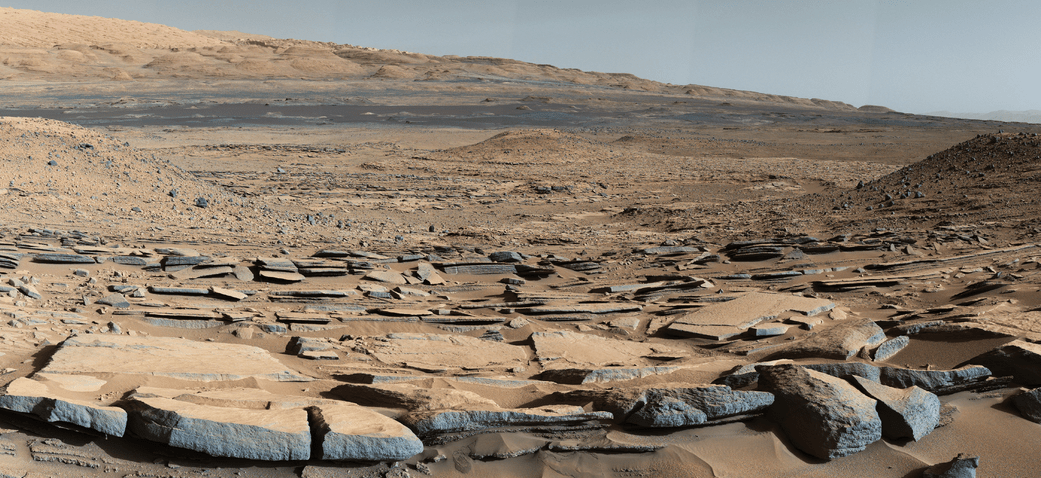
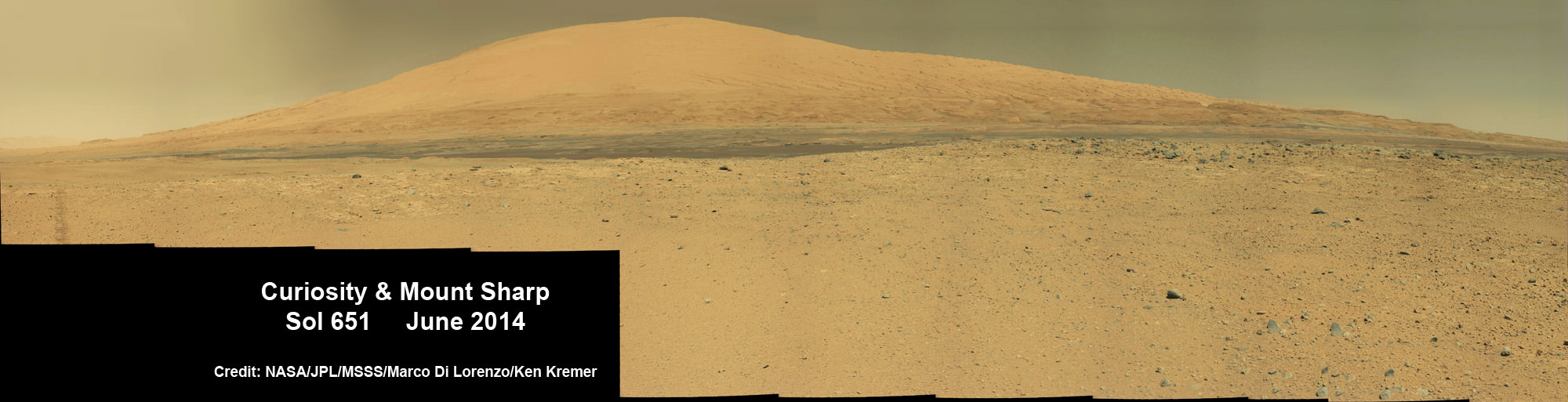
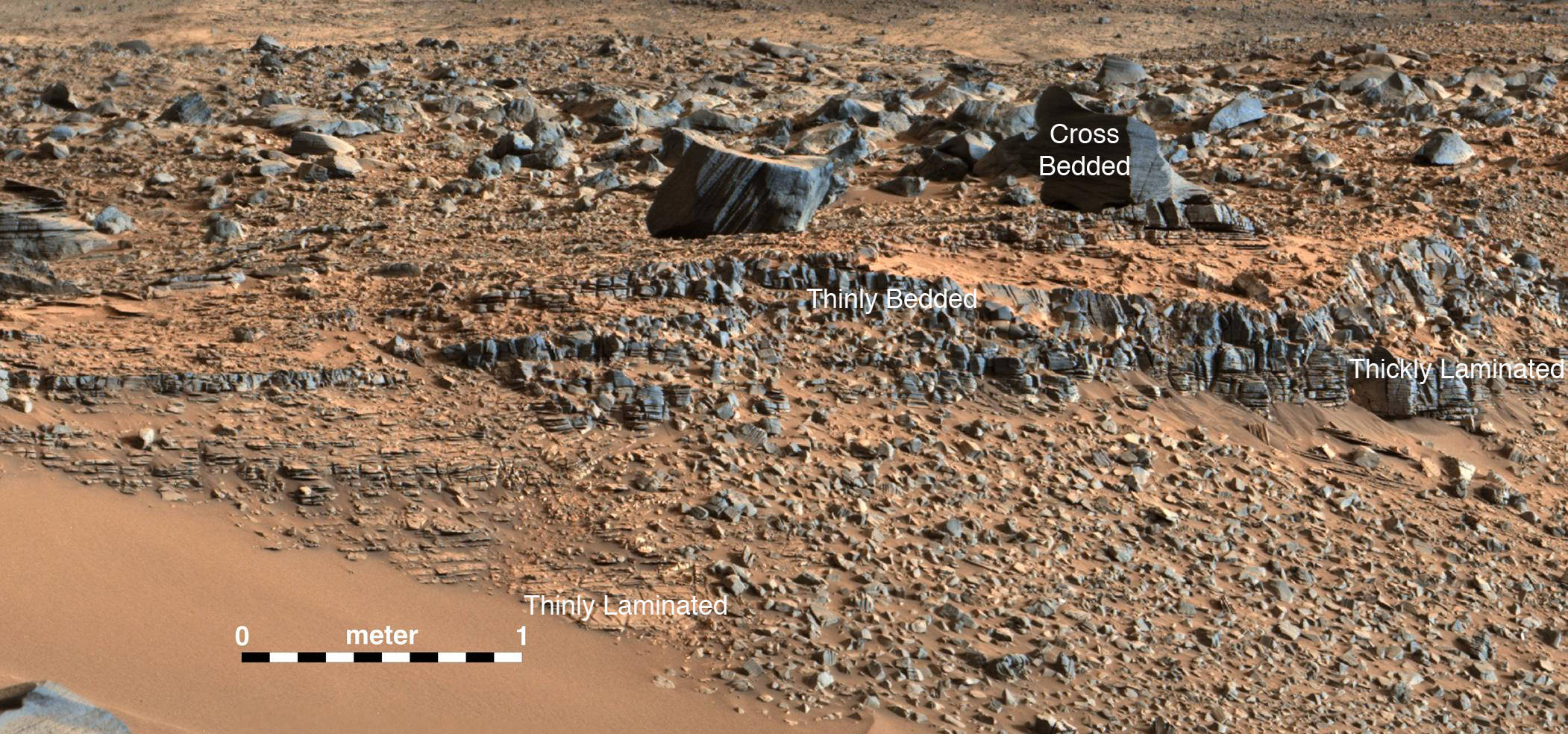
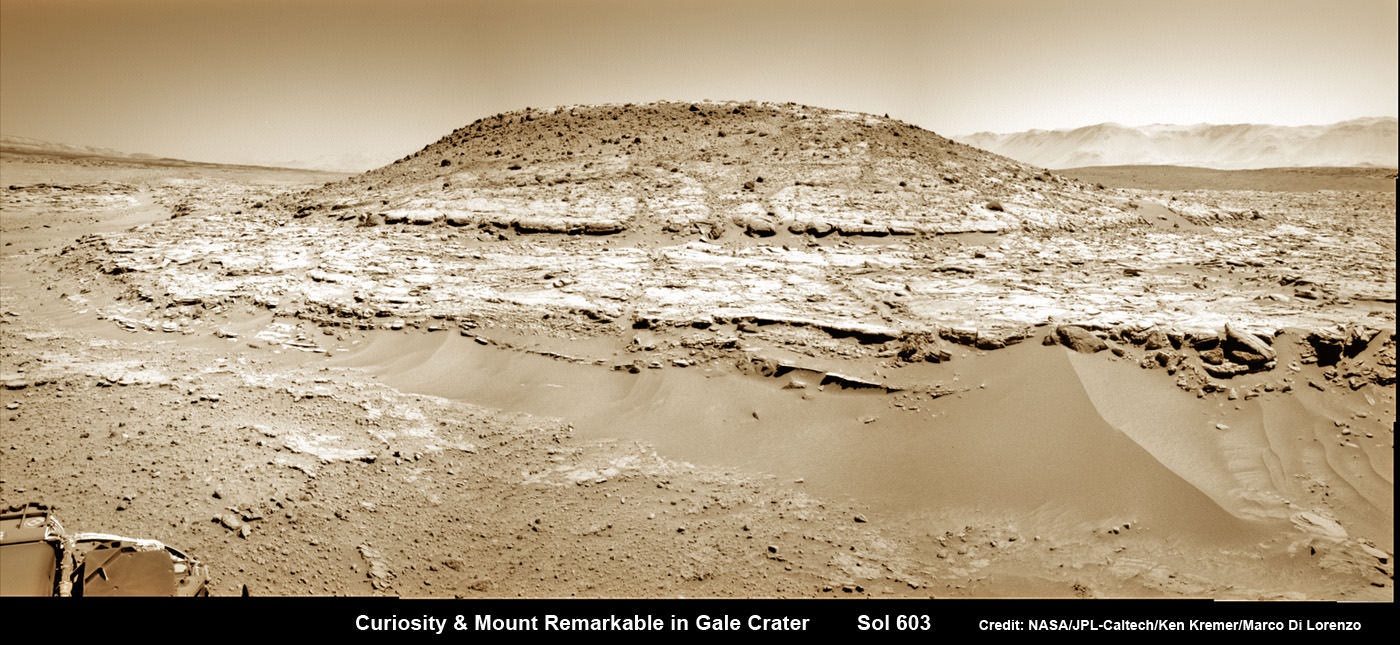
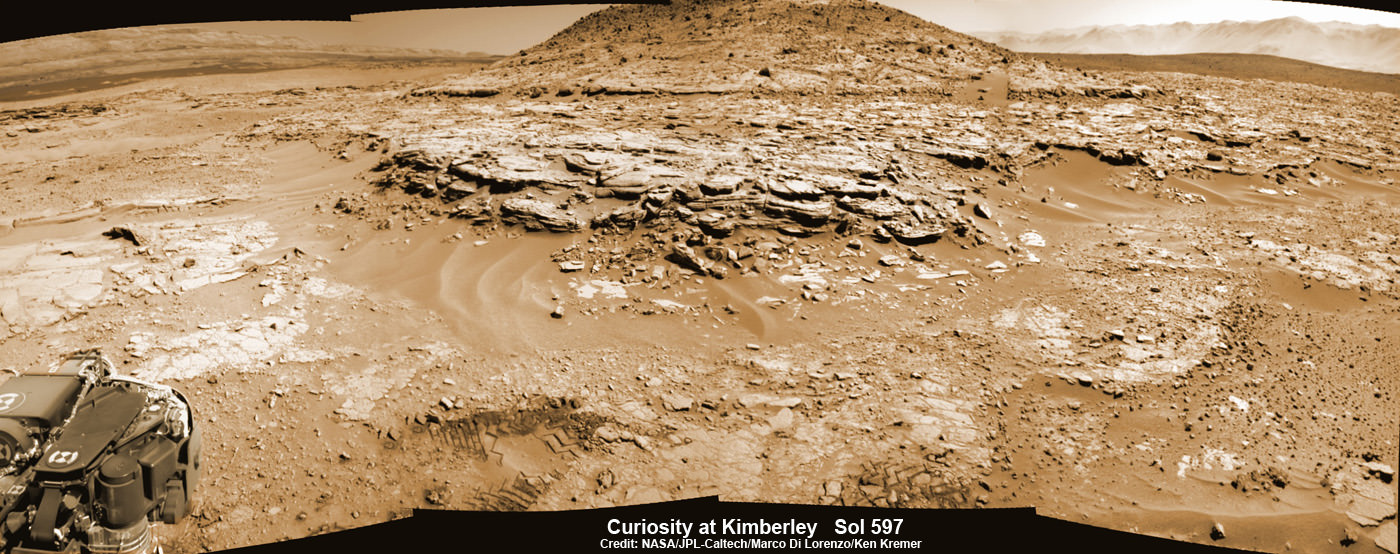
