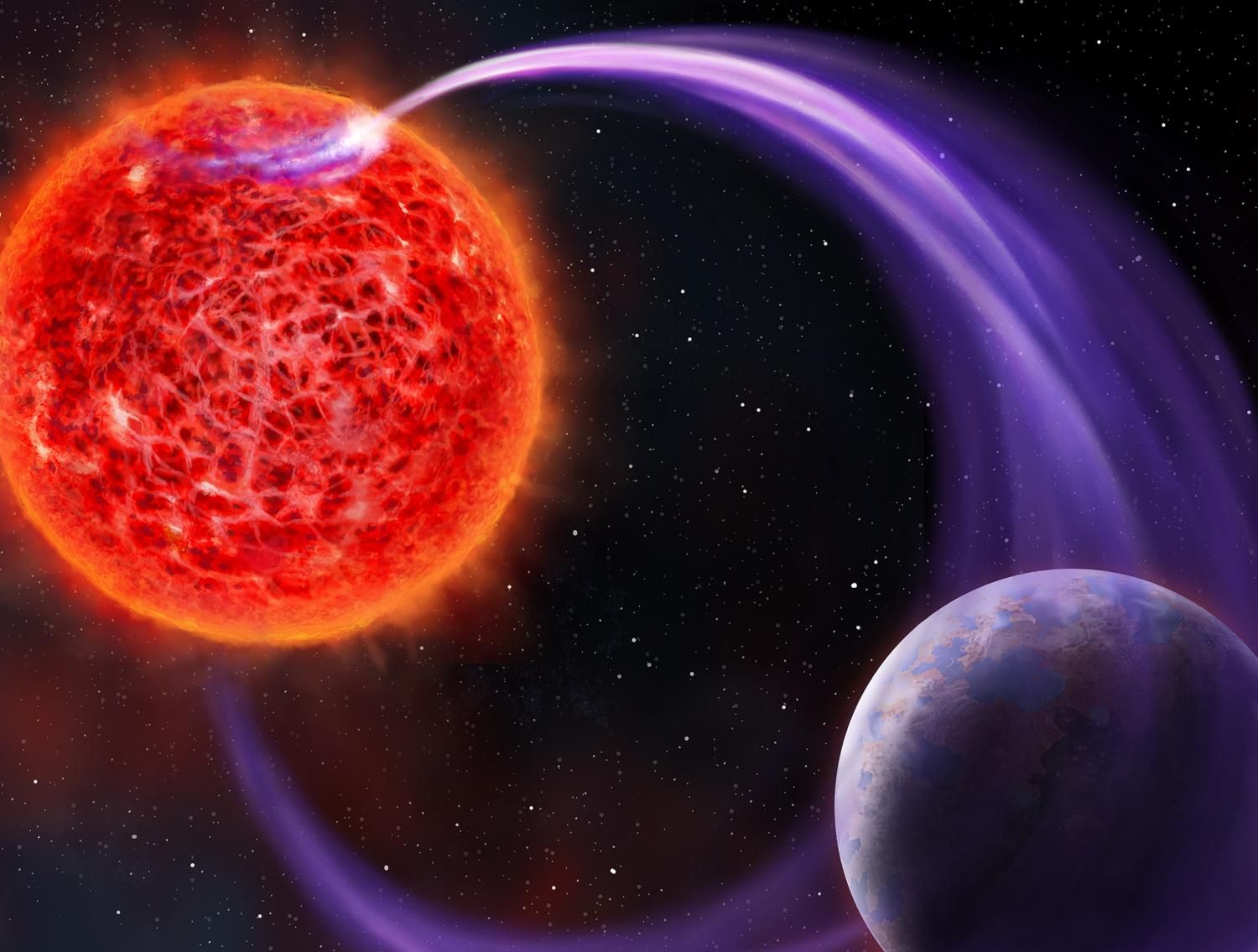
The question of whether or not red dwarf stars can support habitable planets has been subject to debate for decades. With the explosion in exoplanet discoveries in the past two decades, the debate has become all the more significant. For starters, M-type (red dwarf) stars are the most common in the Universe, accounting for 75% of the stars in our galaxy. Additionally, exoplanet surveys indicate that red dwarfs are particularly good at forming Earth-like rocky planets that orbit within their circumsolar habitable zones (CHZs).