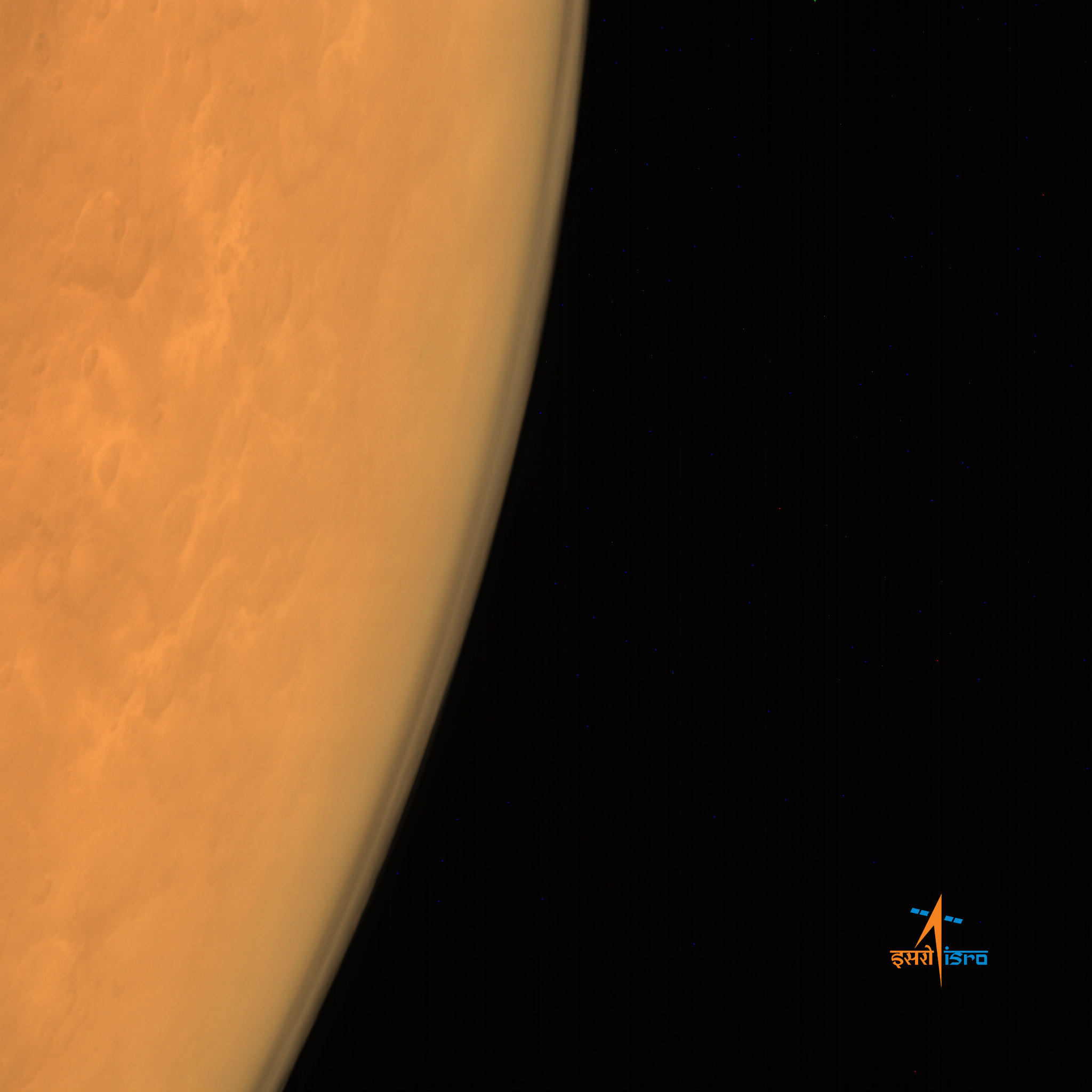
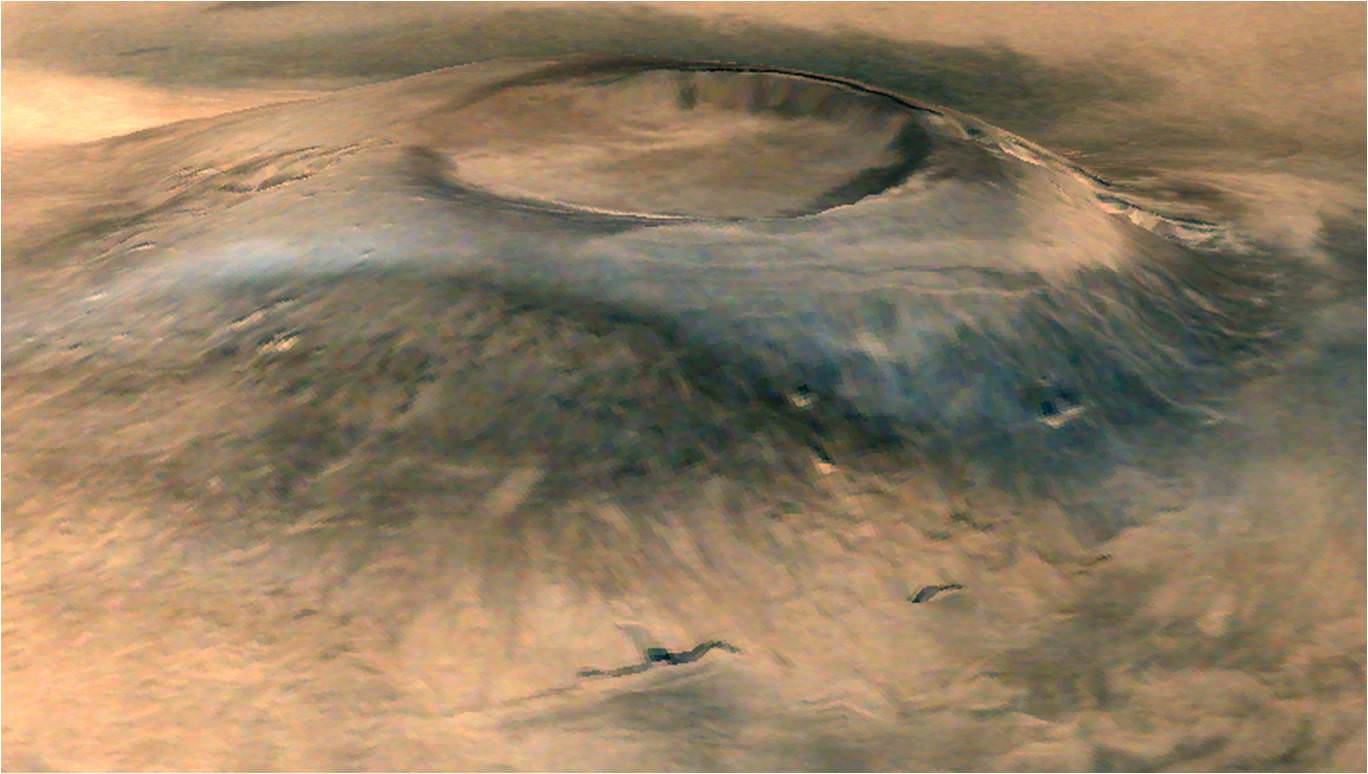
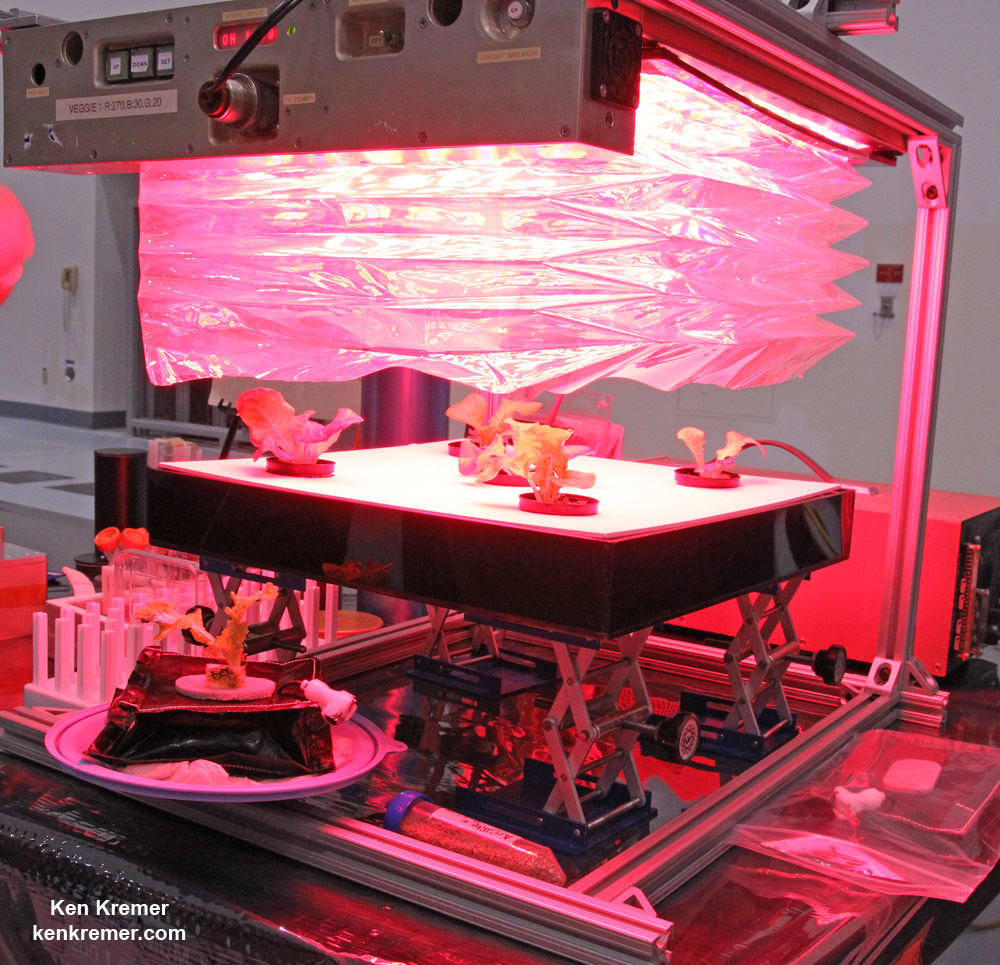
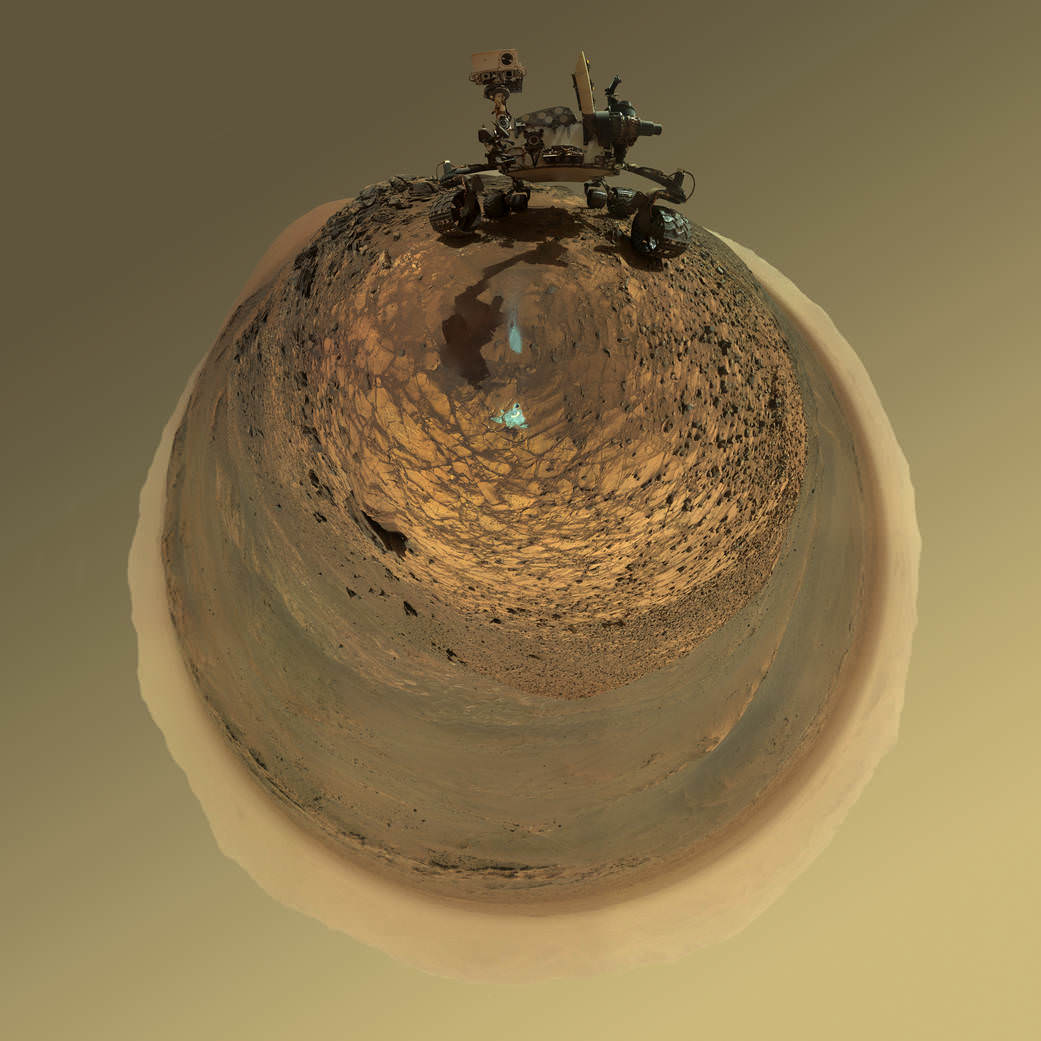
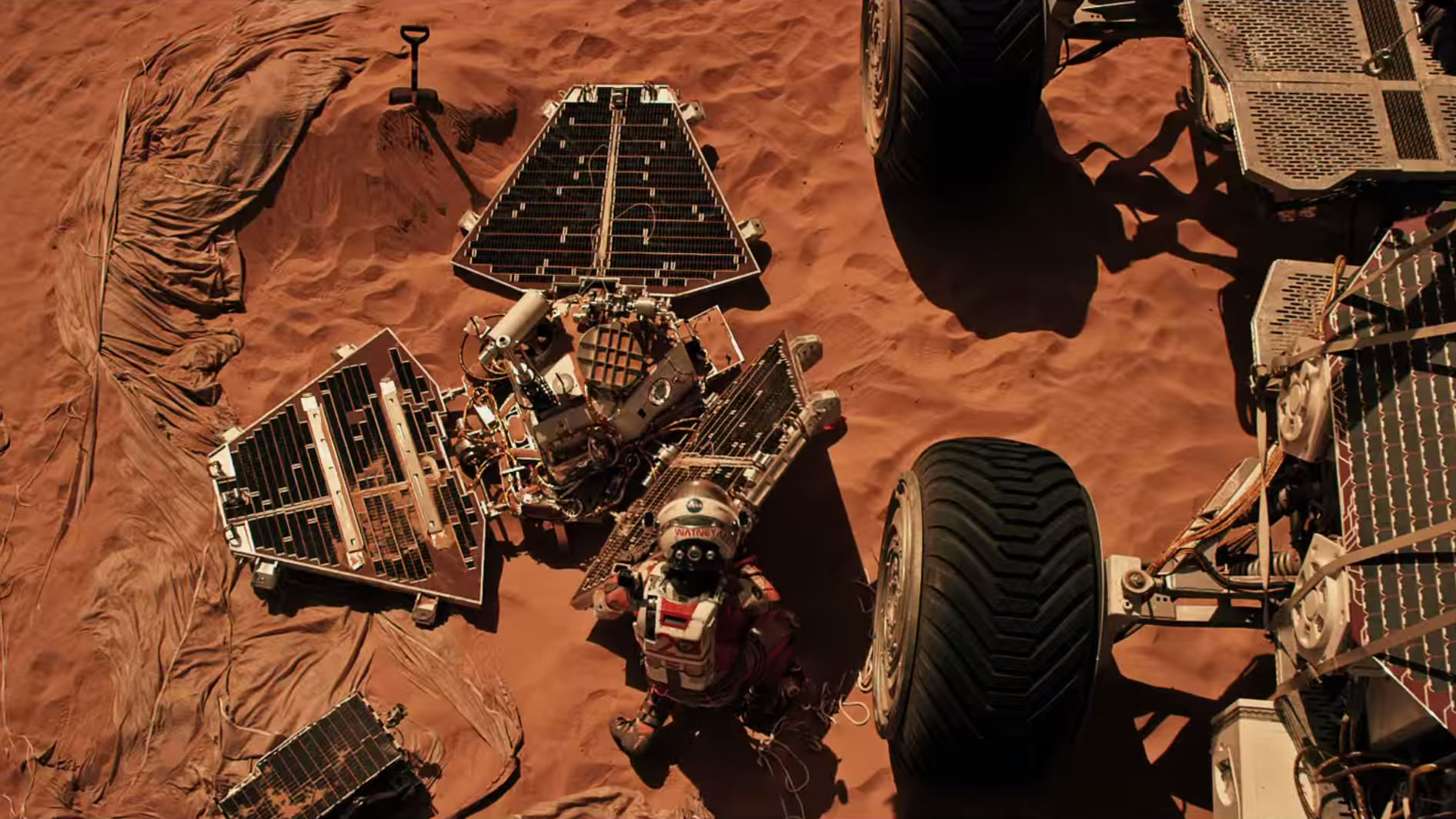
Scene from ‘The Martian’ starring Matt Damon as NASA astronaut Mark Watney contemplating magnificent panoramic vista while stranded alone on Mars.