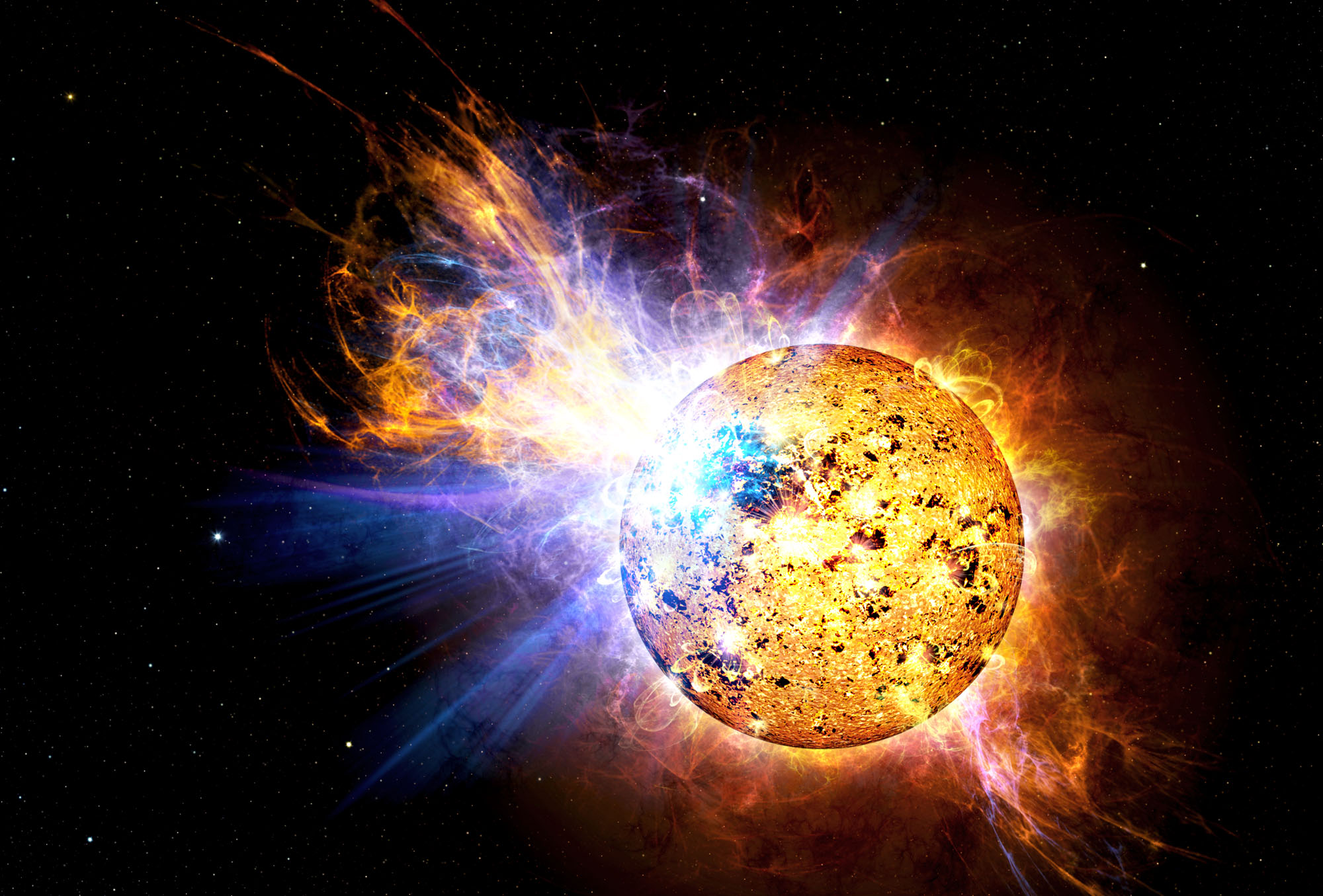
Unfortunately, a considerable body of research has shown that planets orbiting red dwarf suns would be subject to lots of flare activity – including some so powerful they’re known as “superflares.” In a recent study led by the University of Hawai’i, a team of astrophysicists revealed that red dwarf stars can produce stellar flares with significantly more far-ultraviolet radiation than previously expected. Their findings could have drastic implications for exoplanet studies and the search for extraterrestrial life on nearby rocky planets.
Continue reading “Habitable Planet’s Orbiting Red Dwarf Suns Could at Risk from Far-Ultraviolet Radiation”