Credits: 20th Century Fox
See real Martian maps and flyover video from DLR and NSA below
Story/imagery updated[/caption]
Go now and experience Hollywood’s blockbuster new space epic ‘The Martian’ helmed by world renowned director Ridley Scott and starring Matt Damon as the protagonist, NASA astronaut Mark Watney. And you can follow Watney’s dramatic fictional path across the Red Planet in newly released real photos and a flyover video of the region, from DLR and NASA, as it looks today.
‘The Martian’ is a mesmerizingly enjoyable cinematic triumph for everyone that’s all about science, space exploration and one man’s struggle to survive while left totally isolated on the Red Planet in the face of seemingly insurmountable odds – relying on his wits alone to endure “on a planet where nothing grows” while hoping somehow for a rescue by NASA four years in the future.
The movie combines compelling and plausible storytelling with outstanding special effects that’s clearly delighting huge audiences worldwide with a positive and uplifting view of what could be achieved in the future – if only we really put our minds to it!
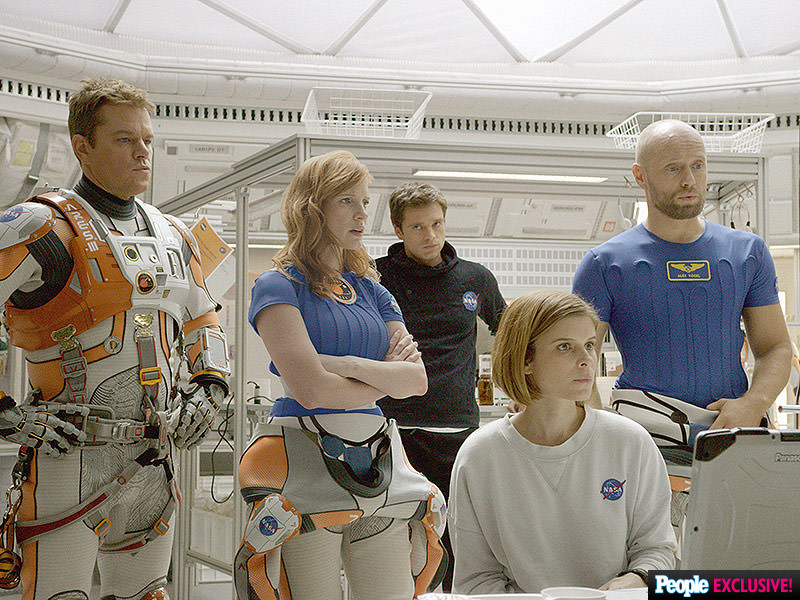
Based on the bestselling book by Andy Weir, ‘The Martian’ movie from 20th Century Fox tells the spellbinding story of how NASA astronaut Mark Watney is accidentally stranded on the surface of Mars during the future Ares 3 manned expedition in 2035, after a sudden and unexpectedly fierce dust storm forces the rest of the six person crew – commanded by Jessica Chastain as Commander Lewis – to quickly evacuate after they believe he is dead.

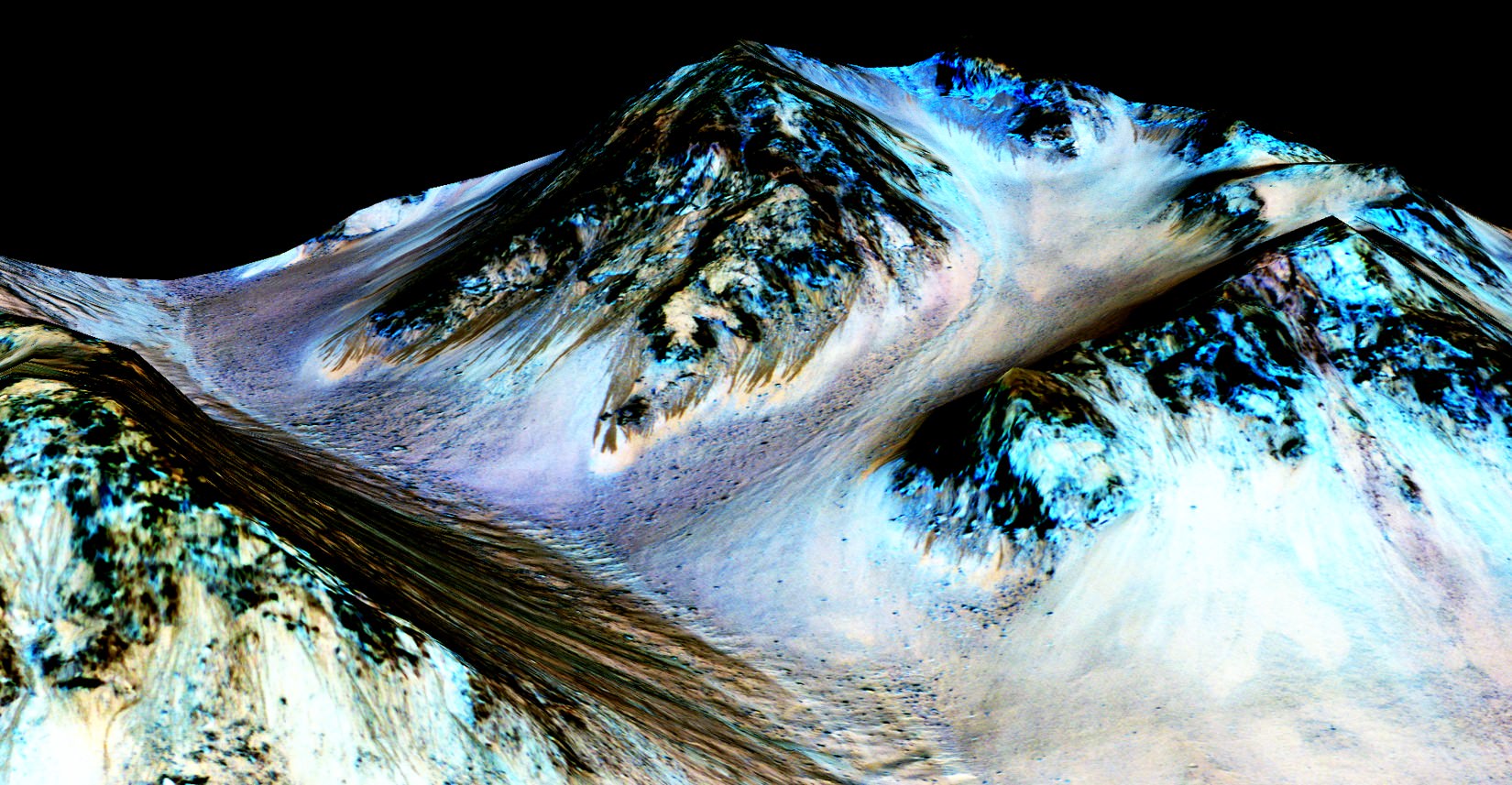
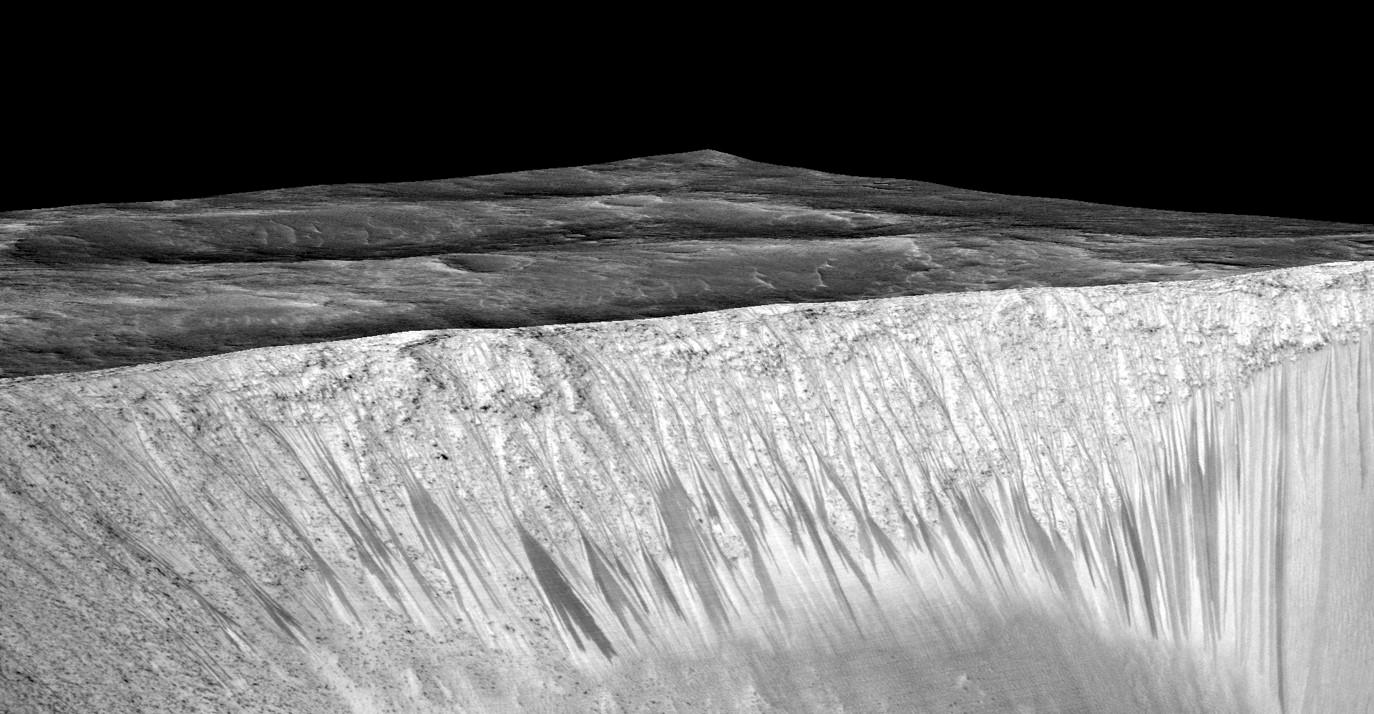
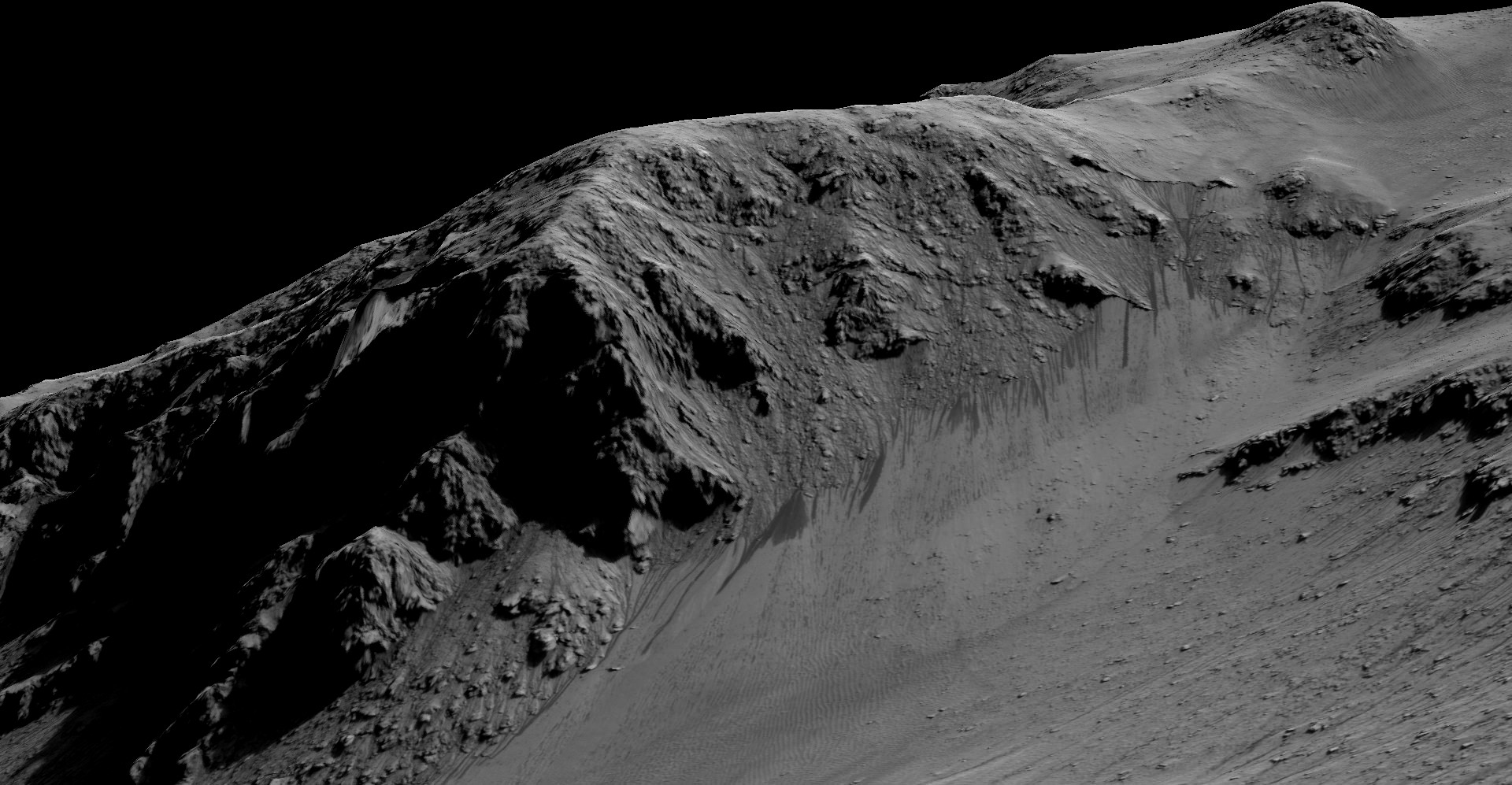
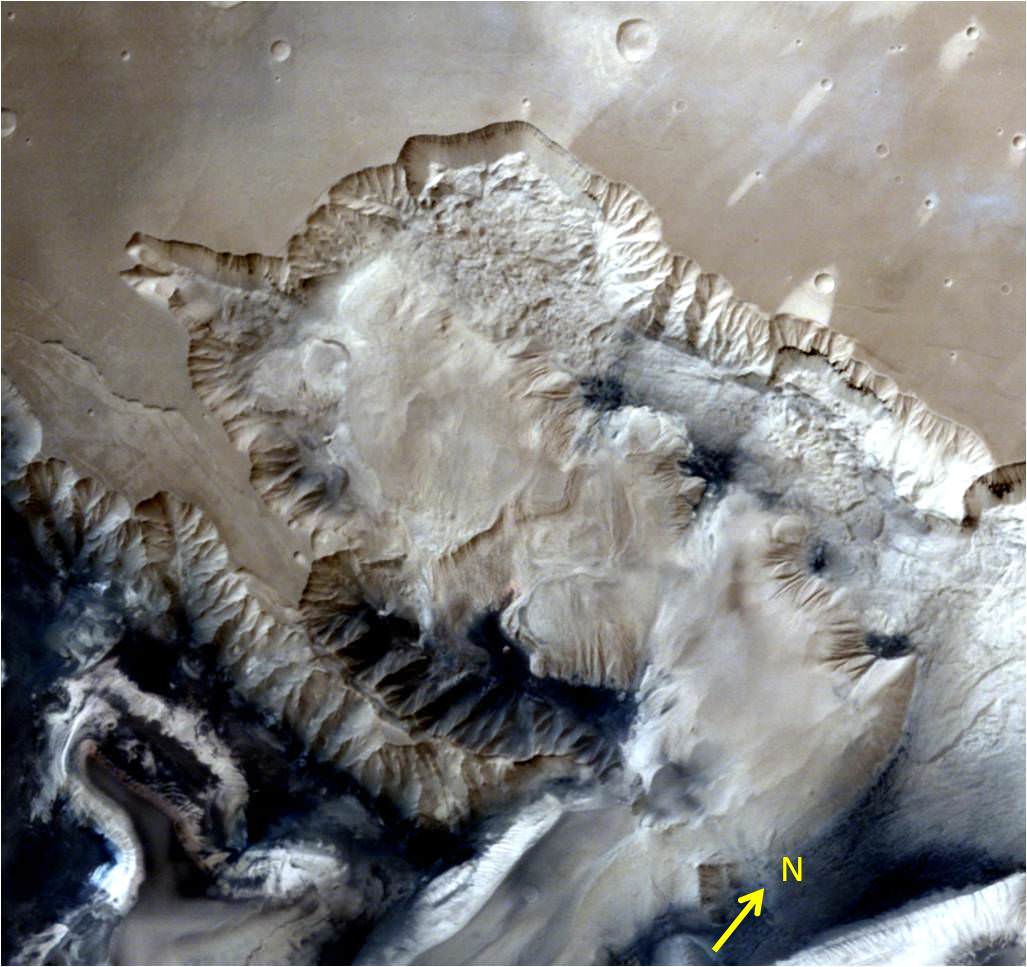
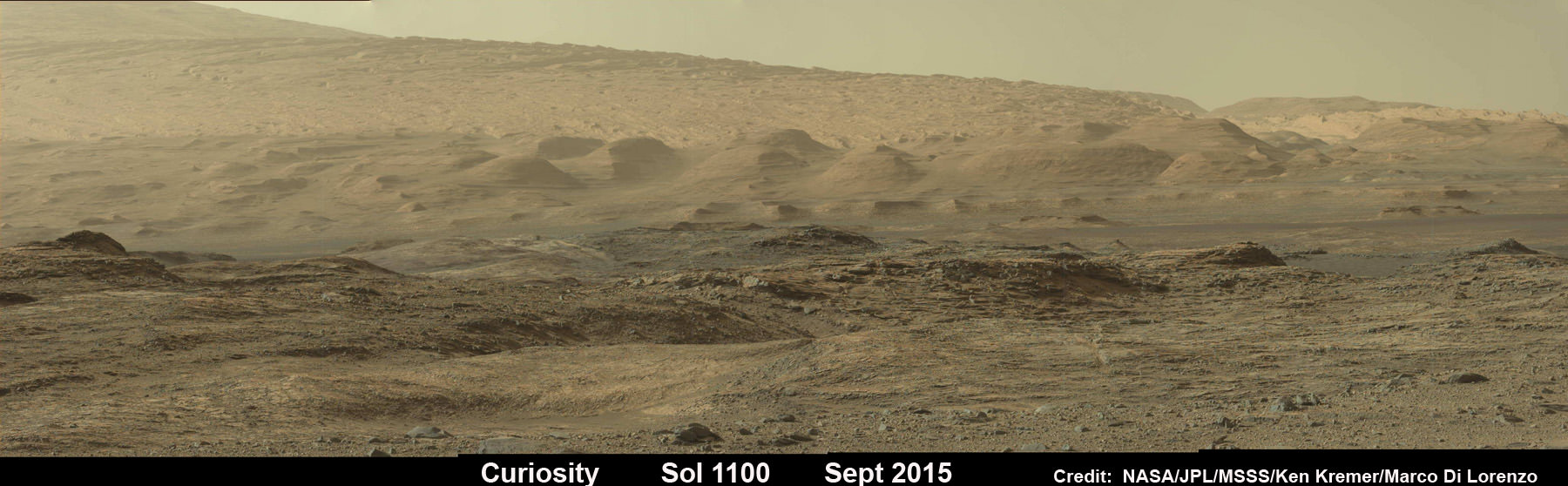
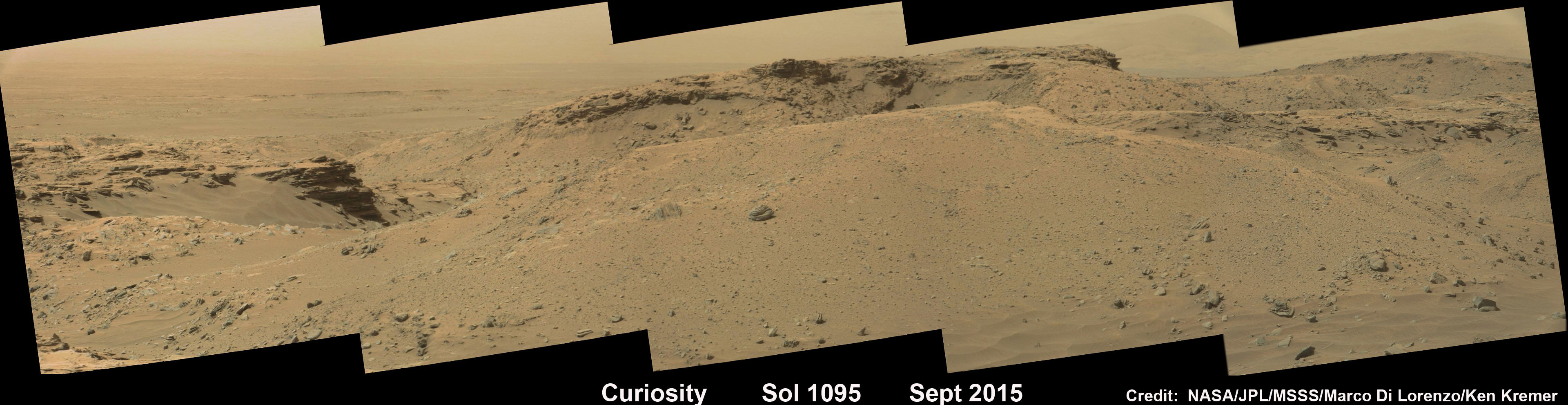
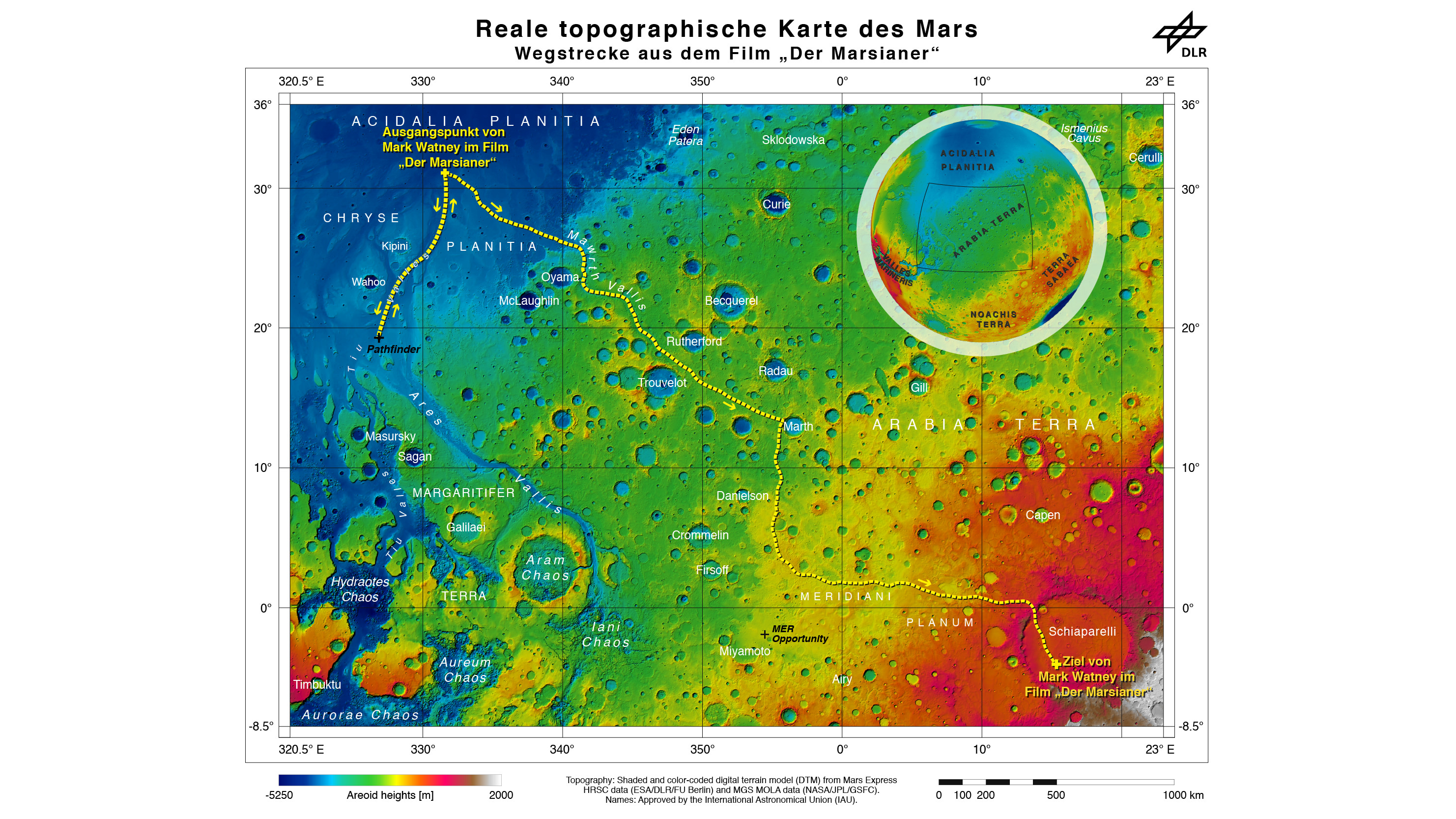
Now you can follow the fictional exploits of Mark Watney’s stunningly beautiful trail across the real Mars through a set of newly released maps, imagery and a 3D video created by the DLR, the German Aerospace Agency, and NASA – and based on photos taken by the European Space Agency’s Mars Express orbiter and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
DLR’s stunning 3D overflight video sequence was created from a dataset of 7300 stereo images covering roughly two-and-a-half million square kilometres of precisely mapped Martian landscape captured over the past 12 years by Mars Express High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The electric score is by Stephan Elgner.
Video Caption: Following the path of The Martian – video generated using images acquired by the Mars Express orbiter. Scientists from German Aerospace Center, DLR– who specialise in producing highly accurate topographical maps of Mars – reconstructed Watney’s route using stereo image data acquired by the High Resolution Stereo Camera on board European Space Agency’s #MarsExpress spacecraft. They then compiled this data into a video that shows the spectacular landscape that the protagonist would see ‘in the future’ on his trek from Ares 3 at Acidalia Planitia/Chryse Planitia to Ares 4 at Schiaparelli Crater. Credit: DLR/ESA
Ridley Scotts ‘The Martian’ takes place mostly on the surface of the Red Planet and is chock full of breathtakingly beautiful panoramic vistas. In the book you can only imagine Mars. In the movie Scott’s talents shine as he immerses you in all the action on the alien world of Mars from the opening scene.
Starting with the landing site for Watney’s Ares 3 mission crew at Acidalia Planitia, the book and movie follows his triumphs and tribulations, failures and successes as he logically solves one challenging problem after another – only to face increasingly daunting and unexpected hurdles as time goes by and supplies run low.
The DLR route map shows a real topographic view of Watney’s initial journey back and forth from the fictional Ares 3 landing site to the actual landing site of NASA’s 1997 Mars Pathfinder lander and Sojourner rover mission at the mouth of Ares Vallis.
The map continues with Watney’s months-long epic trek to the fictional landing site of Ares 4 Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV) spacecraft at Schiaparelli Crater, by way of Marth Valles and other Martian landmarks, craters and valleys.
At the request of Andy Weir, the HiRISE camera on NASA’s MRO orbiter took photos of the Martian plain at the Ares 3 landing site in Acidalia Planitia, which is within driving distance from the Pathfinder lander and Sojourner rover in the book and movie.

The Martian is all about how Watney uses his botany, chemistry and engineering skills to “Science the sh** out of it” to grow food and survive until the hoped for NASA rescue.
Learning how to live off the land will be a key hurdle towards enabling NASA’s real strategy for long term space voyages on a ‘Journey to Mars’ and back.
‘The Martian’ is a must see movie that broadly appeals to space enthusiasts and general audiences alike who can easily identify with Watney’s ingenuity and will to live.
Since its worldwide premiere on Oct. 2, ‘The Martian’ has skyrocketed to the top of the US box office for the second weekend in a row, hauling in some $37.3 million. The total domestic box office receipts now top $108 million and rockets to over $228 million worldwide in the first 10 days alone.
I absolutely loved ‘The Martian’ when I first saw the movie on opening weekend. And enjoyed it even more the second time, when I could pick up a few details I missed the first time around.
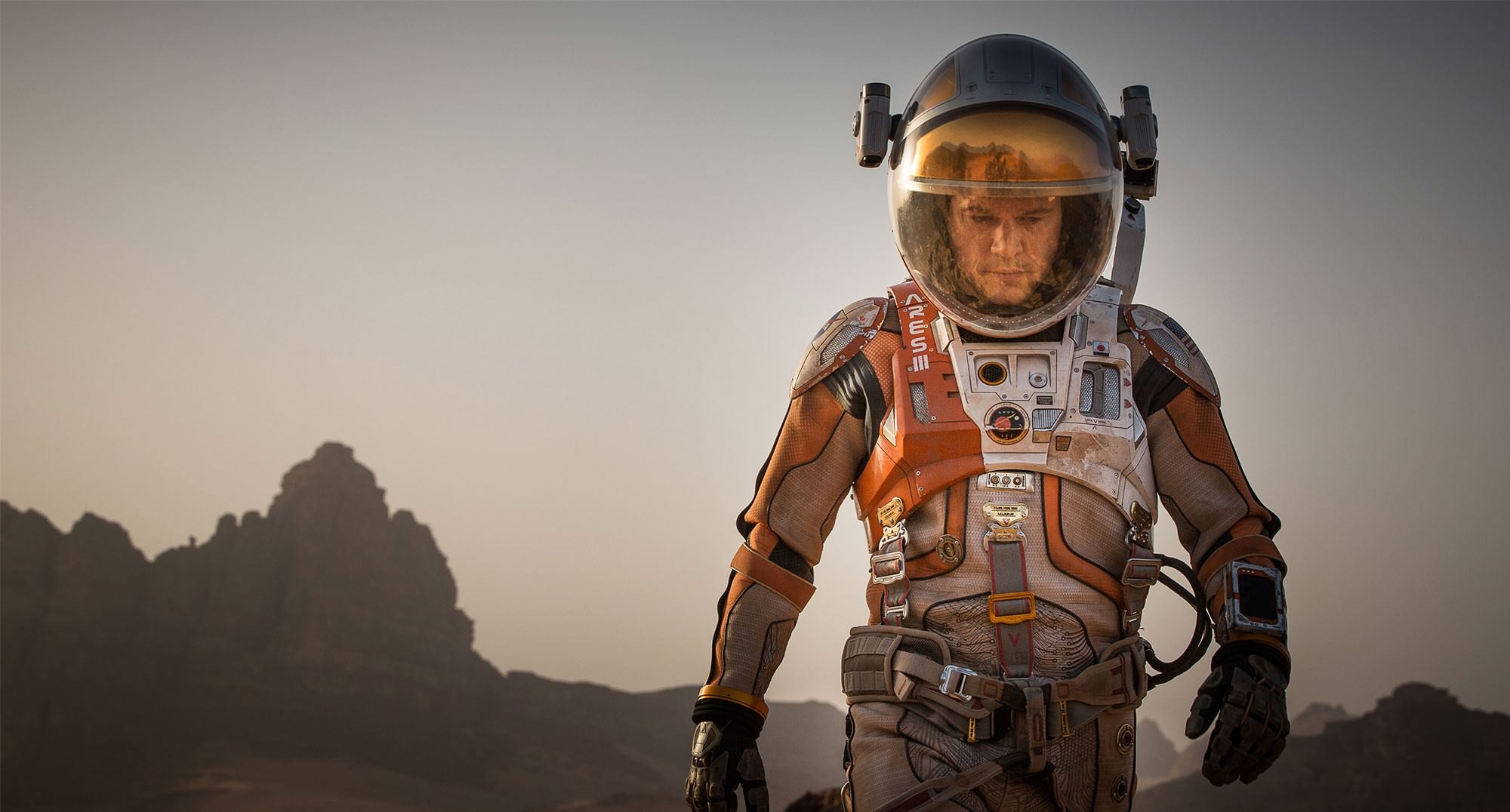

The movie begins as the crew evacuates after they believe Watney was killed by the dust storm. Watney actually survived the storm but lost contact with NASA. The film recounts his ingenious years long struggle to survive, figure out how to tell NASA he is alive and send a rescue crew before he starves to death on a planet where nothing grows. Watney’s predicament is a survival lesson to all including NASA.
‘The Martian’ was written by Andy Weir in 2010 and the film could well break the October movie box office record currently held by ‘Gravity.’
The movie closely follows the book, which I highly recommend you read at some point.
By necessity, the 2 hour 20 minute movie cannot capture every event in the book. So there is an abbreviated sense of Watney’s detailed science to survive and lengthy overland trips.
All the heroics and difficulties in traveling to Pathfinder and back and getting communications started, as well as the final month’s long journey to Schiaparelli crater are significantly condensed, but captured in spirit.
The Martian is brilliant and intelligent and rivals Stanley Kubrik’s space epic ‘2001: A Space Odyssey’ as one of the top movies about humanities space exploration quest.
The one big science inaccuracy takes place right at the start with the violent Martian dust storm.
On Mars the atmosphere is so thin that the winds would not be anywhere near as powerful or destructive as portrayed. This is acknowledged by Weir and done for dramatic license. We can look past that since the remainder of the tale portrays a rather realistic architectural path to Mars and vision of how scientists and engineers think. Plus the dust storms can in fact kick up tremendous amounts of particles that significantly block sunlight from impinging on solar energy generating panels.
Personally I can’t wait for the ‘Directors Cut’ with an added 30 to 60 minutes of scenes that were clearly filmed – but not included in the original theatrical release.
THE MARTIAN features a star studded cast that includes Matt Damon, Jessica Chastain, Kristen Wiig, Kate Mara, Michael Pena, Jeff Daniels, Chiwetel Ejiofor, and Donald Glover.
“NASA has endorsed “The Martian’” Jim Green, NASA’s Director of Planetary Sciences, told Universe Today. Green served as technical consultant on the film.

The DLR film was created by a team led by Ralf Jaumann from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research, Principal Investigator for HRSC. He believes that producing the overflight video was not just a gimmick for a science fiction film:
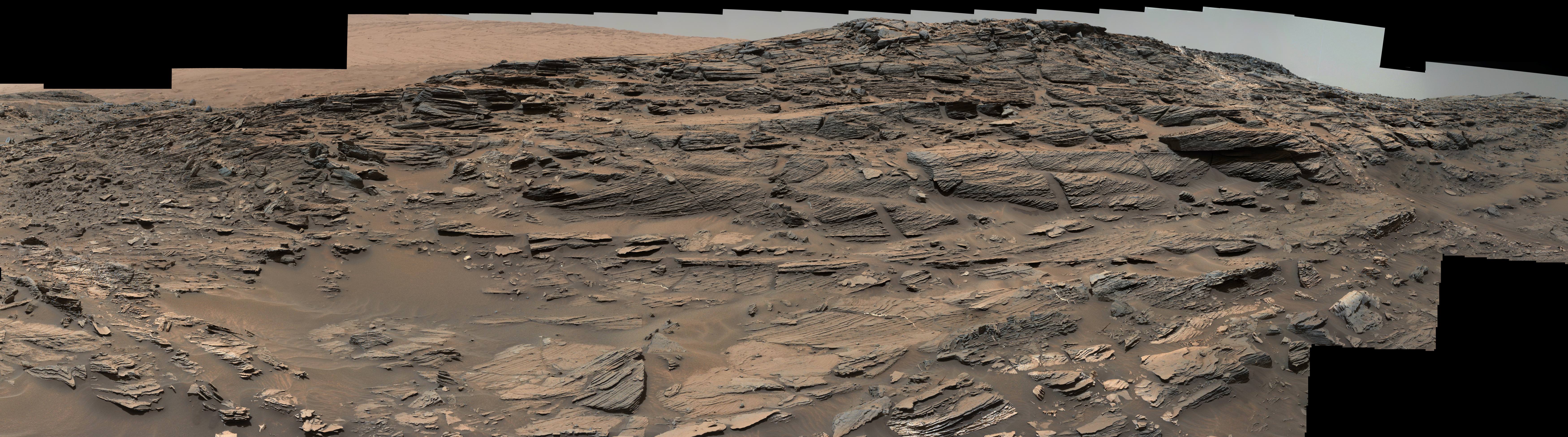
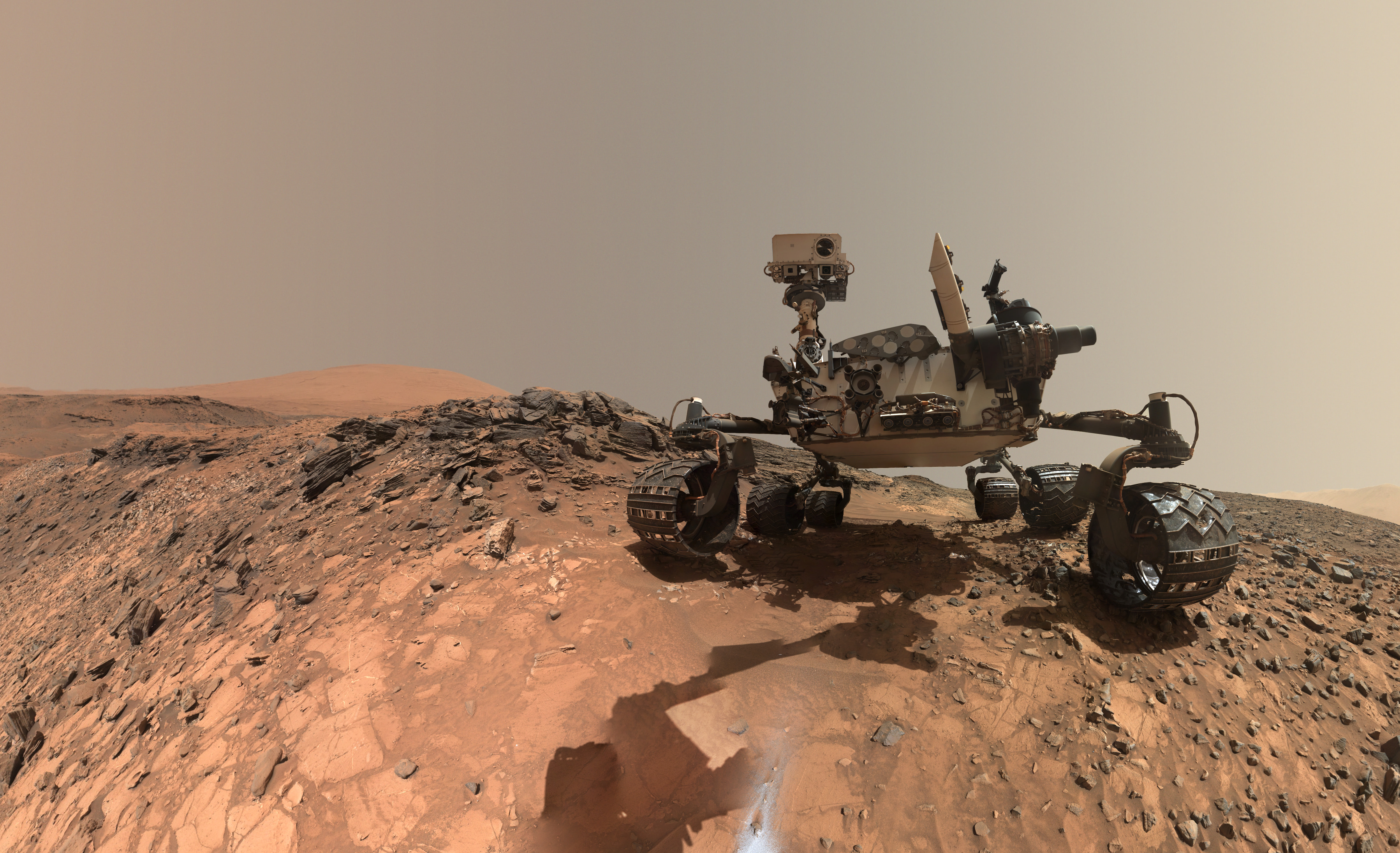
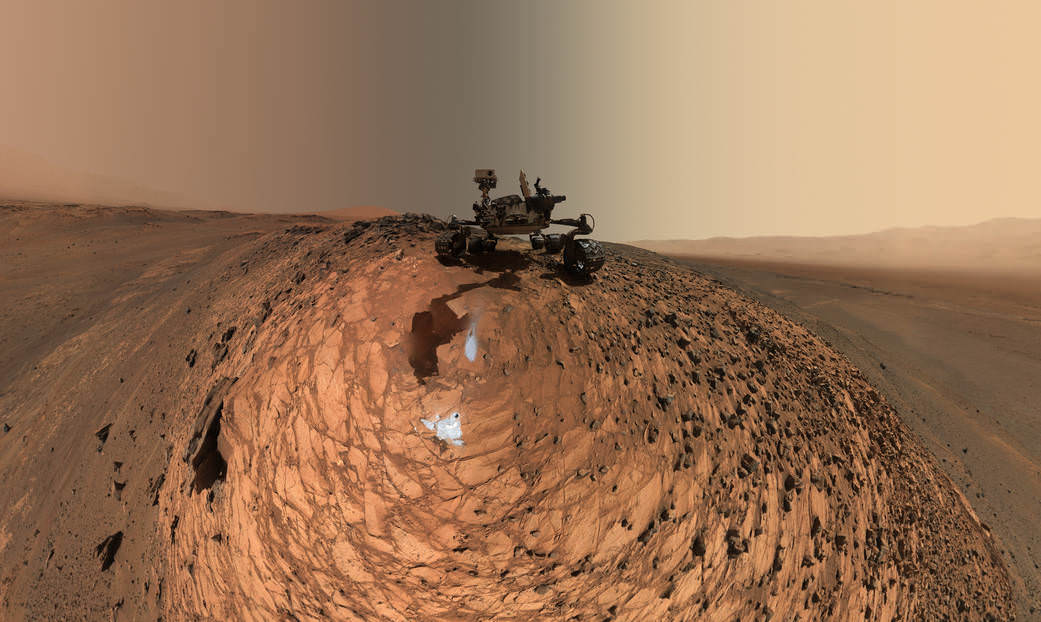
“Mars generates immense fascination, and our curiosity continues to grow! Many people are interested in our research, and young people in particular want to know what it is really like up there, and how realistic the idea that one day people will leave their footprints on the surface of Mars truly is. The data acquired by HRSC shows Mars with a clarity and detail unmatched by any other experiment. Only images acquired directly on the surface, for instance by rovers like Curiosity, are even closer to reality, but they can only show a small part of the planet. Thanks to this animation, we have even noticed a few new details that we had not seen in a larger spatial context. That is why we made the film – it helps everyone see what it would be like for Watney to travel through these areas… the clouds were the only creative touches we added, because, fortunately, they do not appear in the HRSC data,” according to a DLR statement.
Here’s the second official trailer for The Martian:
As a scientist and just plain Earthling, my most fervent hope is that ‘The Martian’ will inspire our young people to get interested in all fields of science, math and engineering and get motivated to become the next generation of explorers – here on Earth and beyond to the High Frontier to benefit all Mankind.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.



Route map in original German (Deutsch):